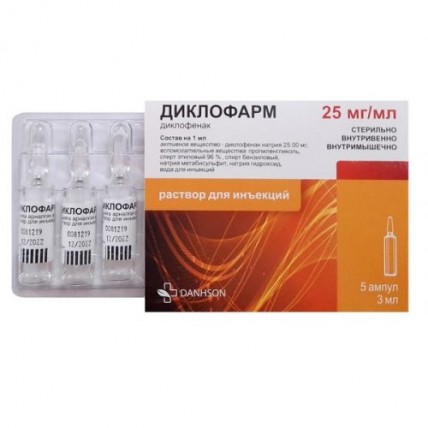
Diklopharm 25 mg / ml 3 ml 5's injection
- $9.40
The instruction for medical use of DIKLOFARM medicine the Trade name Diklopharm the International unlicensed name Diclofenac Dosage Form Solution for injections, 25 mg/ml Structure One ampoule contains active agent – diclofenac of sodium of 25 mg, excipients: propylene glycol, alcohol of 96%, benzyl alcohol, sodium metabisulphite, sodium hydroxide, water for injections. The description Transparent or slightly opalescent, colourless or slightly yellowish color solution, with a slight smell of benzyl alcohol, free from visible mechanical inclusions. Pharmacotherapeutic Musculoskeletal system group. Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic drugs. Anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic drugs, nonsteroid. Acetic acid derivative and related connections. Diclofenac. The ATX M01AB05 code the Pharmacological Pharmacokinetics Absorption Later properties of intramuscular introduction of 75 mg of diclofenac, its absorption begins immediately. The maximum concentration in plasma which average value is about 2.5 mkg/ml ± 8 µmol/l is reached approximately in 20 minutes. Right after its achievement the fast decrease in concentration of drug in plasma is observed. The amount of the soaking-up active agent is in linear dependence on drug dose size. If 75 mg of diclofenac are entered intravenously within 2 hours, average concentration in blood plasma will make about 1.9 mkg/ml ± 5.9 µmol/l. Area size under a curve concentration time (AUC) after intramuscular administration of drug diclofenac is approximately twice more, than after its oral or rectal administration as in the last cases about a half of amount of diclofenac is metabolized at the first passing through a liver. After repeated use of drug the pharmacokinetic indicators do not change. On condition of observance of the recommended intervals between administrations of drug of cumulation it is not noted. Distribution Linking with serum proteins makes 99.7%, it happens, mainly to albumine (99.4%). The approximate volume of distribution is 0.12-0.17 l/kg. Diclofenac gets into synovial fluid where its maximum concentration is reached at 2-4 o'clock later, than in blood plasma. Approximate elimination half-life makes 3-6 hours of synovial fluid. In 2 hours after achievement of the maximum concentration in plasma the concentration of diclofenac in synovial fluid is higher, than in plasma, and its values remain higher till 12 o'clock. Metabolism Metabolism of diclofenac is carried out partially by a glyukuronization of not changed molecule, but, mainly, by means of a single and repeated metoksilirovaniye that leads to formation of several phenolic metabolites (3 '-hydroxy, 4' - hydroxy, 5 '-hydroxy, 4', 5-digidroksi- and 3 '-hydroxies-4 '-metoksidiklofenaka), the majority of which turns into glyukuronidny conjugates. Two of these phenolic a metabolite are biologically active, but in much smaller degree, than diclofenac. The general system plasma clearance of diclofenac is 263±56 ml/min. Final elimination half-life makes 1-2 hours. Elimination half-life of 4 metabolites, including two pharmacological active, is also short and makes 1-3 hours. One of metabolites, 3 '-hydroxies-4 '-metoksi-diclofenac, has longer elimination half-life, however this metabolite is completely inactive. Removal About 60% of the accepted dose of drug is removed with urine in the form of glucuronic conjugates of not changed active agent and also in the form of metabolites, the majority of which is represented by glucuronic conjugates. In not changed look less than 1% of diclofenac are removed. The rest of the accepted dose of drug is removed in the form of metabolites with bile, with a stake and urine. The pharmacokinetics at separate groups of patients At some patients of advanced age 15-minute intravenous infusion resulted in concentration, higher for 50%, in plasma, than it was observed at young healthy faces. At patients with a renal failure when prescribing drug it was not noted Diklopharm in usual single doses of accumulation of diclofenac. However eventually metabolites are removed with bile. At patients with chronic hepatitis or the compensated cirrhosis the indicators of pharmacokinetics of diclofenac are similar to that at patients without liver diseases. The pharmacodynamics Diklopharm is nonsteroid means with the significant analgetic / anti-inflammatory properties. It is inhibitor of prostaglandins of a sintetaza (cyclooxygenase). Diclofenac of in vitro sodium does not suppress biosynthesis of the proteoglycans of cartilaginous tissue equivalent to concentration reached at people. At simultaneous use with opioids for treatment of postoperative pain Diklopharm considerably reduces the need for opioids. Indications Intramuscular introduction − aggravation of inflammatory and degenerative forms of rheumatism: the pseudorheumatism ankylosing a spondylitis, an osteoarthritis, a spondylarthritis, a pain syndrome in backbone diseases, extraarticular rheumatism − a bad attack of gout − renal or hepatic gripes − a posttraumatic and postoperative pain