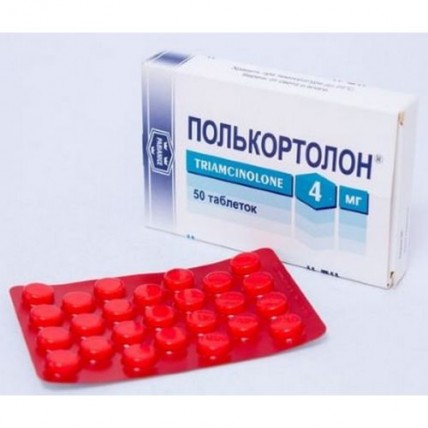
Polkortolon 4 mg (50 tablets)
- $27.00
Sku:
8fedaed5f22f
Ingredient:
Triamcinolone
The instruction
for medical use
of POLCORTOLONUM medicine
A trade name Polcortolonum
the International unlicensed
name Triamcinolonum Dosage Form
of the Tablet of 4 mg
Structure
One tablet contains
active agent of Triamcinolonum of 4 mg,
excipients: lactoses monohydrate, potato starch, magnesium stearate.
The description
of the Tablet of white or almost white color, round shape, the dvukhstoroyena
flat, engraved on the one hand ○, and with another.
Diameter of a tablet is from 9.5 to 10.5 mm.
The pharmacotherapeutic group
Glucocorticosteroids
the Code of automatic telephone exchange H 02 AB 08
the Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Biological Availability properties of Triamcinolonum after oral administration makes from 20 to 30%. Food slows down absorption of Triamcinolonum in an initial phase, but does not affect the general bioavailability of drug. Triamcinolonum contacts proteins of serum in 40%, generally globulins, binding is characterized by high affinity, but small capacity of communication, with albumine - on the contrary. The volume of distribution of free fraction of drug is 0.6-2 dm3/kg of body weight. Triamcinolonum is metabolized in a liver, to a lesser extent in kidneys. Elimination half-life of Triamcinolonum of blood serum makes from 2 to more hours, of fabrics - 18-36 hours. It is brought out of an organism generally with urine in the form of inactive metabolites, less than 15% are made by not changed Triamcinolonum.
Triamcinolonum passes through a placental barrier and also gets into maternal milk.
The pharmacodynamics
Polcortolonum is a synthetic glucocorticosteroid, to the fluorinated Prednisolonum derivatives possessing strong anti-inflammatory action. The effect is shown in 1-2 hours and remains within about 6 - 8 hours. Time of action is 2.25 days. Consider that 4 mg of drug possess anti-inflammatory action, equivalent 4 mg of Methylprednisolonum, 5 mg of Prednisolonum, 0.75 mg of dexamethasone, 0.6 mg of betamethasone and 20 mg of a hydrocortisone. Possesses weak mineralokortikoidny action. Polcortolonum slows down development of symptoms of inflammation, without influencing its reason. Brakes an accumulation of macrophages, leukocytes and other cells around the inflammatory center. Inhibits phagocytosis, release of lysosomic enzymes and also synthesis and release of chemical mediators of inflammation. Causes reduction of expansion and permeability of capillaries, slowing down of migration of leukocytes and formation of hypostases. Strengthens synthesis of a lipomodulin, inhibitor of a phospholipase A2 releasing arachidonic acid from a phospholipidic membrane with simultaneous inhibition of its synthesis.
Mechanisms of immunodepressive effect are up to the end not studied, but Polcortolonum can inhibit cellular immunological reactions, as well as the specific mechanisms connected with the immune response. Reduces quantity of T lymphocytes, monocytes and acidophilic granulocytes. Reduces also accession of immunoglobulins to receptors by surfaces of cells and slows down synthesis or release of interleukins by braking of a blasttransformation of T lymphocytes and weakening of the early immune response. Slows down penetration of the circulating cell-bound immune complexes through the main membranes and reduces concentration of components of a complement and immunoglobulins.
Polcortolonum inhibits secretion of AKTG a hypophysis that leads to reduction of development of corticosteroids and androgens bark of adrenal glands. Development of insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands and recovery time of its function depends, first of all on duration of treatment and to a lesser extent on a dose, time and frequency of administration of drug, as well as on time of its semi-removal.
At one-time reception from 60 to 100 mg of Triamcinolonum the activity of adrenal glands remains oppressed within 24-48 hours and returns to norm within 30-40 days. Practically at each patient accepting Polcortolonum in doses of 12-16 mg a day more, than 7-10 days, insufficiency of adrenal glands can develop. After long reception of high doses the function of adrenal glands can be restored within about 1 year, and at some patients the adrenal insufficiency all life can remain.
Polcortolonum strengthens catabolism of proteins and induces the enzymes participating in metabolism of amino acids. Slows down synthesis and strengthens degradation of proteins in lymphatic, connective, muscle and skin tissue. At prolonged use the atrophy of these fabrics can be observed.
