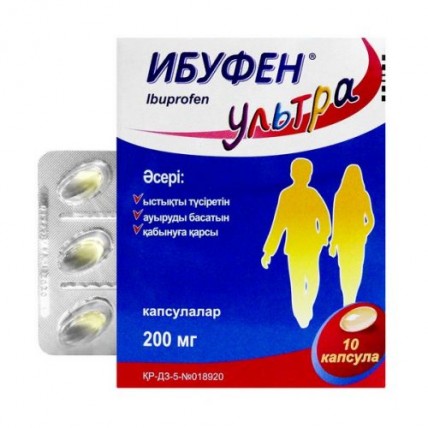
Ibufen Ultra 200 mg (10 capsules)
- $8.00
The instruction for medical use
of ULTRA IBUFENUM medicine
the Trade name
Ibufenum the Ultra
International unlicensed
name Ibuprofen Dosage Form
of the Capsule of 200 mg
Structure
One capsule contains
active agent - an ibuprofen of 200 mg,
excipients: a macrogoal 600, potassium hydroxide, water purified
a cover: the liquid sorbitol which is not crystallizing maltitol liquid, gelatin.
The description
Light yellow gelatin capsules
the Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic drugs containing viscous liquid Pharmacotherapeutic group. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Propionic acid derivatives. The ibuprofen
ATX M01AE01 Code
the Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Later properties of oral administration more than 80% of an ibuprofen is soaked up from a digestive tract. 90% of drug contact proteins of blood plasma (generally with albumine).
The period of achievement of the maximum concentration in blood plasma at reception on an empty stomach 45 minutes, at reception after a meal 1.5-2.5 hours, in synovial fluid 2-3 hours where high concentrations, than in blood plasma are created.
Drug does not kumulirutsya in an organism.
The ibuprofen, mainly, in a liver is metabolized. Is exposed to presistemny and post-system metabolism. After absorption about 60% pharmacological of inactive R form of an ibuprofen are slowly transformed to active S form.
60-90% of drug are removed by kidneys in the form of metabolites and products of their connection with glucuronic acid, to a lesser extent, with bile and in an invariable look no more than 1% are allocated. After reception of a single dose, drug is completely removed within 24 hours.
The pharmacodynamics
Ultra Ibufenum is derivative propionic acid. Has anesthetic, febrifugal and anti-inflammatory effect.
The mechanism of effect of Ultra Ibufenum is caused, first of all, by suppression of biosynthesis of prostaglandins due to decrease of the activity of cyclooxygenase (COG) of the enzyme regulating transformation of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins, prostacyclin and thromboxane. At the same time as a result of irreversible braking of a cyclooxygenase way of metabolism of arachidonic acid the formation of prostaglandins decreases. Decrease in concentration of prostaglandins in the place of inflammation is followed by reduction of formation of bradykinin, endogenous pyrogens, other biologically active agents, radicals of oxygen and NO. All this leads to decrease of the activity of inflammatory process (anti-inflammatory effect of an ibuprofen) and is followed by reduction of painful reception (analgeziruyushchy effect). Reduction of concentration of prostaglandins in cerebrospinal liquid leads to normalization of body temperature (antipyretic effect).
Soft gelatin capsules Ultra Ibufenum contain an ibuprofen in the liquid state. The gelatin capsule provides high precision of dosing of the substances placed in them. The cover of the capsule provides protection of active ingredient against light, air and moisture, and also excludes unpleasant taste and a smell of medicinal substance at reception. The capsule breaks up in a GIT quicker, than the dragee and tablets, and its liquid contents is quicker and easier absorbed in a human body, providing high bioavailability of an ibuprofen.
Indications
of Pain of various etiology and intensity from easy to moderate:
- a headache (also migraine)
- a toothache
- muscle, joints and bones pain
- posttraumatic pain
- neuralgia
- pains in cold and flu
- painful periods
- ear pain in average otitis.
Feverish conditions of various genesis (also in flu, cold or other infections).
A route of administration and doses
Attentively read the instruction before administration of drug.
For intake. Only for short-term use.
