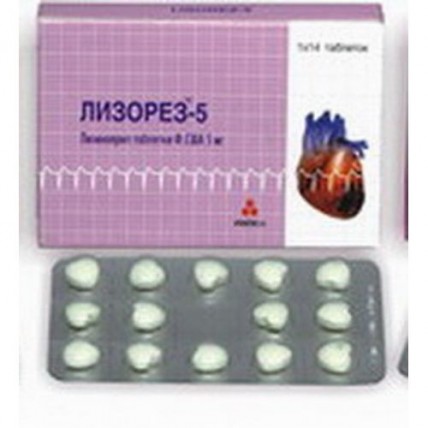
Lizorez (Lisinopril) 5 mg, 14 tablets
- $6.00
The instruction for use
of medicine for experts
of LIZOREZ-2.5/5/10
the Trade name
of Lizorez-2.5, Lizorez-5, Lizorez-10
the International unlicensed
name Lisinopril Dosage Form
of the Tablet of 2.5 mg, 5 mg and 10 mg
Structure
One tablet contains
active agent: lisinopril F. To the USA it is equivalent to lisinopril anhydrous: 2.5 to mg, 5 mg, 10 mg,
excipients: disubstituted phosphate B. F. of calcium, corn starch B. F., starch sodium glycollate B. F., povidone B. F., water the cleaned B.F., talc the cleaned B.F., magnesium B.F. stearate.
Description
of Light yellow color biconvex not coated tablets of a heart-shaped form.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
of Means, the systems influencing renin-angiotenzinovuyu, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, single-component drugs.
The code of automatic telephone exchange C09AA03
the Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Later properties of intake peak plasma concentration of lisinopril are reached within 7 hours. Lisinopril does not contact proteins of plasma, is not exposed to metabolism and is removed completely in not changed view with urine. Absorption of lisinopril averages 25%, differs in big variability (6 - 60%) at use of doses from 5 to 80 mg. Absorption of lisinopril in digestive tract does not depend on meal. Lisinopril badly passes through hematoencephalic and placentary barriers. At use of lisinopril in the period of a lactation, it is necessary to resolve an issue of the breastfeeding termination.
The effect of drug begins in 1 hour after reception, the maximum effect – in 6-7 hours, duration – 24 hours. Stable effect of drug develops in 1 - 1.5 months. The t ½ makes 12 hours. Because drug is removed with urine, in a renal failure the removal of lisinopril decreases that less than 30 ml/min. are important clinically only in case of reduction in the rate of glomerular filtration. Lisinopril can be removed from an organism by means of a hemodialysis.
The pharmacodynamics
Lisinopril suppresses the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) which catalyzes transformation of angiotensin I into vasoconstrictive substance angiotensin II. Effect of lisinopril in arterial hypertension and heart failure is connected with suppression of a system renin-angiotensin-Aldosteronum. Suppression of APF leads to decrease in plasma level of angiotensin II that causes reduction of its vasoconstrictive action and decrease in secretion of Aldosteronum. Decrease in secretion of Aldosteronum can cause small increase in potassium concentration in plasma.
The lack of negative influence of angiotensin II on secretion of renin leads to increase in activity of renin of plasma. Though it is considered that lisinopril reduces arterial blood pressure generally due to suppression system renin-angiotensin-aldosteronovoy, lisinopril has antihypertensive effect at patients with hypertensia even at the low level of renin.
Indications
- arterial hypertension
- chronic heart failure
- an acute myocardial infarction
- damage of kidneys in diabetes.
A route of administration and doses
the Recommended average effective dose - from 5 to 20 mg once a day.
Treatment of arterial hypertension:
Initial therapy: 10 mg once a day. Average range of doses is from 20 to 40 mg once in day.
In heart failure: 5 mg once day.
Acute myocardial infarction: the first dose makes 5 mg, then in 24 hours of 5 mg, in 48 hours – 10 mg, and further on 10 mg once a day.
A dosage in a renal failure: 10 mg to patients with clearance of creatinine more than 30 ml/min. (plasma creatinine approximately up to 3 mg/dl)
the Dosage at patients with heart failure and a renal failure (plasma creatinine more than 3 mg/dl) or a hyponatremia (plasma sodium less than 130 mekv/l): the initial dose makes 2.5 mg under stringent medical control once a day.