Drug increases utilization of glucose by induction of enzymes of a gluconeogenesis in a liver, stimulation of catabolism of proteins (that increases amount of amino acids for a gluconeogenesis) and reduction of use of glucose in peripheral fabrics. It leads to the increased accumulation of a glycogen in a liver, to increase in concentration of glucose in blood and to increase in insulin resistance. Strengthens a lipolysis and will mobilize fatty acids from fatty tissue that increases concentration of fatty acids in blood serum. At long-term treatment the disturbance of redistribution of fats can be noted. Synthesis of a bone tissue oppresses and strengthens its resorption. Reduces concentration of calcium in blood serum that leads to secondary hyperfunction of epithelial bodies and simultaneous stimulation of osteoclasts and to inhibition of osteoblasts. These effects together with secondary reduction of quantity of proteinaceous components as a result of catabolism of proteins can lead to growth inhibition of bones at children and teenagers and ment of osteoporosis in sick all age.
Strengthens action endo- and exogenous catecholamines.
Indications
- acute insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands, insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands primary (Addison's disease) and secondary, an adrenogenital syndrome (adrenal struma), preoperative preparation, a serious illness and injuries at patients with insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands
- a thyroiditis (not purulent)
- allergic diseases (contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, a serum disease, hypersensitivity reactions to medicines, a constant or seasonal pollinosis (allergic rhinitis)), resistant to treatment by other drugs
- a heart trouble and connective tissue: rheumatic and not rheumatic myocarditis, a pericarditis, a dermatomyositis, a system lupus erythematosus, a recurrent polychondritis, rheumatic polymyalgia, inflammation of vessels, rheumatic diseases (as auxiliary treatment during aggravation): an ankylosing spondylitis, artropatichesky psoriasis, a pseudorheumatism, a juvenile pseudorheumatism (in the cases resistant to other methods of treatment), acute gouty arthritis, a bursitis at patients with an osteoarthritis, a disease of Reuters, rheumatic fever
- vasculites, mesoarteritis a granulomatozny giant-cell, nodular periarteritis
- a serious skin illness: exfoliative dermatitis, herpetiform violent dermatitis, heavy seborrheal dermatitis, a heavy polymorphic erythema (Stephens-Johnson's syndrome), mycosis, a bladderwort, a severe form of eczema and psoriasis, pemphigoid
- nonspecific ulcer colitis, Crohn's disease, a Gee's disease of heavy degree
- the acquired hemolytic anemia, inborn aplastic anemia, anemia owing to a selection hypoplasia of marrow, secondary thrombocytopenia at adults, an idiopathic Werlhof's disease (Verlgof's disease) at adults
- alcoholic hepatitis with encephalopathy, hepatic encephalopathy
- a hypercalcemia in oncological diseases or a sarcoidosis
- an acute and subacute bursitis, an epicondylitis, a nonspecific acute tendovaginitis, a posttraumatic osteoarthritis
- an acute and chronic lymphoblastoid leukosis, granulosa and agranulezny lymphoma, a breast cancer, a prostate cancer a multiple myeloma, the fever connected with an oncological disease (as palliative treatment, along with the corresponding oncological treatment)
- a nephrotic syndrome: for strengthening of a diuresis at hard currency, prevention of a recurrence and a proteinuria at an idiopathic renal syndrome without uraemia
- tubercular meningitis with likvorny blockade (in structure with antibacterial therapy), a disseminate pulmonary tuberculosis
- multiple sclerosis during aggravation, a heavy myasthenia (resistant to treatment by other antimyasthenic drugs, after thymectomy at patients 40 years (long-term treatment))
- an iridocyclitis, a chorioretinitis, a disseminated back uveitis, inflammation of an optic nerve, a sympathetic choroiditis, allergic conjunctivitis, a keratitis (not virus and fungal etiology), an allergic peripheral helcoma
- not herpetic stomatitis resistant to treatment by other drugs
- bronchial asthma, a berylliosis, Leffler's syndrome, aspiration pneumonia, a symptomatic sarcoidosis, chronic emphysema of lungs (resistant to treatment by aminophylline and betamimetics)
- prevention of rejection of an implant (along with other immunodepressants are more senior).
A route of administration and doses
Individually, depending on a disease and treatment response.
Administration of drug according to a day-night rhythm, usually once a day, is recommended in the morning. However, more frequent intake of Polcortolonum can be in certain cases necessary.
To adults and teenagers 14 years are more senior: from 4 mg to 48 mg a day in one or several receptions, after meal.
To children: usually 0.416 - 1.7 mg/kg of body weight or 12.5 - 50 mg/sq.m of a body surface a day, in one or several receptions.
At insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands: 0.117 mg/kg of body weight or 3.3 mg/sq.m of a body surface a day, in one or several receptions.
In case of the admission of reception it is necessary to take the drug as soon as possible or if time of the following reception comes, to pass this dose.