Adults and children are more senior than 12 years (more than 40 kg): inside on 1 capsule (200 mg), without chewing, up to 3-4 times a day. The capsule should be washed down with water. The interval between administrations of drug has to make 6-8 hours.
For achievement of faster therapeutic effect at adults the single dose can be increased up to 2 capsules (400 mg) up to 3 times a day.
The maximum daily dose makes 1200 mg.
The maximum daily dose for children of 12-17 years makes 1000 mg.
If at administration of drug within 2-3 days the symptoms remain or amplify, it is necessary to stop treatment and to see a doctor.
Side effects
Assessment of frequency of emergence of side reactions is made on the basis of the following criteria: very often (& ge, 1/10), it is frequent (from & ge, 1/100 to & lt, 1/10), infrequently (from & ge, 1/1000 to & lt, 1/100), is rare (from & ge, 1/10,000 to & lt, 1/1000), is very rare (& gt, 1/10,000).
Infrequently:
- allergic reactions with skin rash and an itching
- an abdominal pain, nausea, dyspepsia, an abdominal distension
- a headache
Seldom:
- diarrhea, a meteorism, a constipation and vomiting
- a headache, dizziness, insomnia, excitement, irritability, feeling of fatigue
it is Very rare:
- hemopoiesis disturbances (anemia, a leukopenia, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, a pancytopenia, an agranulocytosis)
- appearance of hypostases, arterial hypertension, heart failure in connection with use of drugs from the NPVP group
- heavy reactions of hypersensitivity, including edema of face, language and a throat, short wind, tachycardia, arterial hypotension (anaphylaxis, a Quincke's edema or a heavy acute anaphylaxis)
- a round ulcer, perforation or gastrointestinal bleeding, a melena, a hematemesis, in certain cases with a lethal outcome (especially at patients of advanced age), a stomacace, exacerbation of ulcer colitis and Crohn's disease
- an abnormal liver function (especially at long-term treatment), hepatitis and jaundice, a nephrotic syndrome, the acute renal failure (compensated and dekompensirovanny), interstitial nephrite, cystitis
- symptoms of aseptic meningitis: the stiff neck, a headache, nausea, vomiting, fever or disturbance of orientation, especially at patients with the preexisting autoimmune disorders (system lupus erythematosus, the mixed disease of connective tissue)
- hypostases, including peripheral
- reduction of a hematocrit or hemoglobin
- a disorder of vision, sonitus, dizziness
- psychotic reactions, a depression
Results of clinical trials assume presence of possible interrelation between reception of the ibuprofen which is especially accepted in high doses (& ge, 2400 mg a day), and the small increased risk of development of the arterial trombotichesky phenomena (for example, a myocardial infarction and a stroke).
At emergence of side effects it is necessary to stop drug use.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to an ibuprofen or other components
of drug and also to other nonsteroid anti-inflammatory
medicines
- manifestations ever before allergy symptoms in the form of cold, skin
rashes or bronkhospastichesky reactions after use
of acetylsalicylic acid or other
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- a digestive tract canker (peptic ulcer of a stomach and duodenum, ulcer colitis)
- gastrointestinal bleedings
- existence in the anamnesis of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation, connected with therapy of NPVS
- heavy heart failure (NYHA IV)
- hemophilia and other disturbances of blood clotting (including hypocoagulation), hemorrhagic diathesis
- a heavy renal or liver failure
- the III trimester of pregnancy
- children's age up to 12 years
Medicinal interactions
Ultra Ibufenum (just as other medicines groups of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) it is not necessary to use along with following medicines:
- acetylsalicylic acid, other NPVP and corticosteroids: risk of development of side effects from a GIT increases
Acetylsalicylic acid
simultaneous use of an ibuprofen and acetylsalicylic acid in connection with possible increase in development of the undesirable phenomena is not recommended.
By results of laboratory researches it is supposed that the ibuprofen at simultaneous use with low doses of acetylsalicylic acid can inhibit aggregation of thrombocytes competitively. Though the admissibility of extrapolation of these data on clinical practice remains uncertain, it is impossible to exclude potential impact of regular long reception of an ibuprofen on decrease in cardiotyre-tread action of low doses of acetylsalicylic acid. Influence of incidental use of an ibuprofen on cardiotyre-tread properties of acetylsalicylic acid is represented improbable.
