Augmentin® (Amoxicillin, Clavulanic Acid)
- $26.00
What is Augmentin®?
Augmentin® is a combination antibiotic that contains two active ingredients: amoxicillin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic effective against many bacteria, and clavulanic acid, which prevents bacterial resistance by inhibiting beta-lactamase enzymes.
This makes Augmentin® suitable for treating infections caused by bacteria that may otherwise resist amoxicillin alone.
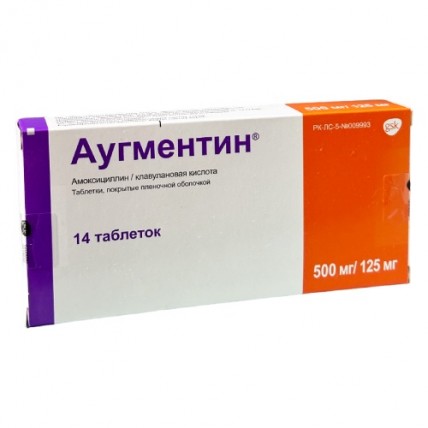
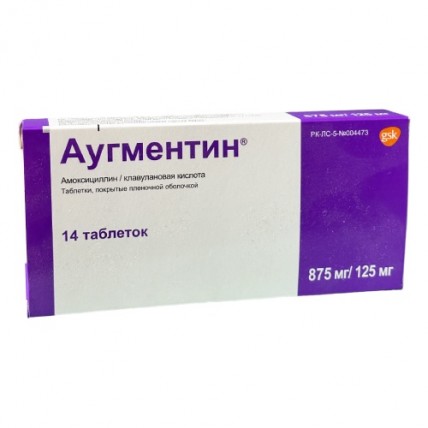
Augmentin® is available in film-coated tablets with two dosage options:
- 500 mg amoxicillin + 125 mg clavulanic acid
- 875 mg amoxicillin + 125 mg clavulanic acid
The combination of these two agents allows for a broader range of bacterial infections to be treated effectively.
What Infections Does Augmentin® Treat?
Augmentin® is prescribed to treat a variety of bacterial infections, particularly those that may resist other antibiotics. These infections include:
- Acute bacterial sinusitis: Infections of the sinuses that cause pain, congestion, and inflammation.
- Acute middle ear infections (otitis media): Common in children, causing ear pain, fever, and irritability.
- Chronic bronchitis exacerbations: Helps manage flare-ups in chronic bronchitis, reducing symptoms like cough, mucus production, and breathlessness.
- Community-acquired pneumonia: Treats pneumonia developed outside of hospital settings, alleviating symptoms like cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs), including cystitis (bladder infection) and pyelonephritis (kidney infection): Used to relieve painful urination, frequent urination, and abdominal or flank pain associated with UTIs.
- Skin and soft tissue infections: Effective against infections in the skin layers and soft tissues, such as cellulitis, abscesses, and even animal bites.
- Bone and joint infections (osteomyelitis): Treats more severe infections like osteomyelitis, which affects the bones.
When using Augmentin®, it is essential to follow official guidelines for antibiotic use to prevent the development of bacterial resistance.
What Precautions Should You Consider Before Taking Augmentin®?
Certain precautions are necessary to avoid adverse reactions or reduced effectiveness:
- Allergies: Inform your healthcare provider of any known allergies to penicillins, cephalosporins, or other beta-lactam antibiotics. Augmentin® can cause allergic reactions, especially in those with a history of antibiotic allergies.
- Liver Issues: Augmentin® is not recommended if you have experienced liver dysfunction or jaundice linked to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid in the past. Liver function should be carefully monitored during treatment, especially in those with existing liver conditions.
- Kidney Function: Reduced kidney function can affect how your body processes Augmentin®. Dose adjustments may be needed to prevent accumulation, which could lead to adverse effects.
These precautions help ensure the safe and effective use of Augmentin®.
How Should Augmentin® Be Taken?
The dosage and administration of Augmentin® vary depending on the infection severity, patient’s age, weight, and kidney function.
Adults and Children over 40 kg:
- 500 mg/125 mg tablets: Typically, one tablet three times daily (every 8 hours) for moderate infections.
- 875 mg/125 mg tablets: Commonly prescribed as one tablet twice daily (every 12 hours) or, for severe infections, three times daily (every 8 hours).
Children under 40 kg:
- Dosage is generally weight-based. Pediatric patients may require a suspension form or pediatric sachets of Augmentin® for accurate dosing.
Special Populations:
- Elderly patients: No specific dose adjustments are usually required, but close monitoring is recommended due to age-related health factors.
- Liver impairment: Use with caution, as these patients may need regular liver function assessments throughout treatment.
- Kidney impairment: Dose adjustments are often required, especially for patients with severely reduced kidney function, to avoid excessive drug accumulation.
Administration Tip: Take Augmentin® with food to minimize gastrointestinal discomfort. Swallow tablets whole with water; do not crush, chew, or split the tablets.
What Potential Side Effects Might Occur with Augmentin®?
As with all medications, Augmentin® may cause side effects. While many are mild, some may require medical attention:
- Very common: Diarrhea is a frequently reported side effect.
- Common: Nausea, vomiting, and candidiasis (fungal infections affecting the skin or mucosa) can occur. Taking Augmentin® with food can help minimize nausea.
- Uncommon: Side effects like dizziness, headaches, digestive issues, and skin rash may appear.
- Rare: Blood cell changes, such as reversible leukopenia (low white blood cell count) and thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), as well as skin conditions and prolonged blood clotting times, can develop.
- Very rare: Severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), liver issues (hepatitis or jaundice), and severe skin reactions (Stevens-Johnson syndrome) have been reported.
If you experience any severe or prolonged symptoms, discontinue use and seek medical advice immediately.
What Should You Do in Case of Overdose?
In cases of overdose, symptoms may include gastrointestinal disturbances and electrolyte imbalance.
High doses or impaired kidney function may increase the risk of seizures.
Treatment for Overdose: Promptly consult a healthcare provider if an overdose occurs.
Hemodialysis can help remove Augmentin® from the bloodstream if necessary.
How Should You Store Augmentin®?
Store Augmentin® in a cool, dry place below 25°C (77°F) and ensure it is out of reach of children.
Do not use the medication past its expiration date, as it may lose effectiveness or cause adverse effects.