It is not necessary to accept two doses at once.
Side effects
Short-term use of Triamcinolonum, as well as other glucocorticosteroids, results in undesirable effects only in exceptional cases. The risk of the undesirable effects described below concerns, first of all the patients accepting Triamcinolonum for a long time.
- a delay of sodium and liquids, a circulatory unefficiency, potassium loss, a gipokaliyemichesky alkalosis, increase in arterial blood pressure
- weakening of muscles, a steroid myopathy, loss of muscle bulk,
osteoporosis, bone fractures
- a round ulcer and its consequences: perforation, bleeding, perforation of a large or small intestine, especially at patients with inflammatory process in intestines, pancreatitis, a meteorism, an ulcer esophagitis, digestion disturbances, the increased appetite, nausea
- atrophic striya, eels, the slowed-down healing of wounds, thinning of skin, a petechia and a hematoma, an erythema, the increased perspiration,
- spasms, increase in intracranial pressure with a stagnant optic papilla, dizzinesses and headaches, mental disturbances, sleep disorders
- disturbances of a menstrual cycle, an Icenco-Cushing syndrome, growth inhibition at children, secondary insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands and a hypophysis, especially in stressful situations, such as disease, injury, surgery, detection of diabetes and the increased need for insulin and antidiabetic drugs at patients with manifest diabetes, a hirsutism
- a cataract, increase in intraocular pressure, glaucoma, an exophthalmos
- negative balance of nitrogen, increase in concentration of glucose of blood and in urine
- reaction of hypersensitivity (allergic dermatitis, a small tortoiseshell, the Quincke's disease) obliterating thrombophlebitis, increase in body weight
of the Contraindication
- hypersensitivity to Triamcinolonum or other components of drug
- mycoses
- children's age up to 6 years
Medicinal interactions
Combined use of Polcortolonum with:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, alcohol: the increased risk of ulceration and bleeding of a digestive tract,
- Amphotericinum B, karboangidraza inhibitors: a hypopotassemia, a hypertrophy of a cardiac muscle, a circulatory unefficiency,
- paracetamol: a hypernatremia, hypostases, the increased calcium removal, risk of a hypocalcemia and osteoporosis. The increased risk of hepatotoxicity of paracetamol,
- anabolic steroids, androgens: hypostases, eels,
- cholinolytic drugs (atropine): increase in intraocular pressure,
- anticoagulants (coumarin derivatives, indadion, heparin, streptokinase, an urokinase): decrease, and some patients have an increase in their efficiency, the increased risk of ulceration and bleeding of a digestive tract,
- oral antidiabetic drugs, insulin: easing of antidiabetic effect,
- anti-thyroid drugs, hormones of a thyroid gland: change of activity of a thyroid gland, change of a dose or the termination of intake of anti-thyroid drug or hormone of a thyroid gland can be necessary,
- the oral contraceptive drugs containing estrogen: strengthening of effect of Triamcinolonum,
- foxglove glycosides: the increased risk of disturbances of a warm rhythm and toxicity of glycosides,
- diuretic drugs: the reduced effect of diuretics, a hypopotassemia,
- folic acid: the increased need for this drug,
- immunodepressants: the increased risk of an infection, development of a lymphoma and other limfoproliferativny diseases,
- an isoniazid: decrease in concentration of an isoniazid in blood plasma, generally at persons with fast acetylation, can be necessary change of a dose,
- meksiletin: the accelerated metabolism of a meksiletin and decrease in its concentration in blood plasma,
- sodium: hypostases, a hypertension, restriction in a diet of sodium and medicines with the high content of sodium can be necessary, use of glucocorticosteroids sometimes demands additional administration of sodium,
- the vaccines containing live viruses: during use of immunosuppressive doses of glucocorticosteroids the development of viral diseases is possible, the efficiency of an inoculation decreases,
- other vaccines: the increased risk of neurologic complications and decrease in development of antibodies.
The special
instructions Triamcinolonum it is contraindicated to patients with system fungal infections because of risk of strengthening of an infection. In fungal infections, treated Amphotericinum B, it can sometimes be applied to reduction of its side effects, however in these cases can cause a circulatory unefficiency and increase in the sizes of heart and also a heavy hypopotassemia. In case of the raised stress at the patients accepting corticosteroids it is necessary to enter the increased dose of a high-speed glucocorticosteroid.
Before an initiation of treatment of diseases of an oral cavity it is necessary to exclude the changes caused by a herpes virus: a desquamative ulitis (if the diagnosis is confirmed with a biopsy research by an immunofluorescence method), the changes in an oral cavity accompanying the diseases responding to treatment by glucocorticosteroids, such as system lupus erythematosus, bladderwort, pemphigoid, Stephens-Johnson's syndrome flat deprive
of the Patients accepting Triamcinolonum, it is not necessary to impart live virus vaccines. Administration of the inactivated virus or bacterial vaccine can not cause the expected increase in quantity of antibodies unless impart the patients receiving glucocorticosteroids as replaceable treatment, for example, in Addison's disease.