It is necessary to be careful at simultaneous use with the following drugs:
- antihypertensive drugs and diuretics: as at simultaneous use with NPVP their efficiency
- antitrombotichesky drugs decreases: NPVP can strengthen effect of the drugs reducing blood clotting
- lithium, a methotrexate, digoxin and Phenytoinum: NPVP can increase concentration of these drugs in plasma (it is recommended to carry out their periodic control in serum)
- a zidovudine: increase in a bleeding time at simultaneous use with an ibuprofen
- antiagregantny medicines and the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) is possible: there is an increased risk of developing gastrointestinal bleeding
- mifepristone: NPVP should not be applied within 8-12 days after intake of mifepristone as NPVP can weaken its action
- takrolimusy, cyclosporine: the risk of nephrotoxic action increases at simultaneous use of an ibuprofen with these medicines
- hinolonovy antibiotics: the patients accepting a combination of NPVP and hinolona can be subject to risk of appearance of spasms
- kaliysberegayushchy diuretics: simultaneous use with an ibuprofen can lead to development of a hyperpotassemia
- probenetsidy, Sulfinpyrazonum: these drugs can slow down removal of an ibuprofen
Special instructions
It is necessary to be careful at persons with a renal failure, insufficiency of the blood circulatory system or disorders of functions of a liver.
To the persons with bronchial asthma or symptoms of allergic reactions to acetylsalicylic acid and also taking other medicines (especially antihypertensive, diuretic, kardiotropny and psychotropic medicines) use of drug it is admissible only on condition of respect for big care.
At use of an ibuprofen, isolated cases of a toxic amblyopia are celebrated.
Considering a possibility of appearance of disorders from digestive system, it is necessary to avoid a concomitant use of an ibuprofen with the substances or medicines having ulcerogenic effect (including acetylsalicylic acid, corticosteroids).
Gastrointestinal bleeding, formation and perforation of an ulcer.
Bleeding from digestive tract, the ulceration or perforation which in certain cases came to an end with death, were noted after use of all NPVP in every period of treatment with or without the previous symptoms or episodes of bleeding from digestive tract (including nonspecific ulcer colitis, Crohn's disease).
The risk of bleeding from digestive tract, expression or perforation increases with increase in doses of NPVP at patients with the peptic ulcer in the anamnesis which is especially complicated by bleeding or perforation and also at elderly people.
In case of approach of bleeding from digestive tract or expression, it is necessary to stop intake of medicine immediately.
Patients with digestive tract diseases in the anamnesis, especially elderly people, it is necessary to warn about need to report to the doctor about all atypical symptoms from digestive tract (especially about bleeding), especially in an initiation of treatment. These patients have to accept a medicine minimal effective dose.
It is necessary to be careful, using medicine at the patients who are at the same time taking other medicines which can increase risk of gastrointestinal disturbances or bleedings, such as corticosteroids, anticoagulative drugs, such as warfarin, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or antiagregant (such as acetylsalicylic acid).
Disturbances from a cardiovascular system and cerebral circulation
Patients with a hypertension and/or heart failure easy and moderate severity in the anamnesis need observation and consultations as at therapy of NPVP the liquid delay, the increased arterial blood pressure and hypostases can be noted.
According to results of clinical trials and epidemiological data, use of an ibuprofen, especially in high doses (2400 mg daily) and for a long time, can be followed by increase in risk of arterial thromboses (for example, a myocardial infarction or a stroke). In general, epidemiological researches show that small doses of an ibuprofen (for example, less than 1200 mg/days) do not lead to increase in risk of developing a myocardial infarction.
Skin reactions
In interrelation with use of NPVP are described very exceptional cases of the significant skin reactions (sometimes from the death), for example, exfoliative dermatitis, Stephens-Johnson's syndrome and a toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's disease). Most likely, patients are subject to the greatest risk of development of skin reactions during an initial stage of therapy as in most cases the specified reactions develop within the first month of treatment. At the first symptoms of skin rash, damages of a mucous membrane of an oral cavity or other symptoms of hypersensitivity the administration of drug should be stopped.