syndrome, inflammation and puffiness − heavy attacks of migraine Intravenous infusion − treatment or prevention of postoperative pain in the conditions of a hospital the Route of administration and doses Within the general recommendation the dose of drug has to be appointed individually. Side effects can be minimized by means of use of a minimal effective dose during the minimum period demanded for control over symptoms. Adult patients the injection should not use drug Diklopharm more than 2 days in a row. If necessary, treatment can be continued by means of diclofenac in tablets or rectal candles. An intramuscular injection At an intramuscular injection, in avoidance of injury of nerves or other fabrics in the place of an injection it is necessary to observe the following instructions. The drug should be administered once a day (or in hard cases twice a day) deeply intramusculary in an upper external quadrant of rump. If are required a repeated injection in day, it is recommended to use opposite rump. As an alternative, one injection of drug a day (75 mg) can be combined with reception of other dosage forms of diclofenac (tablets or rectal candles), at the same time the maximum daily dose makes 150 mg. In renal gripes drug is imported intramusculary in number of 75 mg. If necessary it is possible to enter repeatedly once again in 30 minutes. The recommended maximum daily dose makes 150 mg. Intravenous infusion Just before the beginning of intravenous infusion Diklopharm needs to be diluted in 100-500 ml 0.9% of solution of sodium of chloride, or 5% of solution of glucose. Both solutions have to be zabuferizovanna sodium bicarbonate solution (0.5 ml, 8.4% or 1 ml, 4.2%). It is possible to use only transparent solutions. Diklopharm should not be entered in the form of an intravenous bolyusny injection. Two alternative modes of dosing are recommended: For treatment of moderate and heavy postoperative pain it is necessary to enter constantly 75 mg of Diklopharm into the period of 30 minutes till 2 o'clock. If necessary treatment can be repeated in 4-6 hours, but the dose should not exceed 150 mg within 24 hours. For prevention of postoperative pain it is necessary to enter a load dose of 25-50 mg which should be entered after operation into the period of 15 minutes till 1 o'clock then continuous infusion about 5 mg an hour to the maximum daily dose of 150 mg follows. Special groups of the population Aged patients to Elderly patients, it is necessary to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with extra care since such patients are usually more inclined to side reactions. In particular, it is recommended to use the lowest effective dosage for weak elderly patients or patients with low body weight. Such groups of patients have to be exposed constantly to monitoring regarding gastrointestinal bleeding during therapy of NPVP. Patients with renal failures and a liver Diclofenac is contraindicated to patients with a heavy renal and liver failure. Special researches at patients with a renal and liver failure were not conducted therefore the recommendation about special correction of a dose cannot be provided. Also patients should be careful when prescribing diclofenac with a renal and liver failure easy and moderate severity. Side effects the Following undesirable effects include the phenomena connected with administration of drug Diklopharm, solution for injections and/or other dosage forms of diclofenac in the conditions of short-term and prolonged use. Often (≥ 1/100 to & lt, 1/10) - a headache, dizziness - vertigo - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, an abdominal pain, a meteorism, hyporexia - increase in level of transaminases - a liquid delay, swell, arterial hypertension - rash - reaction in the place of an injection, pain in the place of an injection, hardening in the place of an injection Infrequently (≥1/100 to & lt, 1/1000) - a myocardial infarction, heart failure, a cardiopalmus, a stethalgia Seldom (≥ 1/1000 to & lt, 1/10000) - hypersensitivity, anaphylactic and pseudoanaphylactic reactions (including arterial hypotension and shock) - drowsiness, fatigue - asthma (including dispnoe) - gastritis, gastrointestinal bleedings, vomiting with blood impurity, hemorrhagic diarrhea, a melena, ulcer of stomach or intestines (with bleeding or without it, perforation) - hepatitis, jaundice, an abnormal liver function - urticaria - hypostasis, necrosis in the place of an injection It is very rare (& lt, 1/10000) - thrombocytopenia, a leukopenia, anemia (including hemolytic and aplastic anemia), an agranulocytosis - a Quincke's disease (including a face edema) - a disorientation, a depression, insomnia, nightmares, irritability, mental disorders - paresthesia, disturbance of memory, a spasm, uneasiness, a tremor, aseptic meningitis, disorder of sense of taste, an acute disorder of cerebral circulation - a disorder of vision, illegibility of sight, a diplopia - a ring in ears, the hearing disorder - hypertensia, hypotension, a vasculitis - a pneumonitis - colitis (including hemorrhagic colitis and exacerbation of ulcer colitis or Crohn's disease), a constipation, stomatitis, a