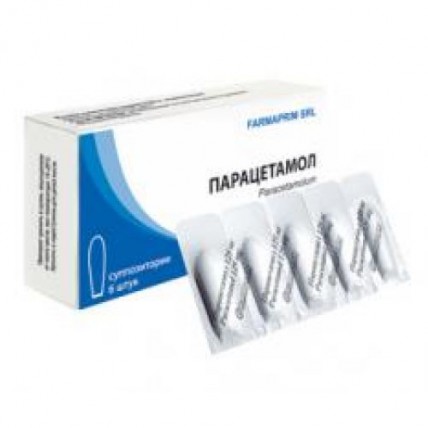
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) 250 mg, 6 suppositories
- $7.00
The instruction for medical use
of PARACETAMOL medicine
the Trade name
Paracetamol
the International unlicensed
name Paracetamol Dosage Form
Suppositories rectal 125 and 250 mg
Structure
One suppository contains
active agent mg paracetamol 125 or 250,
excipients: a basis for suppositories Suppotsir (glycerides semi-synthetic) (Hard fat) up to 1 g.
Description
Suppositories of a tsilindrokonichesky form, color, white or white with a yellowish shade. On a cut the existence of an air and porous core and funneled deepening
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Analgetics, antipyretics is allowed. Anilides.
Code of automatic telephone exchange N02B E01
Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Absorption properties fast and full. The maximum concentration of paracetamol in plasma after use of rectal candles is reached in 0.5-2 h.
Gets into the majority of fabrics and biological liquids of an organism. Gets through a placental barrier and into breast milk.
Linking with proteins of plasma weak-10-15%. The main part of paracetamol is metabolized in a liver on glyukuronidny and sulphatic ways with formation of inactive metabolites, a small part (about 5%) - by hydroxylation with formation of a reactive metabolite - N-acetyl r-aminoquinone (this biotransformation occurs in a liver and kidneys), which is in turn inactivated glutatitonom. It is removed with urine in the form of metabolites, in not changed look less than 5% of paracetamol are removed. Elimination half-life of paracetamol after use of rectal candles makes about 1-4 h.
At elderly patients the clearance of drug decreases and increases elimination half-life
the Pharmacodynamics
Possesses febrifugal, analgetic and weak anti-inflammatory action. Paracetamol blocks TsOG-1 and TsOG-2 mainly in central nervous system, influencing the centers of thermal control and pain. In the inflamed fabrics cellular peroxidases neutralize influence of paracetamol on COG that explains weak anti-inflammatory effect. The lack of the blocking influence on synthesis of prostaglandin in peripheral fabrics causes absence at it negative influence on water salt metabolism and on a mucous membrane of a GIT. It is well soaked up from a GIT. It is metabolized in a liver. It is removed by kidneys.
Indications
- a pain syndrome of weak and moderate intensity of various genesis: an arthralgia, myalgia, neuralgia, migraine, a headache and a toothache, algodismenoreya, etc.
- a feverish syndrome of various origin
- acute respiratory viral diseases, flu, children's infections, infectious and inflammatory diseases, etc.
Route of administration and
Rektalno's doses.
To children: a single dose - 15 mg/kg of body weight, the maximum daily dose - 60 mg/kg of body weight.
Aged from 6 months till 1 year (from 8 to 10 kg): a single dose from 60 mg to 125 mg. If necessary to apply 2-3 times a day with an interval between receptions of 4-6 h.
From 1 year to 3 years (from 10 to 15 kg): single dose of-125 mg. If necessary to apply 4 times a day with an interval between receptions of 4-6 h.
From 3 to 6 years (from 16 to 21 kg): a single dose - 250 mg. If necessary to apply 2-3 times a day with an interval between receptions of 4-6 h.
From 6 to 12 years (from 21 to 35 kg): a single dose from 250 mg. If necessary to apply 3-4 times a day with an interval between receptions of 4-6 h.
To adults and children 12 years are more senior (with body weight more than 60 kg): the minimum single dose - 500 mg, the maximum single dose - 1 g. Frequency rate of reception - 4 times a day with an interval between receptions of 4-6 h. The maximum daily dose - 4 g.
Duration of treatment is 3 days at use as febrifuge and 5 days - as analgetic.
Side effects
Seldom
- anemia, thrombocytopenia, a methemoglobinemia, an agranulocytosis, a leukopenia, a neutropenia, a pancytopenia
- skin rash, an itching, a small tortoiseshell, a Quincke's edema, anaphylactic reactions, including shock.
- at prolonged use in high doses perhaps hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic action
- irritation of a mucous membrane of a rectum, tenesmus.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to paracetamol or any other ingredient of drug
- a concomitant use of others paracetamol of the containing drugs
- recent inflammation or bleeding in a rectum (the contraindication connected with way of introduction)
- the significant disturbances of functions of kidneys and/or a liver
- deficiency of enzyme glyukozo-6-fosfatdegidrogenazy
- a blood disease
- a proctitis
- children's age up to 6 months (for a dose of 125 mg)
- children's age up to 3 years (for a dose of 250 mg)
Medicinal interactions
Paracetamol strengthens effect of anticoagulants.