In exceptional cases, chicken pox can be the cause of serious infectious complications from skin and soft tissues. Now it is impossible to exclude NPVP role in treatment of such infections. Therefore recommend to avoid use of an ibuprofen in smallpox.
At the same time prolonged use of various analgetic medicines can lead to damage of kidneys with risk of developing a renal failure (analgetic nephropathy).
NPVP can mask symptoms of an infection and fever.
At use of an ibuprofen, isolated cases of a toxic amblyopia therefore it is necessary to inform the doctor on all disorders of vision were celebrated.
Children and teenagers with dehydration have a risk of a renal failure.
This drug contains liquid maltitol. At patients with hereditary intolerance of fructose (rare genetic disease) this drug should not be used.
The period of pregnancy and a lactation
Is absent exhaustive information concerning safety of use of an ibuprofen for women during pregnancy. As influence of oppression of synthesis of prostaglandins on a human fruit remains to unknown, it is not recommended to apply an ibuprofen in the first and second trimester of pregnancy.
Use of an ibuprofen in the III trimester of pregnancy is contraindicated as it promotes premature closing of an arterial channel and can cause pulmonary hypertensia in the newborn, also drug suppresses sokratitelny uterine activity that the beginning of childbirth detains and prolongs patrimonial activity and also increases risk of developing bleeding at mother and the child.
A lactation
the Ibuprofen and its metabolites get to breast milk in very low concentration. As messages about negative consequences for newborn children still did not arrive, at short-term use of drug there is no need for the feeding termination by a breast.
Fertility
there Are messages that use of the medicines inhibiting cyclooxygenase/synthesis of prostaglandins can influence an ovulation and by that negatively to affect reproductive ability of women. Such influence stops after the termination of administration of drug.
Features of influence of medicine on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms
At administration of drug Ultra Ibufenum can arise dizziness that should be considered during the driving and service of moving mechanisms.
Overdose
At children the symptoms of overdose can develop after reception of the dose exceeding 400 mg/kg of body weight. At adults the dose-dependent effect of overdose is less significant. Elimination half-life of drug at overdose makes 1.5-3 hours.
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, pain in epigastrialny area or, more rare, diarrhea, sonitus, a headache and gastrointestinal bleeding. In more hard cases manifestations from the central nervous system are observed: drowsiness, excitement, spasms, a disorientation, a coma is rare. In cases of a serious poisoning the metabolic acidosis and increase in a prothrombin time, a renal failure, liver tissue damage, a lowering of arterial pressure, respiratory depression and cyanosis can develop. At patients with bronchial asthma the exacerbation of this disease is possible.
Treatment: gastric lavage within 1 hour after reception of potentially toxic dose of an ibuprofen, intake of activated carbon. If necessary symptomatic treatment, with obligatory ensuring passability of airways, monitoring of the ECG and key indicators of activity up to normalization of a condition of the patient. If the ibuprofen was already absorbed, alkaline drink for the purpose of removal of an acid derivative ibuprofen kidneys, an artificial diuresis can be appointed. Frequent or long spasms should be stopped intravenous administration of diazepam or lorazepam. At deterioration in bronchial asthma the use of bronchodilators is recommended.
The form of release and packing
On 10 capsules place in blister strip packaging from a film of polyvinylchloride/polyvinyldichloride (PVDH/PVH) and aluminum foil.
On 1 or 2 planimetric pack together with the instruction for medical use in the state and Russian languages place in a cardboard pack.
To Store storage conditions in original packing at a temperature not over 25 of 0C.
To store out of children's reach.
Period of storage
2 years.
Not to use drug after expiry date.
