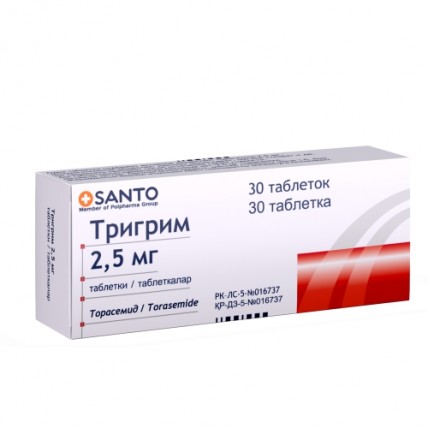
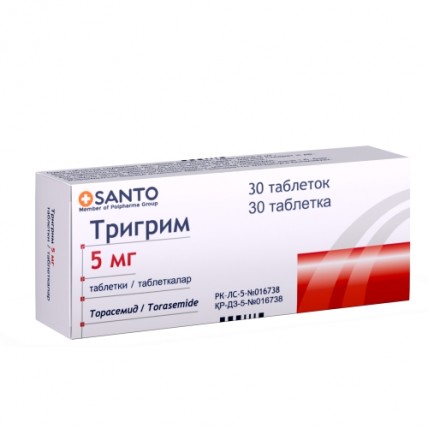
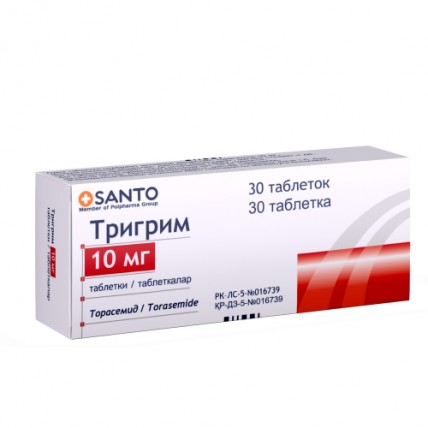
TRIGRIM (Torasemide) 2.5 / 5 / 10 mg, 30 tablets
- $16.00
What is Trigrim (Torasemide)?
Trigrim (Torasemide) is a medication primarily used to treat conditions associated with fluid retention and high blood pressure.
This diuretic works by increasing urine production, helping to reduce excess fluid in the body.
It is commonly prescribed for individuals experiencing swelling due to heart failure, liver disease, kidney problems, or pulmonary issues.
Additionally, it is effective for managing primary arterial hypertension, either as a standalone treatment or in combination with other blood pressure medications.
Trigrim is available in 2.5 mg, 5 mg, and 10 mg tablets, with each dose designed for oral administration.
It is a potent medication and should be used under medical supervision to ensure its effectiveness and safety.
What are the uses of Trigrim?
Trigrim is primarily prescribed for:
- Edema (fluid retention): It helps reduce swelling caused by congestive heart failure, liver diseases, kidney dysfunction, or pulmonary conditions.
- Primary arterial hypertension: It lowers high blood pressure, either alone or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs.
What Makes Torasemide the Best Choice for Edema and Hypertension?
Struggling with fluid retention or high blood pressure? Torasemide is a highly effective diuretic trusted by healthcare professionals to treat edema caused by heart failure, liver disease, or kidney conditions.
It also plays a vital role in managing hypertension by reducing fluid levels and improving blood circulation.
With options in 2.5 mg, 5 mg, and 10 mg tablets, Torasemide offers tailored dosing for your specific needs.
Its fast-acting formula helps relieve swelling while maintaining electrolyte balance when used as directed.
How should you use Trigrim?
Dosage instructions for adults:
Hypertension:
- Start with 2.5 mg taken orally once daily.
- If necessary, the dose may be increased to 5 mg once daily for optimal results.
- Doses above 5 mg typically do not offer additional blood pressure reduction.
Edema:
- Begin with 5 mg once daily.
- If this dose is insufficient, increase to 10 mg daily, with a maximum dosage of 40 mg per day in severe cases.
- Dosage adjustments should always be guided by a healthcare professional.
Special populations:
- Elderly: No specific dose adjustments are needed.
- Children: Trigrim is not recommended for use in individuals under 18 due to insufficient safety data.
What precautions should you take when using Trigrim?
- Monitor electrolyte levels: Long-term use may lead to imbalances in potassium, sodium, or magnesium. Regular blood tests are recommended.
- Watch for dehydration: Excessive urination may cause dehydration or low blood pressure.
- Pre-existing conditions: Use with caution if you have prostate issues, diabetes, or a history of gout.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: This medication is not recommended during pregnancy or lactation due to insufficient safety data.
- Driving or operating machinery: Avoid activities requiring concentration, as Trigrim may cause dizziness.
What are the possible side effects of Trigrim?
Common side effects include:
- Electrolyte imbalances (e.g., low potassium or sodium levels).
- Headaches, dizziness, or fatigue.
- Gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
- Muscle cramps or weakness.
Rare but serious side effects may include:
- Allergic reactions like rash or itching.
- Increased uric acid levels, leading to gout flare-ups.
- Irregular heartbeat or severe drops in blood pressure.
- Vision changes or ringing in the ears.
If you experience severe side effects, seek medical attention promptly.
How should you store Trigrim?
- Keep Trigrim tablets in a dry, cool place at temperatures below 25°C (77°F).
- Protect the medication from light and moisture.
- Store it out of reach of children to prevent accidental ingestion.
What should you do in case of a missed dose or overdose?
- Missed dose: Take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s close to your next scheduled dose. Do not double the dose to compensate for a missed one.
- Overdose: Symptoms include excessive urination, dehydration, and electrolyte disturbances, potentially causing confusion or cardiovascular collapse. Seek immediate medical attention in such cases.