Prescribing of Polcortolonum to patients with an active form of tuberculosis perhaps only in cases of disseminate or lightning tuberculosis and only in combination with antitubercular chemotherapy. The patients with latent tuberculosis or positive tuberculin test accepting Triamcinolonum have to be under observation taking into account a possibility of development of tuberculosis. In case of long-term treatment by glucocorticosteroids such patients have to take the antibacterial drugs preventively.
Triamcinolonum can mask infection symptoms, reduce resistance to an infection and ability to its localization. Can reveal a latent amebiasis. At the persons which arrived from the tropical countries, or patients with the dysentery caused by the unknown reasons before treatment by glucocorticosteroids it is necessary to exclude infection with a dysenteric amoeba.
At patients with hypofunction of a thyroid gland or cirrhosis the effect of Triamcinolonum amplifies. In case of shingles of eyes Triamcinolonum should be applied carefully because of danger of perforation of a cornea.
It is necessary to be careful at treatment of patients with a prothrombinopenia at the same time with Triamcinolonum and aspirin.
At long-term treatment of children and babies it is necessary to watch their psychological development.
Use of glucocorticosteroids can be in certain cases useful at auxiliary treatment of some diseases connected with HIV infection. However, in view of risk of developing infections and new growths, heavy, resistant to treatment, the decision on use of glucocorticosteroids for patients, HIV-positive people and with the developed AIDS syndrome, it is necessary to accept after thorough examination of advantage and risk.
Pregnancy and the period of a lactation
Use of drug at pregnancy is possible only in cases when the expected advantage for mother exceeds potential risk for a fruit. Women of childbearing age have to be warned about potential risk for a fruit.
Triamcinolonum is emitted with breast milk in a small amount. However use of drug in the period of a lactation (breastfeeding), is especially long or in high doses, can cause growth inhibition or disturbance of secretion of endogenous adrenal hormones in the child. In need of prolonged use of drug in the period of a lactation it is necessary to stop breastfeeding.
Influence on ability of control of vehicles and service of potentially dangerous devices
Drug usually does not affect psychomotor ability. However can sometimes cause dizzinesses, headaches, even mental disturbances.
Triamcinolonum it is necessary to take special preventions and measures in minimal effective doses. If the dose decline is possible, it is necessary to reduce it gradually.
The sudden termination of treatment can cause development of insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands therefore the dose of Triamcinolonum should be reduced gradually.
Interruption of treatment after long administration of drug can cause symptoms of a so-called withdrawal of glucocorticosteroids, such as the increased temperature, muscular and articulate pains, feeling sick. These symptoms can appear even in case insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands is noted.
Triamcinolonum in high doses can cause increase in arterial blood pressure, a delay of water and sodium and also the increased potassium removal. Restriction of sodium and increase in potassium in a diet can be necessary. Triamcinolonum causes also increased calcium removal.
Prolonged use of Triamcinolonum can cause a cataract, glaucoma with a possibility of injury of optic nerves and also increases risk of consecutive fungal or viral infections.
During treatment by Triamcinolonum mental disorders, such as euphoria, insomnia, sharp changes of mood, change of the personality, heavy depression, psychosis symptoms can develop. The existing earlier emotional instability or psychotic tendencies can amplify during treatment.
It is necessary to apply carefully Triamcinolonum in nonspecific ulcer colitis if there is a perforation threat, abscesses or other purulent infections, an intestines divertuculosis, a fresh anastomosis of intestines, an active or latent round ulcer, a renal failure, a hypertension, osteoporosis, a myasthenia, diabetes, liver hypofunction, glaucoma, fungal or viral infections, a lipidemia, a hypoalbuminemia.
In case of perforation of a digestive tract at the patients accepting Triamcinolonum in high doses, symptoms of peritonitis can be insignificant or not appear at all.
The drug Polcortolonum contains lactose. It is not recommended to patients with seldom acting hereditary not tolerance of a galactose, deficiency of lactase like Lapp or a glyukozo-galactose malabsorption.
The overdose
is Practically absent threat of acute poisoning, but there is a risk of overdose at prolonged use of Triamcinolonum, especially in high doses.
Symptoms: supertension and hypostases. Besides, the overdose of Triamcinolonum can be shown by emergence of the undesirable effects described above.
Treatment: drug withdrawal or reduction of a dose.
A form of release and packing
On 25 tablets in blister strip packaging from a film of the polyvinylchloride and printing aluminum foil varnished.
On the 2nd blister strip packagings together with the instruction for medical use of medicine in the state and Russian languages put in a pack from cardboard.
To Store storage conditions at a temperature not over 25C, to protect from light and moisture.
To store out of children's reach!