Prescription status
Without prescription
the Producer
of Medan of JSC Pharm
98-200 Seradz, V. Loketk St. 10, Poland
the Owner of the registration certificate
of JSC Khimfarm, Kazakhstan
the Address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products
of JSC Khimfarm,
Shymkent, Republic of Kazakhstan, Rashidov St., 81 Phone number 7252 (610151)
the E-mail address of complaints@santo.kz
the Address of the organization in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan responsible for post-registration observation of safety of medicine
of JSC Khimfarm,
Republic of Kazakhstan, Shymkent, Rashidov St., 81 Phone number +7 7252 (610150)
To develop
of ULTRA IBUFENUM medicine
the Trade name
Ibufenum the Ultra
International unlicensed
name Ibuprofen Dosage Form
of the Capsule of 200 mg
Structure
One capsule contains
active agent - an ibuprofen of 200 mg,
excipients: a macrogoal 600, potassium hydroxide, water purified
a cover: the liquid sorbitol which is not crystallizing maltitol liquid, gelatin.
The description
Light yellow gelatin capsules
the Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic drugs containing viscous liquid Pharmacotherapeutic group. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Propionic acid derivatives. The ibuprofen
ATX M01AE01 Code
the Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Later properties of oral administration more than 80% of an ibuprofen is soaked up from a digestive tract. 90% of drug contact proteins of blood plasma (generally with albumine).
The period of achievement of the maximum concentration in blood plasma at reception on an empty stomach 45 minutes, at reception after a meal 1.5-2.5 hours, in synovial fluid 2-3 hours where high concentrations, than in blood plasma are created.
Drug does not kumulirutsya in an organism.
The ibuprofen, mainly, in a liver is metabolized. Is exposed to presistemny and post-system metabolism. After absorption about 60% pharmacological of inactive R form of an ibuprofen are slowly transformed to active S form.
60-90% of drug are removed by kidneys in the form of metabolites and products of their connection with glucuronic acid, to a lesser extent, with bile and in an invariable look no more than 1% are allocated. After reception of a single dose, drug is completely removed within 24 hours.
The pharmacodynamics
Ultra Ibufenum is derivative propionic acid. Has anesthetic, febrifugal and anti-inflammatory effect.
The mechanism of effect of Ultra Ibufenum is caused, first of all, by suppression of biosynthesis of prostaglandins due to decrease of the activity of cyclooxygenase (COG) of the enzyme regulating transformation of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins, prostacyclin and thromboxane. At the same time as a result of irreversible braking of a cyclooxygenase way of metabolism of arachidonic acid the formation of prostaglandins decreases. Decrease in concentration of prostaglandins in the place of inflammation is followed by reduction of formation of bradykinin, endogenous pyrogens, other biologically active agents, radicals of oxygen and NO. All this leads to decrease of the activity of inflammatory process (anti-inflammatory effect of an ibuprofen) and is followed by reduction of painful reception (analgeziruyushchy effect). Reduction of concentration of prostaglandins in cerebrospinal liquid leads to normalization of body temperature (antipyretic effect).
Soft gelatin capsules Ultra Ibufenum contain an ibuprofen in the liquid state. The gelatin capsule provides high precision of dosing of the substances placed in them. The cover of the capsule provides protection of active ingredient against light, air and moisture, and also excludes unpleasant taste and a smell of medicinal substance at reception. The capsule breaks up in a GIT quicker, than the dragee and tablets, and its liquid contents is quicker and easier absorbed in a human body, providing high bioavailability of an ibuprofen.
Indications
of Pain of various etiology and intensity from easy to moderate:
- a headache (also migraine)
- a toothache
- muscle, joints and bones pain
- posttraumatic pain
- neuralgia
- pains in cold and flu
- painful periods
- ear pain in average otitis.
Feverish conditions of various genesis (also in flu, cold or other infections).
A route of administration and doses
Attentively read the instruction before administration of drug.
For intake. Only for short-term use.
Adults and children are more senior than 12 years (more than 40 kg): inside on 1 capsule (200 mg), without chewing, up to 3-4 times a day. The capsule should be washed down with water. The interval between administrations of drug has to make 6-8 hours.
For achievement of faster therapeutic effect at adults the single dose can be increased up to 2 capsules (400 mg) up to 3 times a day.
The maximum daily dose makes 1200 mg.