Ratio with meal: Meal does not influence absorption of lisinopril in digestive tract.
Maximum single and daily dose: 40 mg.
Side effect
- hypotension and a renal failure
- seldom Quincke's disease (0.1%) which is followed by a laryngeal edema can lead to life-threatening states (in case of a Quincke's disease of the face, extremities, lips, language, the glottis and/or a throat should cancel lisinopril and to immediately begin the corresponding treatment)
- a headache, dizziness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, skin rashes and an itching.
- the cardiopalmus, weakness and cough is rare
- in isolated cases it was reported about development of heavy skin reactions, including a toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stephens-Johnson's syndrome.
- extremely seldom the symptom complex including positive test of ANA (antinuclear antibodies), increase SOE, arthralgia/arthritis, muscular pains, temperature increase, a vasculitis, an eosinophilia and a leukocytosis (patients with a Quincke's disease in the anamnesis even if it was not connected with prescribing of APF inhibitors, enter into group of the increased risk on this side effect)
- constant dry cough developed.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to lisinopril and other APF inhibitors
- hypotension, disturbances of salt metabolism, the profound renal failures
- a concomitant use with kaliysberegayushchy diuretics
- a Quincke's disease in the anamnesis
the Use of lisinopril with kaliysberegayushchy diuretics (Spironolactonum, Triamterenum, amiloride), kaliysoderzhashchy additives, deputies of potassium salts can lead Medicinal interactions to substantial increase of potassium in blood plasma. Therefore in common it is not recommended to use these drugs, or it is necessary to use with extreme care.
At a concomitant use with drugs of lithium the frequent control of level of lithium in blood plasma is necessary.
At the patients accepting diuretics in isolated cases perhaps excessive lowering of arterial pressure at the beginning of therapy by lisinopril. Therefore the dose of lisinopril should be reduced at a concomitant use with diuretics.
At joint reception, lisinopril can reduce effect of indometacin.
Special instructions
at patients with heart failure when prescribing lisinopril some lowering of arterial pressure in 6 - 8 hours after administration of drug therefore it is necessary to be careful at the beginning of performing therapy is noted. It is regularly necessary to control a leukocytic formula at patients with collagenoses and diseases of kidneys.
Extremely seldom at treatment by lisinopril the cholestatic jaundice leading to lightning necrosis of a liver can develop. Therefore patients should be careful when prescribing drug with an abnormal liver function.
At patients with a renal failure at treatment by lisinopril the oliguria and/or the progressing azotemia, and in isolated cases - an acute renal failure can develop.
At patients with arterial hypertension and a unilateral or bilateral stenosis of renal arteries it is necessary to control function of kidneys within the first several weeks of treatment by lisinopril. At big surgical interventions or carrying out anesthesia the drugs causing a lowering of arterial pressure, lisinopril can cause hypotension.
Pregnancy and the period of a lactation
Drug is contraindicated to use at pregnancy as APF inhibitors can cause disturbances in a fruit. It is not established whether drug with breast milk is emitted therefore during treatment it is necessary to stop chest feeding.
The feature of influence on ability to run transport and potentially dangerous mechanisms
Should be careful.
The overdose
At overdose is most probable hypotension for which treatment carry usually out intravenous injection of normal saline solution. Lisinopril can be removed by a hemodialysis.
Form of release
Lizorez-2.5: Tablets of 2.5 mg No. 14.
Lizorez-5: Tablets of 5 mg No. 14.
Lizorez-10: Tablets of 10 mg No. 14.
To Store storage conditions in the dry place at the room temperature not over 250C.
To protect from direct sunshine.
To store out of children's reach!
Not to apply an expiration date of 5 years after an expiration date.
of medicine for experts
of LIZOREZ-2.5/5/10
the Trade name
of Lizorez-2.5, Lizorez-5, Lizorez-10
the International unlicensed
name Lisinopril Dosage Form
of the Tablet of 2.5 mg, 5 mg and 10 mg
Structure
One tablet contains
active agent: lisinopril F. To the USA it is equivalent to lisinopril anhydrous: 2.5 to mg, 5 mg, 10 mg,
excipients: disubstituted phosphate B. F. of calcium, corn starch B. F., starch sodium glycollate B. F., povidone B. F., water the cleaned B.F., talc the cleaned B.F., magnesium B.F. stearate.
