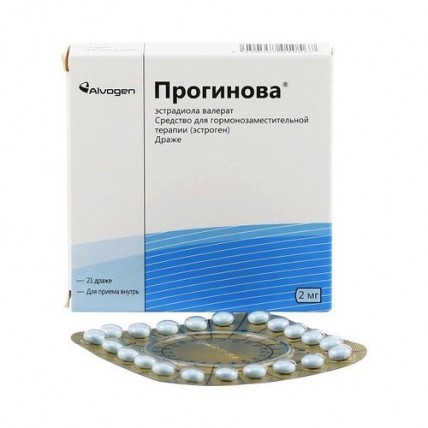
Progynova® (Estradiol Valerate) 2 mg, 21 Dragees
- $50.00
Compound
One tablet contains the active substance - estradiol valerate 2.0 mg
excipients: lactose monohydrate, corn starch, povidone 25000, talc, magnesium stearate
shell composition: sucrose, povidone 700000, macrogol 6000, calcium carbonate, talc, glycerol 85%, titanium dioxide (E171), indigo carmine (E132), montanglycol wax
Indications for use
- hormone replacement therapy (HRT) to treat the signs and symptoms of estrogen deficiency due to natural menopause or sterilization
- prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
Method of administration and dosage
Women with a removed uterus can start taking the drug at any time.
If the patient has not removed the uterus, and menstruation is still continuing, the combined treatment regimen with Proginova in combination with any gestagen (see combined treatment regimen) should be started in the first 5 days of the menstrual cycle.
Patients with amenorrhea or very infrequent periods, as well as postmenopausal women, can start a combination treatment regimen (see combination treatment regimen) at any time, provided that pregnancy is excluded.
When switching from another means of HRT (cyclic or sequential hormone therapy, as well as continuous combination therapy)
When switching from another means of HRT, it is necessary to complete the current cycle of this drug before starting therapy with Proginova®.
Dosage regimen
Take one tablet daily.
Dragee is preferably taken at the same time of day.
Dragee is taken whole with a small amount of liquid.
Each pack is designed for a 21-day intake. After each 21-day course, you can take a break from taking the drug, usually for a week or less (cyclic HRT), or continue to take pills daily (continuous HRT). In the latter case, the pills from the new package begin to be taken immediately after the pills in the previous package have run out.
Combined treatment regimen
Women with an unremoved uterus are advised to additionally take the appropriate progestogen for 10-14 days every 4 weeks (cyclic combined HRT) or together with each estrogen dragee (continuous combined HRT).
It is necessary to carry out adequate medical monitoring of the patient's condition to ensure compliance with the recommended combination regimen.
Taking missed pills
If a woman has forgotten to take pills, she can take it within the next 12 to 24 hours. If treatment is interrupted for a longer time, bleeding may occur.
Additional information for special categories of patients
Elderly patients
No dose adjustment is necessary in elderly patients.
For women aged 65 and over, see the Special Instructions section.
Patients with liver disorders
Proginov's drug has not been specifically studied in women with impaired liver function.
Patients with renal impairment
Progynova drug has not been specifically studied in women with impaired renal function. The available data do not suggest dose adjustments in these patients.
Side effects
Serious side effects associated with taking HRT are also listed in the "Special instructions" section.
The following are adverse drug reactions categorized by organ system according to MedDRA - Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities.
Often (≥1 / 100, <1/10)
- decrease or increase in body weight
- headaches
- abdominal pain, nausea
- itchy skin, skin rash
- uterine / vaginal bleeding, including spotting
Uncommon (≥1 / 1000, <1/100)
- hypersensitivity reactions
- decreased mood
- dizziness
- visual impairment
- heartbeat
- dyspepsia
- erythema nodosum, urticaria
- tension and pain in the mammary glands
- edema
Rarely (<1/1000)
- feeling anxious, decreased or increased libido
- migraine
- intolerance to contact lenses
- bloating, vomiting
- hirsutism, acne
- muscle cramps
- dysmenorrhea, vaginal discharge, a condition similar to premenstrual
noma syndrome, enlargement of the mammary glands
- fatigue
Description of selected adverse reactions
- in women with hereditary angioedema, exogenous estrogens can provoke or exacerbate the symptoms of this disease
In view of the content of glycerol in the composition of 85%, diarrhea may develop.
Contraindications
It is not recommended to start hormone replacement therapy (HRT) if you have any of the conditions listed below. If any of these conditions occurs during HRT, then you should immediately stop using the drug.