The maximum daily dose for children of 12-17 years makes 1000 mg.
If at administration of drug within 2-3 days the symptoms remain or amplify, it is necessary to stop treatment and to see a doctor.
Side effects
Assessment of frequency of emergence of side reactions is made on the basis of the following criteria: very often (& ge, 1/10), it is frequent (from & ge, 1/100 to & lt, 1/10), infrequently (from & ge, 1/1000 to & lt, 1/100), is rare (from & ge, 1/10,000 to & lt, 1/1000), is very rare (& gt, 1/10,000).
Infrequently:
- allergic reactions with skin rash and an itching
- an abdominal pain, nausea, dyspepsia, an abdominal distension
- a headache
Seldom:
- diarrhea, a meteorism, a constipation and vomiting
- a headache, dizziness, insomnia, excitement, irritability, feeling of fatigue
it is Very rare:
- hemopoiesis disturbances (anemia, a leukopenia, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, a pancytopenia, an agranulocytosis)
- appearance of hypostases, arterial hypertension, heart failure in connection with use of drugs from the NPVP group
- heavy reactions of hypersensitivity, including edema of face, language and a throat, short wind, tachycardia, arterial hypotension (anaphylaxis, a Quincke's edema or a heavy acute anaphylaxis)
- a round ulcer, perforation or gastrointestinal bleeding, a melena, a hematemesis, in certain cases with a lethal outcome (especially at patients of advanced age), a stomacace, exacerbation of ulcer colitis and Crohn's disease
- an abnormal liver function (especially at long-term treatment), hepatitis and jaundice, a nephrotic syndrome, the acute renal failure (compensated and dekompensirovanny), interstitial nephrite, cystitis
- symptoms of aseptic meningitis: the stiff neck, a headache, nausea, vomiting, fever or disturbance of orientation, especially at patients with the preexisting autoimmune disorders (system lupus erythematosus, the mixed disease of connective tissue)
- hypostases, including peripheral
- reduction of a hematocrit or hemoglobin
- a disorder of vision, sonitus, dizziness
- psychotic reactions, a depression
Results of clinical trials assume presence of possible interrelation between reception of the ibuprofen which is especially accepted in high doses (& ge, 2400 mg a day), and the small increased risk of development of the arterial trombotichesky phenomena (for example, a myocardial infarction and a stroke).
At emergence of side effects it is necessary to stop drug use.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to an ibuprofen or other components
of drug and also to other nonsteroid anti-inflammatory
medicines
- manifestations ever before allergy symptoms in the form of cold, skin
rashes or bronkhospastichesky reactions after use
of acetylsalicylic acid or other
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- a digestive tract canker (peptic ulcer of a stomach and duodenum, ulcer colitis)
- gastrointestinal bleedings
- existence in the anamnesis of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation, connected with therapy of NPVS
- heavy heart failure (NYHA IV)
- hemophilia and other disturbances of blood clotting (including hypocoagulation), hemorrhagic diathesis
- a heavy renal or liver failure
- the III trimester of pregnancy
- children's age up to 12 years
Medicinal interactions
Ultra Ibufenum (just as other medicines groups of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) it is not necessary to use along with following medicines:
- acetylsalicylic acid, other NPVP and corticosteroids: risk of development of side effects from a GIT increases
Acetylsalicylic acid
simultaneous use of an ibuprofen and acetylsalicylic acid in connection with possible increase in development of the undesirable phenomena is not recommended.
By results of laboratory researches it is supposed that the ibuprofen at simultaneous use with low doses of acetylsalicylic acid can inhibit aggregation of thrombocytes competitively. Though the admissibility of extrapolation of these data on clinical practice remains uncertain, it is impossible to exclude potential impact of regular long reception of an ibuprofen on decrease in cardiotyre-tread action of low doses of acetylsalicylic acid. Influence of incidental use of an ibuprofen on cardiotyre-tread properties of acetylsalicylic acid is represented improbable.