glossitis, disorders from a gullet, diafragmopodobny strictures of intestines, pancreatitis - fulminantny hepatitis, gepatonekroz, a liver failure - violent dermatitis, eczema, an erythema, a multiformny erythema, Stephens-Johnson's syndrome, a toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's disease), exfoliative dermatitis, an alopecia, reaction of photosensitivity, purple, purple of Genokha-Shenleyn, an itching - an acute renal failure, a hamaturia, a proteinuria, a nephrotic syndrome, tubulointerstitsialny nephrite, renal papillary necrosis - impotence Is unknown - abscess in the place of an injection - optical neuritis - ischemic colitis Diclofenac, especially in high doses (150 mg/days) and at prolonged use, can increase risk of developing of an arterial thrombembolia (for example, a myocardial infarction or a stroke). Visual effects Visual disturbances, such as disorder of vision, turbidity of sight or a diplopia, apparently, are effects of class NPVP and, as a rule, are reversible at the treatment termination. The probable origins of visual disturbances is the inhibition of synthesis of prostaglandins and other related connections which change regulation of a blood-groove in a retina that leads to potential changes in sight. If such symptoms arise during treatment by diclofenac, it is possible to perform ophthalmologic examination to exclude other reasons. Contraindications - the increased hypersensitivity to active ingredient, sodium metabisulphite or to any other components of drug - active ulcer of stomach or intestines, bleeding or perforation - the gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation connected with the previous therapy of NPVP - in the presence in the present or in the past of a recurrent round ulcer / hemorrhages (two or more separate cases of the confirmed peptic ulcer or bleedings) - the III trimester of pregnancy and the period of a lactation - a liver failure - a renal failure - chronic heart failure, functional class II-IV on classification NYHA, coronary heart disease, diseases of peripheral arteries and/or cerebrovascular diseases - the bronchial asthma, a Quincke's disease, a small tortoiseshell or acute rhinitis arising at reception of an ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid or other NPVP - children's and teenage age up to 18 years In addition at intravenous administration - combined use of NPVP or anticoagulants (including small doses of heparin). - chronic hemorrhagic diathesis, the confirmed or suspected chronic cerebrovascular bleeding - patients with high risk of developing postoperative bleedings - chronic asthma - a moderate or heavy renal failure (creatinine in serum & gt, 160 µmol/l). - hypovolemia or dehydration Medicinal interactions CYP2C9 Inhibitors: It is recommended to be careful at joint prescribing of diclofenac with CYP2C9 inhibitors (such as vorikonazol) which can lead to significant increase in peak of concentration in blood plasma and exposure of diclofenac. Lithium, digoxin Diklopharm can increase concentration of lithium and digoxin in blood plasma. Monitoring of level of lithium and digoxin in blood serum is recommended. Diuretics and antihypertensive drugs As well as for other NPVP, simultaneous use of diclofenac with diuretics or antihypertensive drugs (for example, beta-blockers, inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme (APF)) can lead to decrease in their antihypertensive influence. Patients, especially elderly people, have to be under careful control of arterial blood pressure. Patients have to receive appropriate hydration, also monitoring of renal function after the beginning of the accompanying therapy and on a regular basis after it, especially concerning diuretics and APF inhibitors, owing to increase in risk of nephrotoxicity is recommended. The accompanying treatment by drugs of potassium can be connected with increase in level of potassium in blood serum that demands stay of patients under constant control. Cyclosporine and takrolimus Influence of NPVP on synthesis of prostaglandins in kidneys can increase nephrotoxicity of cyclosporine and a takrolimus. Diclofenac should be applied in lower doses, than at patients who do not receive cyclosporine or takrolimus. The drugs causing a hyperpotassemia the Accompanying treatment by kaliysberegayushchy diuretics, cyclosporine takrolimusy or Trimethoprimum can increase serumal levels of potassium. It is necessary to control often potassium levels in blood serum. Antibacterial agents - derivatives of a hinolon Are available separate messages about development of spasms in patients, the receiving at the same time derivative hinolon and NPVP. Other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NPVP) and corticosteroids Simultaneous system use of NPVP or corticosteroids with diclofenac can increase the frequency of emergence of the undesirable phenomena from digestive tract. Anticoagulants and antitrombotichesky means Exist messages about increase in risk of bleedings at the patients accepting at the same time Diklopharm and anticoagulants. In case of such combination of medicines the careful and regular observation of patients is recommended. The Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI) Co-administration of system NPVP and SIOZS can increase risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. Antidiabetic drugs Perhaps simultaneous use of drug Diklopharm and antidiabetic drugs, at the same time the efficiency of the last does not change. Separate messages about development in such cases are known, to both a hypoglycemia, and a hyperglycemia that caused need of change of a dose of glucose-lowering drugs during drug use Diklopharm. There were also separate messages about a metabolic acidosis when diclofenac was applied along with metformin, especially at pats
