Description
The instruction for use
of medicine for experts
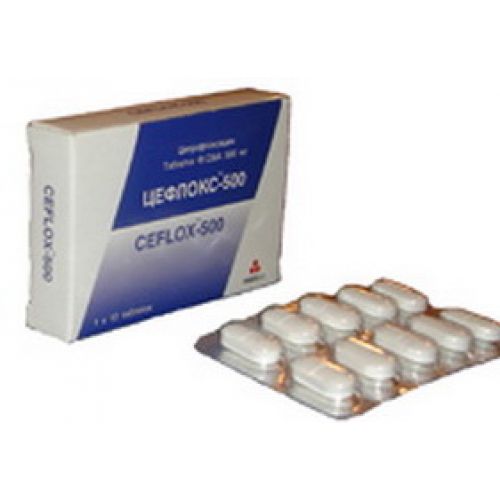
of TsEFLOKS-250/500
the Trade name
of Tsefloks™-250 Tsefloks™-500
the International unlicensed
name Ciprofloxacin Dosage Form
of the Tablet, film coated, 250 mg, 500 mg
Structure
One tablet цефлокс™-250 contains
active agent – ciprofloxacin a hydrochloride is equivalent
to ciprofloxacin of 250 mg,
excipients: corn starch, the microcrystalline cellulose, water purified, the talc purified magnesium stearate, silicon dioxide colloidal, sodium of a crosskarmelloz,
structure of a cover: a hydroksipropilmetiltsellyuloza, the talc purified, polyethyleneglycol-400, propylene glycol, the titan dioxide, water purified.
One tablet цефлокс™-500 contains
active agent – ciprofloxacin a hydrochloride is equivalent
to ciprofloxacin of 500 mg,
excipients: starch sodium glycollate, water purified, the talc purified magnesium stearate, silicon dioxide colloidal, microcrystalline cellulose,
structure of a cover: a hydroksipropilmetiltsellyuloza, the talc purified, polyethyleneglycol-400, propylene glycol, the titan dioxide, water purified.
Description
Tsefloks™-250: round tablets, biconvex, white color, film coated, with risky on one party
Tsefloks™-500: oval tablets, biconvex, white color, film coated, with risky on one party
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antibacterial drugs of systemic action. Ftorkhinolona
Kod of automatic telephone exchange of J01MA02
Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Absorption properties: after intake, ciprofloxacin is quickly soaked up from digestive tract. The absolute bioavailability is about 70%, without considerable losses at metabolism of the first passing. The maximum plasma concentration are reached in 1-2 hours after intake.
Distribution: linking with proteins of plasma makes 20-40%. After intake, ciprofloxacin is widely distributed on all organism. Concentration of drug in fabrics often exceed plasma concentration, especially in tissues of genitals and a prostate. Drug is present at an active form in saliva, nasal and bronchial secretion, mucous sine, a phlegm, contents of skin blisters, a lymph, peritoneal liquid, bile, a prostate secret.
Ciprofloxacin comes to light in lungs, skin, fat, muscular, cartilaginous and bone fabrics. Drug gets into cerebrospinal fluid where concentration usually make less than 10% of peak plasma concentration. Low concentration of drug are found in fluid mediums and a vitreous of an eye.
Removal: plasma elimination half-life at persons with normal function of kidneys makes about 4 hours. About 40-50% of the dose accepted inside are removed with urine in not changed look. Removal of drug happens to urine within 24 hours after administration of drug. From 1 to 2% of the accepted dose are removed with bile in the form of metabolites, about 20-35% of drug are removed with excrements within 5 days after reception.
At patients with a renal failure the elimination half-life is slowed slightly down. Dose adjustment can be required.
When prescribing drug to patients with cirrhosis significant changes in pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin are not noted.
Joint meal slows down ciprofloxacin absorption, however the general absorption significantly does not change.
The pharmacodynamics
Ciprofloxacin is antibacterial agent of a broad spectrum of activity from group of ftorkhinolon. Drug works by suppression of the A-subunit bacterial DNK-girazy that causes a rupture of DNA threads and death of bacteria.
Antibacterial range.
Gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus hemolyticus, koagulazonegativny Staphylococci, Sreptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Gram-negative microorganisms: Enterobacter spp., Haemophilus ducreyi, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella spp., Listeria monocytogenes, Legionella spp., Moraxella catarrhalis, Neisseria spp., Proteus spp., Pseudomonas spp., Shigella spp., Salmonella spp., Vibrio ssp., E.coli.
Others: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. fortuitum, Chlamydia trachomatis and Mycoplasma spp.