It is necessary to be careful at simultaneous use with the following drugs:
- antihypertensive drugs and diuretics: as at simultaneous use with NPVP their efficiency
- antitrombotichesky drugs decreases: NPVP can strengthen effect of the drugs reducing blood clotting
- lithium, a methotrexate, digoxin and Phenytoinum: NPVP can increase concentration of these drugs in plasma (it is recommended to carry out their periodic control in serum)
- a zidovudine: increase in a bleeding time at simultaneous use with an ibuprofen
- antiagregantny medicines and the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI) is possible: there is an increased risk of developing gastrointestinal bleeding
- mifepristone: NPVP should not be applied within 8-12 days after intake of mifepristone as NPVP can weaken its action
- takrolimusy, cyclosporine: the risk of nephrotoxic action increases at simultaneous use of an ibuprofen with these medicines
- hinolonovy antibiotics: the patients accepting a combination of NPVP and hinolona can be subject to risk of appearance of spasms
- kaliysberegayushchy diuretics: simultaneous use with an ibuprofen can lead to development of a hyperpotassemia
- probenetsidy, Sulfinpyrazonum: these drugs can slow down removal of an ibuprofen
Special instructions
It is necessary to be careful at persons with a renal failure, insufficiency of the blood circulatory system or disorders of functions of a liver.
To the persons with bronchial asthma or symptoms of allergic reactions to acetylsalicylic acid and also taking other medicines (especially antihypertensive, diuretic, kardiotropny and psychotropic medicines) use of drug it is admissible only on condition of respect for big care.
At use of an ibuprofen, isolated cases of a toxic amblyopia are celebrated.
Considering a possibility of appearance of disorders from digestive system, it is necessary to avoid a concomitant use of an ibuprofen with the substances or medicines having ulcerogenic effect (including acetylsalicylic acid, corticosteroids).
Gastrointestinal bleeding, formation and perforation of an ulcer.
Bleeding from digestive tract, the ulceration or perforation which in certain cases came to an end with death, were noted after use of all NPVP in every period of treatment with or without the previous symptoms or episodes of bleeding from digestive tract (including nonspecific ulcer colitis, Crohn's disease).
The risk of bleeding from digestive tract, expression or perforation increases with increase in doses of NPVP at patients with the peptic ulcer in the anamnesis which is especially complicated by bleeding or perforation and also at elderly people.
In case of approach of bleeding from digestive tract or expression, it is necessary to stop intake of medicine immediately.
Patients with digestive tract diseases in the anamnesis, especially elderly people, it is necessary to warn about need to report to the doctor about all atypical symptoms from digestive tract (especially about bleeding), especially in an initiation of treatment. These patients have to accept a medicine minimal effective dose.
It is necessary to be careful, using medicine at the patients who are at the same time taking other medicines which can increase risk of gastrointestinal disturbances or bleedings, such as corticosteroids, anticoagulative drugs, such as warfarin, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or antiagregant (such as acetylsalicylic acid).
Disturbances from a cardiovascular system and cerebral circulation
Patients with a hypertension and/or heart failure easy and moderate severity in the anamnesis need observation and consultations as at therapy of NPVP the liquid delay, the increased arterial blood pressure and hypostases can be noted.
According to results of clinical trials and epidemiological data, use of an ibuprofen, especially in high doses (2400 mg daily) and for a long time, can be followed by increase in risk of arterial thromboses (for example, a myocardial infarction or a stroke). In general, epidemiological researches show that small doses of an ibuprofen (for example, less than 1200 mg/days) do not lead to increase in risk of developing a myocardial infarction.
Skin reactions
In interrelation with use of NPVP are described very exceptional cases of the significant skin reactions (sometimes from the death), for example, exfoliative dermatitis, Stephens-Johnson's syndrome and a toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's disease). Most likely, patients are subject to the greatest risk of development of skin reactions during an initial stage of therapy as in most cases the specified reactions develop within the first month of treatment. At the first symptoms of skin rash, damages of a mucous membrane of an oral cavity or other symptoms of hypersensitivity the administration of drug should be stopped.
In exceptional cases, chicken pox can be the cause of serious infectious complications from skin and soft tissues. Now it is impossible to exclude NPVP role in treatment of such infections. Therefore recommend to avoid use of an ibuprofen in smallpox.