3 years
not to apply a period of storage after an expiration date.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
the Producer
the Pabyanitsky pharmaceutical plant Polfa AO
of st. of the marshal Pilsudsky to 5, 95-200 Pabyanitsa, Poland
the Address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products Representative office of Ltd company Polfa in RK Kabangbai St. of the batyr 34, 050010 Almaty ph. / fax + 7 (727) 291 46 46, 293 80 19 the office@polfa.kz mail e-mail address
for medical use
of POLCORTOLONUM medicine
A trade name Polcortolonum
the International unlicensed
name Triamcinolonum Dosage Form
of the Tablet of 4 mg
Structure
One tablet contains
active agent of Triamcinolonum of 4 mg,
excipients: lactoses monohydrate, potato starch, magnesium stearate.
The description
of the Tablet of white or almost white color, round shape, the dvukhstoroyena
flat, engraved on the one hand ○, and with another.
Diameter of a tablet is from 9.5 to 10.5 mm.
The pharmacotherapeutic group
Glucocorticosteroids
the Code of automatic telephone exchange H 02 AB 08
the Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Biological Availability properties of Triamcinolonum after oral administration makes from 20 to 30%. Food slows down absorption of Triamcinolonum in an initial phase, but does not affect the general bioavailability of drug. Triamcinolonum contacts proteins of serum in 40%, generally globulins, binding is characterized by high affinity, but small capacity of communication, with albumine - on the contrary. The volume of distribution of free fraction of drug is 0.6-2 dm3/kg of body weight. Triamcinolonum is metabolized in a liver, to a lesser extent in kidneys. Elimination half-life of Triamcinolonum of blood serum makes from 2 to more hours, of fabrics - 18-36 hours. It is brought out of an organism generally with urine in the form of inactive metabolites, less than 15% are made by not changed Triamcinolonum.
Triamcinolonum passes through a placental barrier and also gets into maternal milk.
The pharmacodynamics
Polcortolonum is a synthetic glucocorticosteroid, to the fluorinated Prednisolonum derivatives possessing strong anti-inflammatory action. The effect is shown in 1-2 hours and remains within about 6 - 8 hours. Time of action is 2.25 days. Consider that 4 mg of drug possess anti-inflammatory action, equivalent 4 mg of Methylprednisolonum, 5 mg of Prednisolonum, 0.75 mg of dexamethasone, 0.6 mg of betamethasone and 20 mg of a hydrocortisone. Possesses weak mineralokortikoidny action. Polcortolonum slows down development of symptoms of inflammation, without influencing its reason. Brakes an accumulation of macrophages, leukocytes and other cells around the inflammatory center. Inhibits phagocytosis, release of lysosomic enzymes and also synthesis and release of chemical mediators of inflammation. Causes reduction of expansion and permeability of capillaries, slowing down of migration of leukocytes and formation of hypostases. Strengthens synthesis of a lipomodulin, inhibitor of a phospholipase A2 releasing arachidonic acid from a phospholipidic membrane with simultaneous inhibition of its synthesis.
Mechanisms of immunodepressive effect are up to the end not studied, but Polcortolonum can inhibit cellular immunological reactions, as well as the specific mechanisms connected with the immune response. Reduces quantity of T lymphocytes, monocytes and acidophilic granulocytes. Reduces also accession of immunoglobulins to receptors by surfaces of cells and slows down synthesis or release of interleukins by braking of a blasttransformation of T lymphocytes and weakening of the early immune response. Slows down penetration of the circulating cell-bound immune complexes through the main membranes and reduces concentration of components of a complement and immunoglobulins.
Polcortolonum inhibits secretion of AKTG a hypophysis that leads to reduction of development of corticosteroids and androgens bark of adrenal glands. Development of insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands and recovery time of its function depends, first of all on duration of treatment and to a lesser extent on a dose, time and frequency of administration of drug, as well as on time of its semi-removal.
At one-time reception from 60 to 100 mg of Triamcinolonum the activity of adrenal glands remains oppressed within 24-48 hours and returns to norm within 30-40 days. Practically at each patient accepting Polcortolonum in doses of 12-16 mg a day more, than 7-10 days, insufficiency of adrenal glands can develop. After long reception of high doses the function of adrenal glands can be restored within about 1 year, and at some patients the adrenal insufficiency all life can remain.
Polcortolonum strengthens catabolism of proteins and induces the enzymes participating in metabolism of amino acids. Slows down synthesis and strengthens degradation of proteins in lymphatic, connective, muscle and skin tissue. At prolonged use the atrophy of these fabrics can be observed.