Indications
– acute and chronic bronchitis, a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,
an empyema, lung abscess, bronchiectasias, pneumonia, a mucoviscidosis
– average otitis, sinusitis and a mastoiditis
– acute and chronic pyelonephritis, cystitis, an urethritis, prostatitis,
an epididymite, the chronic and also complicated and recurrent
infections of urinary tract caused by multiple and resistant
strains of microbes or Pseudomonas aeruginosa
– the surgical and wound fevers caused by gram-negative
microorganisms (Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc.), resistant strains
of stafilokokk and also the infected ulcers, abscess, erysipelatous
inflammation and the infected burns
– peritonitis, intra belly abscess, a cholangitis, cholecystitis, an empyema
of a gall bladder
– acute and chronic osteomyelitis, septic arthritis
– a salpingitis, an endometritis, inflammatory diseases of bodies of a small pelvis
– the gonorrhea including caused by strains the producing
beta lactamazu and also shankroid, the caused H. Ducreyi
– a typhoid, intestinal infections
– a septicaemia, bacteremia, infections at patients with the weakened
immunity.
Route of administration and doses
Adult:
– In infections of easy and average degree: 250-500 mg two times a day.
– In the heavy and complicated infections: 750 mg two times a day.
Treatment duration: Therapy duration ciprofloxacin depends on a look and weight of an infection, at the same time it is necessary to consider the clinical and bacteriological answer at the patient. For the majority of infections the treatment should be continued at least within 48 hours after disappearance of symptoms. The usual duration of therapy is 5 – 10 days, but in the heavy or complicated infections the prolongation of a course of treatment can be required.
The maximum single dose – 750 mg.
The maximum daily dose – 1500 mg.
Contraindications
– hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin and antibacterial drugs of group of hinolon
– pregnancy
– the lactation period
– children’s and teenage age up to 18 years
– epilepsy
Side effects
– nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, an abdominal pain, pseudomembranous colitis
– a headache, concern, spasms, increase in intracranial pressure, toxic psychosis, dizziness, confusion of consciousness, a tremor, hallucinations, a depression
– myalgias, a tendinitis, aggravation of a myasthenia
– increase in level of transaminases
– hypersensitivity reactions: hypostasis of a throat or face, an asthma, urticaria and an itching, temperature increase, an eosinophilia, jaundice, liver necrosis, anaphylactic reactions
– pains, inflammation or a rupture of sinews
– a crystalluria
– photosensitivity.
Medicinal interactions
Pharmaceutical interaction:
At joint prescribing of ciprofloxacin and theophylline it was reported about development of life-threatening states – cardiac arrest, spasms, the epileptic status and disturbance of breath.
In isolated cases at joint prescribing of ciprofloxacin with glibenclamide the heavy hypoglycemia developed.
Pharmacokinetic interaction:
The antacids containing magnesium or aluminum hydroxide can reduce ciprofloxacin absorption that causes decrease in levels of drug in plasma and in urine. Therefore it is necessary to avoid a concomitant use of the specified means.
Joint purpose of a probenetsid and ciprofloxacin leads to decrease in clearance of ciprofloxacin approximately by 50% and increase in concentration of drug in a system blood-groove for 50%.
At joint prescribing of ciprofloxacin with Phenytoinum the plasma concentration of Phenytoinum changed (raised or decreased).Pharmakodinamichesky interaction:
At joint prescribing of ciprofloxacin and cyclosporine the passing increase in level of creatinine was observed.
Ciprofloxacin can influence caffeine metabolism, causing decrease in its clearance.
Ciprofloxacin enhances effect of oral anticoagulant of warfarin and its derivatives. At joint prescribing of these drugs the stringent control of a prothrombin time and other coagulative tests is necessary.
Special instructions
Renal failure: in a heavy renal failure the dose adjustment can be required. At clearance of creatinine less than 20 ml/min. it is necessary to appoint a half of the recommended dose.
Influence on ability to drive the car and potentially dangerous mechanisms.
About influence it was not reported.
Overdose
At acute overdose wash out a stomach by calling of vomiting or gastric lavage. The patient has to be under strict medical observation, maintenance therapy is carried out. It is necessary to appoint enough liquid. By a hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis ciprofloxacin is removed from an organism only in a small amount (less than 10%).
A form of release and packing
of Tsefloks-250 – a tablet of 250 mg No. 10.
Tsefloks-500 – tablets of 500 mg No. 10.
Primary packing – 10 tablets in the blister.
Secondary packing – 1 blister with the instruction for use in cardboard packing.
To Store storage conditions in the dry place at the room temperature not higher than + 250C.
To protect from direct sunshine.
To store out of children’s reach!
Not to apply an expiration date of 5 years after an expiration date.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
Plethico Pharmaceuticals Ltd/Pletkhiko Pharmasyyutikalz Ltd Adres Producer of location:
A.B. the Road, Mangliya – 453,771, Indore (L. S.), India
the Legal address:
37/37A, Indastrial Isteyt, Polograund, Indore (L. S.), 452,015, India
to Develop
Additional information
| Ingredient |
|---|














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.