The concomitant use with salicylates considerably increases risk of nephrotoxic action.
The concomitant use with inductors of microsomal oxidation and hepatotoxic drugs (barbiturates, anticonvulsants, tricyclic antidepressants, rifampicin, an isoniazid, Butadionum, ethanol) increases risk of hepatotoxic action of drug.
The concomitant use with Metoclopramidum can increase paracetamol absorption.
The concomitant use with probenetsidy reduces clearance of paracetamol and increases elimination half-life.
At combined use with Colestyraminum within less than 1 hour after intake of paracetamol the paracetamol absorption reduction is possible.
The concomitant use with levomycetinum, leads to increase in toxic properties of the last.
Special instructions
With care apply at a benign hyperbilirubinemia (including Gilbert's syndrome), in liver diseases (including alcoholic defeat) and kidneys and also to elderly patients.
Intake of paracetamol can distort indicators of laboratory researches at quantitative definition of glucose and uric acid in blood plasma.
At drug use more than 7 days control of a picture of peripheral blood and a functional condition of a liver is necessary.
To apply pregnancy and the period of a lactation With care at pregnancy and in the period of a lactation.
Features influence of medicine on ability to driving of motor transport and to control of potentially dangerous mechanisms
does not influence.
Overdose
Symptoms: the pallor of integuments, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, an abdominal pain, increase in hepatic transaminases in blood plasma, increase in a prothrombin time, appears later morbidity in a liver, glucose metabolism disturbance, metabolic atsidozirovanny In hard cases the liver failure, gepatonekroz, encephalopathy and coma develops. Seldom liver failure develops immediately and can be complicated by an acute renal failure against the background of tubular necrosis. Pancreatitis.
Treatment: introduction of donators of SH-group and predecessors of synthesis of glutathione of methionine, inside, not later than 10 hours after overdose and N-Acetylcysteinum, intravenously within 8 hours after overdose (at once 150 mg/kg, after 50 mg/kg are each 4 hours and after 100 mg/kg within 16 hours), symptomatic therapy, in heavy intoxications resort to a hemodialysis
the Form of release and packing
On 6 suppositories in blister strip packagings from a film polyvinylchloride laminated by polyethylene.
On 1 blister strip packaging together with the instruction for use in the state and Russian languages put in a pack cardboard
Storage conditions
to Store in the dry, protected from light place, at a temperature from 15 to 25 Pages.
To store out of children's reach!
A period of storage
3 years
not to use after an expiration date
of PARACETAMOL medicine
the Trade name
Paracetamol
the International unlicensed
name Paracetamol Dosage Form
Suppositories rectal 125 and 250 mg
Structure
One suppository contains
active agent mg paracetamol 125 or 250,
excipients: a basis for suppositories Suppotsir (glycerides semi-synthetic) (Hard fat) up to 1 g.
Description
Suppositories of a tsilindrokonichesky form, color, white or white with a yellowish shade. On a cut the existence of an air and porous core and funneled deepening
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Analgetics, antipyretics is allowed. Anilides.
Code of automatic telephone exchange N02B E01
Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Absorption properties fast and full. The maximum concentration of paracetamol in plasma after use of rectal candles is reached in 0.5-2 h.
Gets into the majority of fabrics and biological liquids of an organism. Gets through a placental barrier and into breast milk.
Linking with proteins of plasma weak-10-15%. The main part of paracetamol is metabolized in a liver on glyukuronidny and sulphatic ways with formation of inactive metabolites, a small part (about 5%) - by hydroxylation with formation of a reactive metabolite - N-acetyl r-aminoquinone (this biotransformation occurs in a liver and kidneys), which is in turn inactivated glutatitonom. It is removed with urine in the form of metabolites, in not changed look less than 5% of paracetamol are removed. Elimination half-life of paracetamol after use of rectal candles makes about 1-4 h.
At elderly patients the clearance of drug decreases and increases elimination half-life
the Pharmacodynamics
Possesses febrifugal, analgetic and weak anti-inflammatory action. Paracetamol blocks TsOG-1 and TsOG-2 mainly in central nervous system, influencing the centers of thermal control and pain. In the inflamed fabrics cellular peroxidases neutralize influence of paracetamol on COG that explains weak anti-inflammatory effect. The lack of the blocking influence on synthesis of prostaglandin in peripheral fabrics causes absence at it negative influence on water salt metabolism and on a mucous membrane of a GIT. It is well soaked up from a GIT. It is metabolized in a liver. It is removed by kidneys.