Drug increases utilization of glucose by induction of enzymes of a gluconeogenesis in a liver, stimulation of catabolism of proteins (that increases amount of amino acids for a gluconeogenesis) and reduction of use of glucose in peripheral fabrics. It leads to the increased accumulation of a glycogen in a liver, to increase in concentration of glucose in blood and to increase in insulin resistance. Strengthens a lipolysis and will mobilize fatty acids from fatty tissue that increases concentration of fatty acids in blood serum. At long-term treatment the disturbance of redistribution of fats can be noted. Synthesis of a bone tissue oppresses and strengthens its resorption. Reduces concentration of calcium in blood serum that leads to secondary hyperfunction of epithelial bodies and simultaneous stimulation of osteoclasts and to inhibition of osteoblasts. These effects together with secondary reduction of quantity of proteinaceous components as a result of catabolism of proteins can lead to growth inhibition of bones at children and teenagers and ment of osteoporosis in sick all age.
Strengthens action endo- and exogenous catecholamines.
Indications
- acute insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands, insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands primary (Addison's disease) and secondary, an adrenogenital syndrome (adrenal struma), preoperative preparation, a serious illness and injuries at patients with insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands
- a thyroiditis (not purulent)
- allergic diseases (contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, a serum disease, hypersensitivity reactions to medicines, a constant or seasonal pollinosis (allergic rhinitis)), resistant to treatment by other drugs
- a heart trouble and connective tissue: rheumatic and not rheumatic myocarditis, a pericarditis, a dermatomyositis, a system lupus erythematosus, a recurrent polychondritis, rheumatic polymyalgia, inflammation of vessels, rheumatic diseases (as auxiliary treatment during aggravation): an ankylosing spondylitis, artropatichesky psoriasis, a pseudorheumatism, a juvenile pseudorheumatism (in the cases resistant to other methods of treatment), acute gouty arthritis, a bursitis at patients with an osteoarthritis, a disease of Reuters, rheumatic fever
- vasculites, mesoarteritis a granulomatozny giant-cell, nodular periarteritis
- a serious skin illness: exfoliative dermatitis, herpetiform violent dermatitis, heavy seborrheal dermatitis, a heavy polymorphic erythema (Stephens-Johnson's syndrome), mycosis, a bladderwort, a severe form of eczema and psoriasis, pemphigoid
- nonspecific ulcer colitis, Crohn's disease, a Gee's disease of heavy degree
- the acquired hemolytic anemia, inborn aplastic anemia, anemia owing to a selection hypoplasia of marrow, secondary thrombocytopenia at adults, an idiopathic Werlhof's disease (Verlgof's disease) at adults
- alcoholic hepatitis with encephalopathy, hepatic encephalopathy
- a hypercalcemia in oncological diseases or a sarcoidosis
- an acute and subacute bursitis, an epicondylitis, a nonspecific acute tendovaginitis, a posttraumatic osteoarthritis
- an acute and chronic lymphoblastoid leukosis, granulosa and agranulezny lymphoma, a breast cancer, a prostate cancer a multiple myeloma, the fever connected with an oncological disease (as palliative treatment, along with the corresponding oncological treatment)
- a nephrotic syndrome: for strengthening of a diuresis at hard currency, prevention of a recurrence and a proteinuria at an idiopathic renal syndrome without uraemia
- tubercular meningitis with likvorny blockade (in structure with antibacterial therapy), a disseminate pulmonary tuberculosis
- multiple sclerosis during aggravation, a heavy myasthenia (resistant to treatment by other antimyasthenic drugs, after thymectomy at patients 40 years (long-term treatment))
- an iridocyclitis, a chorioretinitis, a disseminated back uveitis, inflammation of an optic nerve, a sympathetic choroiditis, allergic conjunctivitis, a keratitis (not virus and fungal etiology), an allergic peripheral helcoma
- not herpetic stomatitis resistant to treatment by other drugs
- bronchial asthma, a berylliosis, Leffler's syndrome, aspiration pneumonia, a symptomatic sarcoidosis, chronic emphysema of lungs (resistant to treatment by aminophylline and betamimetics)
- prevention of rejection of an implant (along with other immunodepressants are more senior).
A route of administration and doses
Individually, depending on a disease and treatment response.
Administration of drug according to a day-night rhythm, usually once a day, is recommended in the morning. However, more frequent intake of Polcortolonum can be in certain cases necessary.
To adults and teenagers 14 years are more senior: from 4 mg to 48 mg a day in one or several receptions, after meal.
To children: usually 0.416 - 1.7 mg/kg of body weight or 12.5 - 50 mg/sq.m of a body surface a day, in one or several receptions.
At insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands: 0.117 mg/kg of body weight or 3.3 mg/sq.m of a body surface a day, in one or several receptions.
In case of the admission of reception it is necessary to take the drug as soon as possible or if time of the following reception comes, to pass this dose.
It is not necessary to accept two doses at once.
Side effects
Short-term use of Triamcinolonum, as well as other glucocorticosteroids, results in undesirable effects only in exceptional cases. The risk of the undesirable effects described below concerns, first of all the patients accepting Triamcinolonum for a long time.