ent with earlier existing renal failure. Kolestipol and holestiramin Simultaneous use of diclofenac and a kolestipol or holestiramin reduces diclofenac absorption approximately by 30% and 60%, respectively. The drugs should be taken at an interval of several hours. A methotrexate It is necessary to be careful when assigning NPVP less than in 24 hours prior to or after reception of a methotrexate as in such cases the concentration of a methotrexate in blood can increase and amplify its toxic action. The inductors CYP2C9 It is recommended to be careful at simultaneous use of diclofenac with the inductors CYP2C9 (such as rifampicin) as it can lead to considerable decrease in concentration in plasma and to diclofenac influence. Phenytoinum Is recommended monitoring of concentration of Phenytoinum in plasma at simultaneous use with diclofenac because of possible increase in Phenytoinum exposure. Pharmaceutical incompatibility it is not necessary to mix drug solution Diklopharm which is contained in ampoules with solutions of other medicines for injections. Special instructions the Cumulative Undesirable side effects can be minimized, using the lowest effective dose during the shortest span necessary for control of symptoms. It is necessary to avoid simultaneous use of Diklopharm with system NPVP, including selection inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2, in a type of lack of any synergy advantage and a possibility of development of additional side effects. It is necessary to be careful when prescribing drug to elderly people. In particular, it is recommended to use the lowest effective dose at elderly people with poor health or patients with low body weight. As well as in a case with other NPVP, including diclofenac, there can be allergic reactions, including anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, in the absence of former exposure to drug. Diklopharm, as well as other NPVP, thanks to the pharmakodinamichesky properties, can mask manifestations and symptoms of infectious diseases. The sodium metabisulphite which is present at composition of solution for injections can lead to the isolated heavy reaction of hypersensitivity and a bronchospasm. At intramuscular administration of drug, it is necessary to observe strictly instructions in the instruction for medical use, in order to avoid side effects in the place of an injection which can lead to muscle weakness, paralysis of muscles, a hypesthesia and necrosis of the place of an injection. Influence on digestive system As well as at use of other NPVP, when prescribing drug Diklopharm to patients with the symptoms demonstrating disturbances from digestive system with presence of stomach ulcer or intestines, bleeding or perforation in the anamnesis, is obligatory medical observation and extra care. The risk of developing of bleeding in digestive tract increases with increase in a dose of drug at patients with an ulcer in the anamnesis, especially with complications in the form of bleeding or perforation, and at people of advanced age. If at drug use Diklopharm patients have gastrointestinal bleedings or an ulceration, treatment should be stopped. At elderly people the frequency of side reactions increases by NPVP, especially gastrointestinal bleedings and perforation which can lead to a lethal outcome. To reduce risk of toxicity of digestive tract at patients with an ulcer in the anamnesis, especially with complications in the form of bleeding or perforation, and at people of advanced age, treatment should be begun and supported in the lowest effective dose. Combination therapy using protective equipment (for example, mizoprostoly or inhibitors of the proton pump) has to be considered for these patients and also for the patients demanding simultaneous use of medicines, containing low doses of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA/aspirin) or other medicines which can increase risk of undesirable impact on digestive system. Patients with chronic toxicity of digestive tract, especially advanced age, have to report about any unusual abdominal symptoms (especially about digestive tract bleeding). It is necessary to be careful at the patients receiving the accompanying drugs which can increase risk development of ulcers or bleedings, such as system corticosteroids, anticoagulants (warfarin), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or antitrombotichesky means (acetylsalicylic acid). At appointment of