At the same time prolonged use of various analgetic medicines can lead to damage of kidneys with risk of developing a renal failure (analgetic nephropathy).
NPVP can mask symptoms of an infection and fever.
At use of an ibuprofen, isolated cases of a toxic amblyopia therefore it is necessary to inform the doctor on all disorders of vision were celebrated.
Children and teenagers with dehydration have a risk of a renal failure.
This drug contains liquid maltitol. At patients with hereditary intolerance of fructose (rare genetic disease) this drug should not be used.
The period of pregnancy and a lactation
Is absent exhaustive information concerning safety of use of an ibuprofen for women during pregnancy. As influence of oppression of synthesis of prostaglandins on a human fruit remains to unknown, it is not recommended to apply an ibuprofen in the first and second trimester of pregnancy.
Use of an ibuprofen in the III trimester of pregnancy is contraindicated as it promotes premature closing of an arterial channel and can cause pulmonary hypertensia in the newborn, also drug suppresses sokratitelny uterine activity that the beginning of childbirth detains and prolongs patrimonial activity and also increases risk of developing bleeding at mother and the child.
A lactation
the Ibuprofen and its metabolites get to breast milk in very low concentration. As messages about negative consequences for newborn children still did not arrive, at short-term use of drug there is no need for the feeding termination by a breast.
Fertility
there Are messages that use of the medicines inhibiting cyclooxygenase/synthesis of prostaglandins can influence an ovulation and by that negatively to affect reproductive ability of women. Such influence stops after the termination of administration of drug.
Features of influence of medicine on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms
At administration of drug Ultra Ibufenum can arise dizziness that should be considered during the driving and service of moving mechanisms.
Overdose
At children the symptoms of overdose can develop after reception of the dose exceeding 400 mg/kg of body weight. At adults the dose-dependent effect of overdose is less significant. Elimination half-life of drug at overdose makes 1.5-3 hours.
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, pain in epigastrialny area or, more rare, diarrhea, sonitus, a headache and gastrointestinal bleeding. In more hard cases manifestations from the central nervous system are observed: drowsiness, excitement, spasms, a disorientation, a coma is rare. In cases of a serious poisoning the metabolic acidosis and increase in a prothrombin time, a renal failure, liver tissue damage, a lowering of arterial pressure, respiratory depression and cyanosis can develop. At patients with bronchial asthma the exacerbation of this disease is possible.
Treatment: gastric lavage within 1 hour after reception of potentially toxic dose of an ibuprofen, intake of activated carbon. If necessary symptomatic treatment, with obligatory ensuring passability of airways, monitoring of the ECG and key indicators of activity up to normalization of a condition of the patient. If the ibuprofen was already absorbed, alkaline drink for the purpose of removal of an acid derivative ibuprofen kidneys, an artificial diuresis can be appointed. Frequent or long spasms should be stopped intravenous administration of diazepam or lorazepam. At deterioration in bronchial asthma the use of bronchodilators is recommended.
The form of release and packing
On 10 capsules place in blister strip packaging from a film of polyvinylchloride/polyvinyldichloride (PVDH/PVH) and aluminum foil.
On 1 or 2 planimetric pack together with the instruction for medical use in the state and Russian languages place in a cardboard pack.
To Store storage conditions in original packing at a temperature not over 25 of 0C.
To store out of children's reach.
Period of storage
2 years.
Not to use drug after expiry date.
Prescription status
Without prescription
the Producer
of Medan of JSC Pharm
98-200 Seradz, V. Loketk St. 10, Poland
the Owner of the registration certificate
of JSC Khimfarm, Kazakhstan
the Address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products
of JSC Khimfarm,
Shymkent, Republic of Kazakhstan, Rashidov St., 81 Phone number 7252 (610151)
the E-mail address of complaints@santo.kz
the Address of the organization in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan responsible for post-registration observation of safety of medicine
of JSC Khimfarm,
Republic of Kazakhstan, Shymkent, Rashidov St., 81 Phone number +7 7252 (610150)
To develop