- a delay of sodium and liquids, a circulatory unefficiency, potassium loss, a gipokaliyemichesky alkalosis, increase in arterial blood pressure
- weakening of muscles, a steroid myopathy, loss of muscle bulk,
osteoporosis, bone fractures
- a round ulcer and its consequences: perforation, bleeding, perforation of a large or small intestine, especially at patients with inflammatory process in intestines, pancreatitis, a meteorism, an ulcer esophagitis, digestion disturbances, the increased appetite, nausea
- atrophic striya, eels, the slowed-down healing of wounds, thinning of skin, a petechia and a hematoma, an erythema, the increased perspiration,
- spasms, increase in intracranial pressure with a stagnant optic papilla, dizzinesses and headaches, mental disturbances, sleep disorders
- disturbances of a menstrual cycle, an Icenco-Cushing syndrome, growth inhibition at children, secondary insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands and a hypophysis, especially in stressful situations, such as disease, injury, surgery, detection of diabetes and the increased need for insulin and antidiabetic drugs at patients with manifest diabetes, a hirsutism
- a cataract, increase in intraocular pressure, glaucoma, an exophthalmos
- negative balance of nitrogen, increase in concentration of glucose of blood and in urine
- reaction of hypersensitivity (allergic dermatitis, a small tortoiseshell, the Quincke's disease) obliterating thrombophlebitis, increase in body weight
of the Contraindication
- hypersensitivity to Triamcinolonum or other components of drug
- mycoses
- children's age up to 6 years
Medicinal interactions
Combined use of Polcortolonum with:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, alcohol: the increased risk of ulceration and bleeding of a digestive tract,
- Amphotericinum B, karboangidraza inhibitors: a hypopotassemia, a hypertrophy of a cardiac muscle, a circulatory unefficiency,
- paracetamol: a hypernatremia, hypostases, the increased calcium removal, risk of a hypocalcemia and osteoporosis. The increased risk of hepatotoxicity of paracetamol,
- anabolic steroids, androgens: hypostases, eels,
- cholinolytic drugs (atropine): increase in intraocular pressure,
- anticoagulants (coumarin derivatives, indadion, heparin, streptokinase, an urokinase): decrease, and some patients have an increase in their efficiency, the increased risk of ulceration and bleeding of a digestive tract,
- oral antidiabetic drugs, insulin: easing of antidiabetic effect,
- anti-thyroid drugs, hormones of a thyroid gland: change of activity of a thyroid gland, change of a dose or the termination of intake of anti-thyroid drug or hormone of a thyroid gland can be necessary,
- the oral contraceptive drugs containing estrogen: strengthening of effect of Triamcinolonum,
- foxglove glycosides: the increased risk of disturbances of a warm rhythm and toxicity of glycosides,
- diuretic drugs: the reduced effect of diuretics, a hypopotassemia,
- folic acid: the increased need for this drug,
- immunodepressants: the increased risk of an infection, development of a lymphoma and other limfoproliferativny diseases,
- an isoniazid: decrease in concentration of an isoniazid in blood plasma, generally at persons with fast acetylation, can be necessary change of a dose,
- meksiletin: the accelerated metabolism of a meksiletin and decrease in its concentration in blood plasma,
- sodium: hypostases, a hypertension, restriction in a diet of sodium and medicines with the high content of sodium can be necessary, use of glucocorticosteroids sometimes demands additional administration of sodium,
- the vaccines containing live viruses: during use of immunosuppressive doses of glucocorticosteroids the development of viral diseases is possible, the efficiency of an inoculation decreases,
- other vaccines: the increased risk of neurologic complications and decrease in development of antibodies.
The special
instructions Triamcinolonum it is contraindicated to patients with system fungal infections because of risk of strengthening of an infection. In fungal infections, treated Amphotericinum B, it can sometimes be applied to reduction of its side effects, however in these cases can cause a circulatory unefficiency and increase in the sizes of heart and also a heavy hypopotassemia. In case of the raised stress at the patients accepting corticosteroids it is necessary to enter the increased dose of a high-speed glucocorticosteroid.
Before an initiation of treatment of diseases of an oral cavity it is necessary to exclude the changes caused by a herpes virus: a desquamative ulitis (if the diagnosis is confirmed with a biopsy research by an immunofluorescence method), the changes in an oral cavity accompanying the diseases responding to treatment by glucocorticosteroids, such as system lupus erythematosus, bladderwort, pemphigoid, Stephens-Johnson's syndrome flat deprive
of the Patients accepting Triamcinolonum, it is not necessary to impart live virus vaccines. Administration of the inactivated virus or bacterial vaccine can not cause the expected increase in quantity of antibodies unless impart the patients receiving glucocorticosteroids as replaceable treatment, for example, in Addison's disease.
Prescribing of Polcortolonum to patients with an active form of tuberculosis perhaps only in cases of disseminate or lightning tuberculosis and only in combination with antitubercular chemotherapy. The patients with latent tuberculosis or positive tuberculin test accepting Triamcinolonum have to be under observation taking into account a possibility of development of tuberculosis. In case of long-term treatment by glucocorticosteroids such patients have to take the antibacterial drugs preventively.