Diklopharm it is necessary to be careful and also careful medical observation at patients with ulcer colitis or with Crohn's disease, in connection with their potential aggravation. Influence on a liver At appointment of Diklopharm is necessary for patients with abnormal liver functions careful medical observation as the condition of such patients can become aggravated. As well as at use of other NPVP, including diclofenac, level of one or several enzymes of a liver can raise. During long-term treatment by diclofenac, regular monitoring of function of a liver is specified as a precautionary measure. If abnormal liver functions remain or worsen and also if the symptoms connected with the progressing liver diseases or other manifestations are observed (for example, an eosinophilia, rash), drug use Diklopharm should be stopped. The course of diseases, such as hepatitis, can pass without prodromal symptoms. It is necessary to be careful when prescribing diclofenac at patients with a hepatic porphyria as it can cause an attack. Influence on kidneys As at treatment of NPVP, including diclofenac, is noted a delay of liquid and hypostasis, patients need extra care when prescribing drug with disturbances of functions of heart or kidneys, arterial hypertension in the anamnesis, to the patients of advanced age, patients receiving the accompanying treatment by diuretics or medicines which can influence considerably function of kidneys, and to patients with significant decrease in extracellular volume of liquid for any reason, for example to or after serious surgical intervention. In such cases, as a precautionary measure when using diclofenac, monitoring renal function is recommended. The termination of therapy of NPVP usually leads to return to a state which preceded treatment. Skin reactions Due to the use of NPVP, including diclofenac, it was very seldom reported about heavy skin reactions some of which came to an end with a lethal outcome, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stephens-Johnson's syndrome and a toxic epidermal necrolysis. To the highest risk of these reactions, patients are exposed at the beginning of a therapy course, and development of these reactions is noted in most cases within the first month of treatment. Use of Diklopharm should be stopped at the first appearance of skin rash, damages of a mucous membrane or any other signs of hypersensitivity. The hard currency and the mixed diseases of connective tissue At patients with the system lupus erythematosus (SLE) and the mixed disturbances of connective tissue can raise risk of aseptic meningitis (see the section Side effects). Influence on a cardiovascular system Patients with essential risk factor of cardiovascular diseases (for example hypertensia, a lipidemia, diabetes, smoking) should accept Diklopharm only after thorough examination. As the risk of developing of cardiovascular diseases at treatment of diclofenac can will increase with a dose and duration of exposure, it is necessary to use the most minimum period of treatment and the lowest effective daily dose. Need of the patient for symptomatic simplification and reaction to therapy should be overestimated periodically. As at treatment of NPVP, including diclofenac, the delay of liquid and hypostasis is noted, the corresponding monitoring and recommendations for patients with a hypertension in the anamnesis and/or heart failure from easy to moderate degree is required. Treatment of NPVP, including diclofenac, especially in high doses (150 mg a day) and during the long period of treatment, can be connected with the increased risk of developing arterial trombotichesky diseases (for example a myocardial infarction or a stroke). Patients with uncontrollable arterial hypertension, the stagnant heart failure established by coronary heart disease, a disease of peripheral arteries and/or cerebrovascular diseases should accept Diklopharm only after thorough examination. Influence on hematologic indicators during long-term treatment by diclofenac, as well as other NPVP, is recommended blood test monitoring. Diklopharm can inhibit aggregation of thrombocytes reversibly. Patients with disturbances of a hemostasis, the bleeding diathesis or hematologic disturbances should be observed carefully. Asthma in the anamnesis At patients with bronchial asthma, seasonal allergic rhinitis, a rhinedema (nasal polyps), with the chronic obstructive diseases of lungs or persistent infections of airways (which are especially connected with allergic, similar to rhinitises, symptoms) more often than others have reactions to NPVP similar to exacerbation of asthma, a Quincke's edema or urticaria. Therefore for such patients it is necessary to observe extra care and special measures (readiness for emergency situations and rendering emergency aid) are recommended. It is also applicable also to patients with an allergy to other substances, for example, with skin reactions, an itching or urticaria. As well as other NPVP which inhibit activity of synthesis of prostaglandin diclofenac can accelerate a bronchospasm if it is appointed to the patients having chronic bronchial asthma. Pregnancy