- hypersensitivity to any of the components of the drug
- pregnancy and lactation
- vaginal bleeding of unknown origin
- confirmed or suspected diagnosis of breast cancer
- a confirmed or suspected diagnosis of a hormone-dependent pre-
disease or hormone-dependent malignant tumor
- availability in current or history of liver tumors (benign or malignant)
- severe liver disease
- acute arterial thromboembolism (eg, myocardial infarction, stroke)
- acute deep vein thrombosis, current or history of thromboembolic disorders
- high risk of developing venous or arterial thrombosis
- severe hypertriglyceridemia
- children and adolescents up to 18 years old
- hereditary fructose intolerance, deficiency of the enzyme Lapp-lactase, malabsorption of glucose-galactose
Drug interactions
When starting HRT, it is necessary to stop using hormonal contraceptives. If necessary, the patient should be recommended non-hormonal contraceptives.
Long-term treatment with drugs that induce liver enzymes (for example, some anticonvulsants and antimicrobial drugs) can increase the clearance of sex hormones and reduce their clinical efficacy. A similar property to induce liver enzymes has been found in hydantoins, barbiturates, primidone, carbamazepine, and rifampicin; this feature is also suggested for oxcarbazepine, topiramate, felbamate, and griseofulvin. The maximum induction of enzymes is usually observed not earlier than after 2 - 3 weeks, but then it can persist for at least 4 weeks after stopping the drug intake.
In rare cases, against the background of concomitant use of certain types of antibiotics (for example, the penicillin and tetracycline groups), a decrease in the level of estradiol was observed.
Substances that undergo significant conjugation (for example, paracetamol) can increase the bioavailability of estradiol due to competitive inhibition of the conjugation system during absorption.
Due to the effect of HRT on glucose tolerance, in some cases, the need for oral antidiabetic drugs or insulin may change.
Interaction with alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption during HRT can lead to an increase in circulating estradiol levels.
Special instructions
Before starting treatment, all the conditions and risk factors listed below should be considered when assessing the ratio of individual risk to the benefit of treating a patient.
It is necessary to immediately stop HRT when contraindications appear, as well as the following violations:
- attacks of migraine or unusually severe and frequent headaches for the first time, as well as other symptoms - precursors of cerebrovascular occlusion
- with recurrence of cholestatic jaundice or cholestatic pruritus, which were first observed during pregnancy or previous treatment with sex steroid hormones
- symptoms of thrombotic disorders or if their occurrence is suspected.
If the state of health or risk factors change (the appearance of new disorders, worsening of existing ones), it is necessary to re-evaluate the risk / benefit ratio for the patient, taking into account the possible need to discontinue therapy.
Consideration should be given to the likelihood of an increased synergistic risk of thrombosis in women, for whom the increased risk may be higher than the normal cumulative risk factor. HRT should not be prescribed if the risk / benefit ratio is negative.
Venous thromboembolism
Results from epidemiological and randomized controlled trials indicate an increased relative risk of developing venous thromboembolism (VTE), such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. Therefore, when prescribing HRT for women with risk factors for VTE, the ratio of risk and benefit of treatment should be carefully weighed and discussed with the patient.
In general, risk factors for the development of VTE include individual and family history (the presence of VTE in close relatives at a relatively young age may indicate a genetic predisposition) and severe obesity. The risk of VTE also increases with age. The question of the possible role of varicose veins in the development of VTE remains controversial.
The risk of VTE may temporarily increase with prolonged immobilization, "large" planned and traumatological operations, or massive trauma. Depending on the cause and duration of immobilization, the question of the advisability of temporarily discontinuing HRT should be resolved.
Arterial thromboembolism
In the course of two clinical studies with long-term combined use of conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) and medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA), a possible increase in the risk of coronary disease (CB) in the first year of use was revealed with the subsequent absence of a positive effect.
One large clinical study using ELE alone found a potential reduction in the incidence of KB among women aged 50-59 years, with no overall beneficial effect among the general population of the study. As a secondary result in two large-scale clinical trials using ELE alone or in combination with MPA, there was
There was a 30-40% increase in the risk of stroke. However, it is not known whether this increased risk extends to other HRT drugs or non-oral routes of administration.
Gallbladder disease
Estrogens increase the lithogenicity of bile. Some women are prone to developing gallstone disease when treated with estrogen.
Dementia
There is limited evidence to suggest that hormone therapy first given to women 65 years of age or older may increase the risk of developing dementia. At the same time, the risk of developing dementia may be reduced if treatment is started in early menopause, as has been observed in other studies. It is not known whether these facts may apply to other HRT medications.
Tumors
Mammary cancer
Found an increase in the relative risk of developing breast cancer in women using HRT for several years. This may be due to earlier diagnosis, acceleration of the growth of an existing tumor on the background of HRT, or a combination of both factors.
More than 50 epidemiological studies have suggested an increased risk of developing breast cancer (risk ranges from 1 to 2). The relative risk increases with duration, but may be absent or reduced with estrogen-only treatment.