Indications
- a pain syndrome of weak and moderate intensity of various genesis: an arthralgia, myalgia, neuralgia, migraine, a headache and a toothache, algodismenoreya, etc.
- a feverish syndrome of various origin
- acute respiratory viral diseases, flu, children's infections, infectious and inflammatory diseases, etc.
Route of administration and
Rektalno's doses.
To children: a single dose - 15 mg/kg of body weight, the maximum daily dose - 60 mg/kg of body weight.
Aged from 6 months till 1 year (from 8 to 10 kg): a single dose from 60 mg to 125 mg. If necessary to apply 2-3 times a day with an interval between receptions of 4-6 h.
From 1 year to 3 years (from 10 to 15 kg): single dose of-125 mg. If necessary to apply 4 times a day with an interval between receptions of 4-6 h.
From 3 to 6 years (from 16 to 21 kg): a single dose - 250 mg. If necessary to apply 2-3 times a day with an interval between receptions of 4-6 h.
From 6 to 12 years (from 21 to 35 kg): a single dose from 250 mg. If necessary to apply 3-4 times a day with an interval between receptions of 4-6 h.
To adults and children 12 years are more senior (with body weight more than 60 kg): the minimum single dose - 500 mg, the maximum single dose - 1 g. Frequency rate of reception - 4 times a day with an interval between receptions of 4-6 h. The maximum daily dose - 4 g.
Duration of treatment is 3 days at use as febrifuge and 5 days - as analgetic.
Side effects
Seldom
- anemia, thrombocytopenia, a methemoglobinemia, an agranulocytosis, a leukopenia, a neutropenia, a pancytopenia
- skin rash, an itching, a small tortoiseshell, a Quincke's edema, anaphylactic reactions, including shock.
- at prolonged use in high doses perhaps hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic action
- irritation of a mucous membrane of a rectum, tenesmus.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to paracetamol or any other ingredient of drug
- a concomitant use of others paracetamol of the containing drugs
- recent inflammation or bleeding in a rectum (the contraindication connected with way of introduction)
- the significant disturbances of functions of kidneys and/or a liver
- deficiency of enzyme glyukozo-6-fosfatdegidrogenazy
- a blood disease
- a proctitis
- children's age up to 6 months (for a dose of 125 mg)
- children's age up to 3 years (for a dose of 250 mg)
Medicinal interactions
Paracetamol strengthens effect of anticoagulants.
The concomitant use with salicylates considerably increases risk of nephrotoxic action.
The concomitant use with inductors of microsomal oxidation and hepatotoxic drugs (barbiturates, anticonvulsants, tricyclic antidepressants, rifampicin, an isoniazid, Butadionum, ethanol) increases risk of hepatotoxic action of drug.
The concomitant use with Metoclopramidum can increase paracetamol absorption.
The concomitant use with probenetsidy reduces clearance of paracetamol and increases elimination half-life.
At combined use with Colestyraminum within less than 1 hour after intake of paracetamol the paracetamol absorption reduction is possible.
The concomitant use with levomycetinum, leads to increase in toxic properties of the last.
Special instructions
With care apply at a benign hyperbilirubinemia (including Gilbert's syndrome), in liver diseases (including alcoholic defeat) and kidneys and also to elderly patients.
Intake of paracetamol can distort indicators of laboratory researches at quantitative definition of glucose and uric acid in blood plasma.
At drug use more than 7 days control of a picture of peripheral blood and a functional condition of a liver is necessary.
To apply pregnancy and the period of a lactation With care at pregnancy and in the period of a lactation.
Features influence of medicine on ability to driving of motor transport and to control of potentially dangerous mechanisms
does not influence.
Overdose
Symptoms: the pallor of integuments, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, an abdominal pain, increase in hepatic transaminases in blood plasma, increase in a prothrombin time, appears later morbidity in a liver, glucose metabolism disturbance, metabolic atsidozirovanny In hard cases the liver failure, gepatonekroz, encephalopathy and coma develops. Seldom liver failure develops immediately and can be complicated by an acute renal failure against the background of tubular necrosis. Pancreatitis.
Treatment: introduction of donators of SH-group and predecessors of synthesis of glutathione of methionine, inside, not later than 10 hours after overdose and N-Acetylcysteinum, intravenously within 8 hours after overdose (at once 150 mg/kg, after 50 mg/kg are each 4 hours and after 100 mg/kg within 16 hours), symptomatic therapy, in heavy intoxications resort to a hemodialysis
the Form of release and packing
On 6 suppositories in blister strip packagings from a film polyvinylchloride laminated by polyethylene.
On 1 blister strip packaging together with the instruction for use in the state and Russian languages put in a pack cardboard
Storage conditions
to Store in the dry, protected from light place, at a temperature from 15 to 25 Pages.
To store out of children's reach!
A period of storage
3 years
not to use after an expiration date