and the period of a lactation Inhibition of synthesis of prostaglandins can negatively influence pregnancy and/or development of an embryo or fruit. There is a big risk of a miscarriage and/or development of heart diseases and a gastroshizis after use of inhibitors of synthesis of prostaglandins in the early stages of pregnancy. It is considered that the risk increases with increase in a dose and increase in duration of therapy. Use of inhibitors of synthesis of prostaglandins can lead to increase in quantity pre- and post-implantation losses and cases of embriofetalny lethality. Besides, at use of inhibitors of synthesis of prostaglandins in the period of an organogenesis, there is a risk of increase in frequency of various malformations, including cardiovascular. If Diklopharm is accepted by the woman who tries to become pregnant or is in I or II trimester of pregnancy, the dose has to be as low as possible, and treatment duration as it is possible well. Diclofenac is contraindicated in the III trimester of pregnancy. All inhibitors of synthesis of prostaglandins can cause the following risks: for a fruit: - toxic damage of heart and a respiratory system (with premature closing of an arterial channel and development of pulmonary hypertensia), - a renal failure which can progress to a renal failure which is followed oligogidramniozy, for mother and the child: - lengthening of a bleeding time and influence on inhibition of aggregation of thrombocytes, even at use in low doses, - inhibition of reductions of a uterus that leads to a delay and lengthening of childbirth. As well as other NPVP, diclofenac in small amounts gets into breast milk. In this connection, it is not necessary to accept diclofenac during feeding by a breast to avoid undesirable influence on the baby. If treatment is extremely necessary, it is necessary to stop feeding by a breast and to transfer the child to artificial feeding. The fertility Diklopharm can negatively affect female fertility in this connection, drug is not recommended to use to the women planning pregnancy. The women having complications with fertilization or those which underwent inspection owing to an infertilnost have to stop Diklopharm use. Features of influence of drug on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms Patients at whom during drug treatment Diklopharm disorders of vision, dizziness, drowsiness or other disturbances are observed from the central nervous system have to abstain from control of motor transport and work with mechanisms. Overdose Symptoms: vomiting, gastrointestinal bleeding, diarrhea, dizziness, a ring in ears or spasms. In case of a serious poisoning the acute renal failure and damage of a liver is possible. Treatment: the supporting measures and symptomatic treatment which are necessary for elimination of such complications as arterial hypotension, a renal failure, spasms, gastrointestinal break
to Develop
ent with earlier existing renal failure. Kolestipol and holestiramin Simultaneous use of diclofenac and a kolestipol or holestiramin reduces diclofenac absorption approximately by 30% and 60%, respectively. The drugs should be taken at an interval of several hours. A methotrexate It is necessary to be careful when assigning NPVP less than in 24 hours prior to or after reception of a methotrexate as in such cases the concentration of a methotrexate in blood can increase and amplify its toxic action. The inductors CYP2C9 It is recommended to be careful at simultaneous use of diclofenac with the inductors CYP2C9 (such as rifampicin) as it can lead to considerable decrease in concentration in plasma and to diclofenac influence. Phenytoinum Is recommended monitoring of concentration of Phenytoinum in plasma at simultaneous use with diclofenac because of possible increase in Phenytoinum exposure. Pharmaceutical incompatibility it is not necessary to mix drug solution Diklopharm which is contained in ampoules with solutions of other medicines for injections. Special instructions the Cumulative Undesirable side effects can be minimized, using the lowest effective dose during the shortest span necessary for control of symptoms. It is necessary to avoid simultaneous use of Diklopharm with system NPVP, including selection inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2, in a type of lack of any synergy advantage and a possibility of development of additional side effects. It is necessary to be careful when prescribing drug to elderly people. In particular, it is recommended to use the lowest effective dose at elderly people with poor health or patients with low body weight. As well as in a case with other NPVP, including diclofenac, there can be allergic reactions, including anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, in the absence of former exposure to drug. Diklopharm, as well as other NPVP, thanks to the pharmakodinamichesky properties, can mask manifestations and symptoms of infectious diseases. The sodium metabisulphite which is present at composition of solution for injections can lead to the isolated heavy reaction of hypersensitivity and a bronchospasm. At intramuscular administration