When KLE was used alone or in constant combination with MPA, calculated risk indicators were obtained equal to 0.77 (95% confidence interval: 0.59 - 1.01) or 1.24 (95% confidence interval: 1.01 - 1, 54) after approximately 6 years of HRT use. It is not known if this increased risk also extends to other HRT drugs.
This increase is comparable to the increase in the risk of breast cancer in women with each year of delay in the onset of natural menopause, as well as with obesity and alcohol abuse.
The increased risk gradually disappears over several years after discontinuation of HRT.
HRT increases the mammographic density of the mammary glands, which in some cases can have a negative effect on X-ray detection of breast cancer.
Endometrial cancer
With prolonged estrogen monotherapy, the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia or carcinoma increases. It is believed that the appropriate addition of gestagens to the therapy regimen will eliminate this increased risk.
Ovarian cancer
Epidemiological studies have found a slight increase in the risk of ovarian cancer in women who have been on estrogen hormone replacement therapy for more than 10 years, while a meta-analysis of 15 studies did not reveal an increased risk. Therefore, the question of the effect of hormone replacement therapy with estrogens on the development of ovarian cancer remains controversial.
Liver tumors
Against the background of the use of hormonal substances, which in particular are contained in preparations for HRT, in rare cases, benign, and even less often, malignant liver tumors were observed. In some cases, these tumors have led to life-threatening intra-abdominal bleeding.
In case of severe pain in the upper abdomen, enlarged liver or signs of intra-abdominal bleeding, liver tumor should be considered when making a differential diagnosis.
Other conditions
The relationship between HRT and the development of clinically expressed arterial hypertension has not been established. In women taking HRT, a slight increase in blood pressure has been described, a clinically significant increase is rarely observed. However, in some cases, when persistent clinically significant arterial hypertension develops against the background of taking HRT, the issue of canceling HRT should be considered.
For mild liver dysfunctions, including various forms of hyperbilirubinemia, such as Dubin-Johnson syndrome or Rotor syndrome, close medical supervision, as well as periodic liver function tests, are necessary. If the indicators of liver function deteriorate, HRT should be canceled.
Special monitoring is necessary for women with moderately elevated triglyceride levels. In such cases, the use of HRT can cause a further increase in the level of triglycerides in the blood, which increases the risk of acute pancreatitis.
Although HRT can affect peripheral insulin resistance and glucose tolerance, there is usually no need to change the treatment regimen for diabetic patients with HRT. However, women with diabetes should be monitored during HRT.
Some patients under the influence of HRT may develop undesirable manifestations as a result of estrogen stimulation, for example, abnormal uterine bleeding. Frequent or persistent pathological uterine bleeding during treatment is an indication for endometrial examination.
Under the influence of estrogens, an increase in the size of uterine fibroids can be observed. In this case, treatment should be discontinued.
It is recommended to discontinue treatment and recurrence of endometriosis on the background of HRT.
In patients with prolactinoma, a thorough medical examination is necessary, including periodic measurement of the level of prolactin in the blood.
In some cases, chloasma may occur, especially in women with a history of chloasma during pregnancy. During HRT, women with a tendency to develop chloasma should avoid prolonged exposure to the sun or ultraviolet radiation.
The following conditions can occur or worsen with HRT.
Although their relationship with HRT has not been proven, women with these conditions during HRT should be under close medical supervision:
- epilepsy
- benign breast tumor
- bronchial asthma
- migraine
- porphyria
- otosclerosis
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- small chorea.
In women with hereditary angioedema, exogenous estrogens can provoke or exacerbate the symptoms of this disease.
Medical examination and counseling
Before starting or resuming taking the drug, you should familiarize yourself with the patient's medical history and conduct a thorough physical examination, taking into account contraindications and special instructions. The examinations should be repeated periodically while taking Proginova®. The frequency and nature of such examinations are based on established practice guidelines and are determined on an individual basis for each woman, but in general, blood pressure, breast, abdominal and pelvic examination should be included, including cytological examination of cervical mucus.
Influence on the results of laboratory tests
Taking sex steroids can affect the biochemical parameters of liver, thyroid, adrenal and kidney function, the content of transport proteins in the plasma, such as corticosteroid-binding globulin and lipid / lipoprotein fractions, indicators of carbohydrate metabolism, coagulation and fibrinolysis.
Application in pediatrics
Proginova® is not indicated for use in children and adolescents.
Pregnancy and lactation
Proginova should not be administered during pregnancy and lactation.
If you suspect pregnancy, you should stop taking pills until pregnancy is ruled out.
Small amounts of sex hormones can be excreted in breast milk.
Features of the influence of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and potentially dangerous mechanisms.
Not noted.
Overdose
There was no risk of serious acute side effects in case of accidental intake of the drug in an amount that is many times higher than the daily therapeutic dose.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C.
Keep out of the reach of children!
Shelf life - 5 years
Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package.