Triamcinolonum can mask infection symptoms, reduce resistance to an infection and ability to its localization. Can reveal a latent amebiasis. At the persons which arrived from the tropical countries, or patients with the dysentery caused by the unknown reasons before treatment by glucocorticosteroids it is necessary to exclude infection with a dysenteric amoeba.
At patients with hypofunction of a thyroid gland or cirrhosis the effect of Triamcinolonum amplifies. In case of shingles of eyes Triamcinolonum should be applied carefully because of danger of perforation of a cornea.
It is necessary to be careful at treatment of patients with a prothrombinopenia at the same time with Triamcinolonum and aspirin.
At long-term treatment of children and babies it is necessary to watch their psychological development.
Use of glucocorticosteroids can be in certain cases useful at auxiliary treatment of some diseases connected with HIV infection. However, in view of risk of developing infections and new growths, heavy, resistant to treatment, the decision on use of glucocorticosteroids for patients, HIV-positive people and with the developed AIDS syndrome, it is necessary to accept after thorough examination of advantage and risk.
Pregnancy and the period of a lactation
Use of drug at pregnancy is possible only in cases when the expected advantage for mother exceeds potential risk for a fruit. Women of childbearing age have to be warned about potential risk for a fruit.
Triamcinolonum is emitted with breast milk in a small amount. However use of drug in the period of a lactation (breastfeeding), is especially long or in high doses, can cause growth inhibition or disturbance of secretion of endogenous adrenal hormones in the child. In need of prolonged use of drug in the period of a lactation it is necessary to stop breastfeeding.
Influence on ability of control of vehicles and service of potentially dangerous devices
Drug usually does not affect psychomotor ability. However can sometimes cause dizzinesses, headaches, even mental disturbances.
Triamcinolonum it is necessary to take special preventions and measures in minimal effective doses. If the dose decline is possible, it is necessary to reduce it gradually.
The sudden termination of treatment can cause development of insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands therefore the dose of Triamcinolonum should be reduced gradually.
Interruption of treatment after long administration of drug can cause symptoms of a so-called withdrawal of glucocorticosteroids, such as the increased temperature, muscular and articulate pains, feeling sick. These symptoms can appear even in case insufficiency of bark of adrenal glands is noted.
Triamcinolonum in high doses can cause increase in arterial blood pressure, a delay of water and sodium and also the increased potassium removal. Restriction of sodium and increase in potassium in a diet can be necessary. Triamcinolonum causes also increased calcium removal.
Prolonged use of Triamcinolonum can cause a cataract, glaucoma with a possibility of injury of optic nerves and also increases risk of consecutive fungal or viral infections.
During treatment by Triamcinolonum mental disorders, such as euphoria, insomnia, sharp changes of mood, change of the personality, heavy depression, psychosis symptoms can develop. The existing earlier emotional instability or psychotic tendencies can amplify during treatment.
It is necessary to apply carefully Triamcinolonum in nonspecific ulcer colitis if there is a perforation threat, abscesses or other purulent infections, an intestines divertuculosis, a fresh anastomosis of intestines, an active or latent round ulcer, a renal failure, a hypertension, osteoporosis, a myasthenia, diabetes, liver hypofunction, glaucoma, fungal or viral infections, a lipidemia, a hypoalbuminemia.
In case of perforation of a digestive tract at the patients accepting Triamcinolonum in high doses, symptoms of peritonitis can be insignificant or not appear at all.
The drug Polcortolonum contains lactose. It is not recommended to patients with seldom acting hereditary not tolerance of a galactose, deficiency of lactase like Lapp or a glyukozo-galactose malabsorption.
The overdose
is Practically absent threat of acute poisoning, but there is a risk of overdose at prolonged use of Triamcinolonum, especially in high doses.
Symptoms: supertension and hypostases. Besides, the overdose of Triamcinolonum can be shown by emergence of the undesirable effects described above.
Treatment: drug withdrawal or reduction of a dose.
A form of release and packing
On 25 tablets in blister strip packaging from a film of the polyvinylchloride and printing aluminum foil varnished.
On the 2nd blister strip packagings together with the instruction for medical use of medicine in the state and Russian languages put in a pack from cardboard.
To Store storage conditions at a temperature not over 25C, to protect from light and moisture.
To store out of children's reach!
3 years
not to apply a period of storage after an expiration date.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
the Producer
the Pabyanitsky pharmaceutical plant Polfa AO
of st. of the marshal Pilsudsky to 5, 95-200 Pabyanitsa, Poland
the Address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products Representative office of Ltd company Polfa in RK Kabangbai St. of the batyr 34, 050010 Almaty ph. / fax + 7 (727) 291 46 46, 293 80 19 the office@polfa.kz mail e-mail address