of drug, it is necessary to observe strictly instructions in the instruction for medical use, in order to avoid side effects in the place of an injection which can lead to muscle weakness, paralysis of muscles, a hypesthesia and necrosis of the place of an injection. Influence on digestive system As well as at use of other NPVP, when prescribing drug Diklopharm to patients with the symptoms demonstrating disturbances from digestive system with presence of stomach ulcer or intestines, bleeding or perforation in the anamnesis, is obligatory medical observation and extra care. The risk of developing of bleeding in digestive tract increases with increase in a dose of drug at patients with an ulcer in the anamnesis, especially with complications in the form of bleeding or perforation, and at people of advanced age. If at drug use Diklopharm patients have gastrointestinal bleedings or an ulceration, treatment should be stopped. At elderly people the frequency of side reactions increases by NPVP, especially gastrointestinal bleedings and perforation which can lead to a lethal outcome. To reduce risk of toxicity of digestive tract at patients with an ulcer in the anamnesis, especially with complications in the form of bleeding or perforation, and at people of advanced age, treatment should be begun and supported in the lowest effective dose. Combination therapy using protective equipment (for example, mizoprostoly or inhibitors of the proton pump) has to be considered for these patients and also for the patients demanding simultaneous use of medicines, containing low doses of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA/aspirin) or other medicines which can increase risk of undesirable impact on digestive system. Patients with chronic toxicity of digestive tract, especially advanced age, have to report about any unusual abdominal symptoms (especially about digestive tract bleeding). It is necessary to be careful at the patients receiving the accompanying drugs which can increase risk development of ulcers or bleedings, such as system corticosteroids, anticoagulants (warfarin), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or antitrombotichesky means (acetylsalicylic acid). At appointment of Diklopharm it is necessary to be careful and also careful medical observation at patients with ulcer colitis or with Crohn's disease, in connection with their potential aggravation. Influence on a liver At appointment of Diklopharm is necessary for patients with abnormal liver functions careful medical observation as the condition of such patients can become aggravated. As well as at use of other NPVP, including diclofenac, level of one or several enzymes of a liver can raise. During long-term treatment by diclofenac, regular monitoring of function of a liver is specified as a precautionary measure. If abnormal liver functions remain or worsen and also if the symptoms connected with the progressing liver diseases or other manifestations are observed (for example, an eosinophilia, rash), drug use Diklopharm should be stopped. The course of diseases, such as hepatitis, can pass without prodromal symptoms. It is necessary to be careful when prescribing diclofenac at patients with a hepatic porphyria as it can cause an attack. Influence on kidneys As at treatment of NPVP, including diclofenac, is noted a delay of liquid and hypostasis, patients need extra care when prescribing drug with disturbances of functions of heart or kidneys, arterial hypertension in the anamnesis, to the patients of advanced age, patients receiving the accompanying treatment by diuretics or medicines which can influence considerably function of kidneys, and to patients with significant decrease in extracellular volume of liquid for any reason, for example to or after serious surgical intervention. In such cases, as a precautionary measure when using diclofenac, monitoring renal function is recommended. The termination of therapy of NPVP usually leads to return to a state which preceded treatment. Skin reactions Due to the use of NPVP, including diclofenac, it was very seldom reported about heavy skin reactions some of which came to an end with a lethal outcome, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stephens-Johnson's syndrome and a toxic epidermal necrolysis. To the highest risk of these reactions, patients are exposed at the beginning of a therapy course, and development of these reactions is noted in most cases within the first month of treatment. Use of Diklopharm should be stopped at the first appearance of skin rash, damages of a mucous membrane or any other signs of hypersensitivity. The hard currency and the mixed diseases of connective tissue At patients with the system lupus erythematosus (SLE) and the mixed disturbances of connective tissue can raise risk of aseptic meningitis (see the section Side effects). Influence on a cardiovascular system Patients with essential risk factor of cardiovascular diseases (for example hypertensia, a lipidemia, diabetes, smoking) should accept Diklopharm only after thorough examination. As the risk of developing of cardiovascular diseases at treatment of diclofenac can will increase with a dose and duration of exposure, it is necessary to use the most minimum period of treatment and the lowest effective daily dose. Need of the patient for symptomatic simplification and reaction to therapy should be overestimated periodically. As at treatment of NPVP, including diclofenac, the delay of liquid and hypostasis is noted, the corresponding monitoring and recommendations for patients with a hypertension in the anamnesis and/or heart failure from easy to moderate degree is required. Treatment of NPVP, including diclofenac, especially in high doses (150 mg a day) and during the long period of treatment, can be connected with the increased risk of developing arterial trombotichesky diseases (for example a myocardial infarction or a stroke). Patients with uncontrollable arterial hypertension, the stagnant heart failure established by coronary heart disease, a disease of peripheral arteries and/or cerebrovascular diseases should accept Diklopharm only after thorough examination. Influence on hematologic indicators during long-term treatment by diclofenac, as well as other NPVP, is recommended blood test monitoring. Diklopharm can inhibit aggregation of thrombocytes reversibly. Patients with disturbances of a hemostasis, the bleeding diathesis or hematologic disturbances should be observed carefully. Asthma in the anamnesis At patients with bronchial asthma, seasonal allergic rhinitis, a rhinedema (nasal polyps), with the chronic obstructive diseases of lungs or persistent infections of airways (which are especially connected with allergic, similar to rhinitises, symptoms) more often than others have reactions to NPVP similar to exacerbation of asthma, a Quincke's edema or urticaria. Therefore for such patients it is necessary to observe extra care and special measures (readiness for emergency situations and rendering emergency aid) are recommended. It is also applicable also to patients with an allergy to other substances, for example, with skin reactions, an itching or urticaria. As well as other NPVP which inhibit activity of synthesis of prostaglandin diclofenac can accelerate a bronchospasm if it is appointed to the patients having chronic bronchial asthma. Pregnancy and the period of a lactation Inhibition of synthesis of prostaglandins can negatively influence pregnancy and/or development of an embryo or fruit. There is a big risk of a miscarriage and/or development of heart diseases and a gastroshizis after use of inhibitors of synthesis of prostaglandins in the early stages of pregnancy. It is considered that the risk increases with increase in a dose and increase in duration of therapy. Use of inhibitors of synthesis of prostaglandins can lead to increase in quantity pre- and post-implantation losses and cases of embriofetalny lethality. Besides, at use of inhibitors of synthesis of prostaglandins in the period of an organogenesis, there is a risk of increase in frequency of various malformations, including cardiovascular. If Diklopharm is accepted by the woman who tries to become pregnant or is in I or II trimester of pregnancy, the dose has to be as low as possible, and treatment duration as it is possible well. Diclofenac is contraindicated in the III trimester of pregnancy. All inhibitors of synthesis of prostaglandins can cause the following risks: for a fruit: - toxic damage of heart and a respiratory system (with premature closing of an arterial channel and development of pulmonary hypertensia), - a renal failure which can progress to a renal failure which is followed oligogidramniozy, for mother and the child: - lengthening of a bleeding time and influence on inhibition of aggregation of thrombocytes, even at use in low doses, - inhibition of reductions of a uterus that leads to a delay and lengthening of childbirth. As well as other NPVP, diclofenac in small amounts gets into breast milk. In this connection, it is not necessary to accept diclofenac during feeding by a breast to avoid undesirable influence on the baby. If treatment is extremely necessary, it is necessary to stop feeding by a breast and to transfer the child to artificial feeding. The fertility Diklopharm can negatively affect female fertility in this connection, drug is not recommended to use to the women planning pregnancy. The women having complications with fertilization or those which underwent inspection owing to an infertilnost have to stop Diklopharm use. Features of influence of drug on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms Patients at whom during drug treatment Diklopharm disorders of vision, dizziness, drowsiness or other disturbances are observed from the central nervous system have to abstain from control of motor transport and work with mechanisms. Overdose Symptoms: vomiting, gastrointestinal bleeding, diarrhea, dizziness, a ring in ears or spasms. In case of a serious poisoning the acute renal failure and damage of a liver is possible. Treatment: the supporting measures and symptomatic treatment which are necessary for elimination of such complications as arterial hypotension, a renal failure, spasms, gastrointestinal break
to Develop