Description
of Light yellow color biconvex not coated tablets of a heart-shaped form.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
of Means, the systems influencing renin-angiotenzinovuyu, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, single-component drugs.
The code of automatic telephone exchange C09AA03
the Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Later properties of intake peak plasma concentration of lisinopril are reached within 7 hours. Lisinopril does not contact proteins of plasma, is not exposed to metabolism and is removed completely in not changed view with urine. Absorption of lisinopril averages 25%, differs in big variability (6 - 60%) at use of doses from 5 to 80 mg. Absorption of lisinopril in digestive tract does not depend on meal. Lisinopril badly passes through hematoencephalic and placentary barriers. At use of lisinopril in the period of a lactation, it is necessary to resolve an issue of the breastfeeding termination.
The effect of drug begins in 1 hour after reception, the maximum effect – in 6-7 hours, duration – 24 hours. Stable effect of drug develops in 1 - 1.5 months. The t ½ makes 12 hours. Because drug is removed with urine, in a renal failure the removal of lisinopril decreases that less than 30 ml/min. are important clinically only in case of reduction in the rate of glomerular filtration. Lisinopril can be removed from an organism by means of a hemodialysis.
The pharmacodynamics
Lisinopril suppresses the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) which catalyzes transformation of angiotensin I into vasoconstrictive substance angiotensin II. Effect of lisinopril in arterial hypertension and heart failure is connected with suppression of a system renin-angiotensin-Aldosteronum. Suppression of APF leads to decrease in plasma level of angiotensin II that causes reduction of its vasoconstrictive action and decrease in secretion of Aldosteronum. Decrease in secretion of Aldosteronum can cause small increase in potassium concentration in plasma.
The lack of negative influence of angiotensin II on secretion of renin leads to increase in activity of renin of plasma. Though it is considered that lisinopril reduces arterial blood pressure generally due to suppression system renin-angiotensin-aldosteronovoy, lisinopril has antihypertensive effect at patients with hypertensia even at the low level of renin.
Indications
- arterial hypertension
- chronic heart failure
- an acute myocardial infarction
- damage of kidneys in diabetes.
A route of administration and doses
the Recommended average effective dose - from 5 to 20 mg once a day.
Treatment of arterial hypertension:
Initial therapy: 10 mg once a day. Average range of doses is from 20 to 40 mg once in day.
In heart failure: 5 mg once day.
Acute myocardial infarction: the first dose makes 5 mg, then in 24 hours of 5 mg, in 48 hours – 10 mg, and further on 10 mg once a day.
A dosage in a renal failure: 10 mg to patients with clearance of creatinine more than 30 ml/min. (plasma creatinine approximately up to 3 mg/dl)
the Dosage at patients with heart failure and a renal failure (plasma creatinine more than 3 mg/dl) or a hyponatremia (plasma sodium less than 130 mekv/l): the initial dose makes 2.5 mg under stringent medical control once a day.
Ratio with meal: Meal does not influence absorption of lisinopril in digestive tract.
Maximum single and daily dose: 40 mg.
Side effect
- hypotension and a renal failure
- seldom Quincke's disease (0.1%) which is followed by a laryngeal edema can lead to life-threatening states (in case of a Quincke's disease of the face, extremities, lips, language, the glottis and/or a throat should cancel lisinopril and to immediately begin the corresponding treatment)
- a headache, dizziness, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, skin rashes and an itching.
- the cardiopalmus, weakness and cough is rare
- in isolated cases it was reported about development of heavy skin reactions, including a toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stephens-Johnson's syndrome.
- extremely seldom the symptom complex including positive test of ANA (antinuclear antibodies), increase SOE, arthralgia/arthritis, muscular pains, temperature increase, a vasculitis, an eosinophilia and a leukocytosis (patients with a Quincke's disease in the anamnesis even if it was not connected with prescribing of APF inhibitors, enter into group of the increased risk on this side effect)
- constant dry cough developed.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to lisinopril and other APF inhibitors
- hypotension, disturbances of salt metabolism, the profound renal failures
- a concomitant use with kaliysberegayushchy diuretics
- a Quincke's disease in the anamnesis
the Use of lisinopril with kaliysberegayushchy diuretics (Spironolactonum, Triamterenum, amiloride), kaliysoderzhashchy additives, deputies of potassium salts can lead Medicinal interactions to substantial increase of potassium in blood plasma. Therefore in common it is not recommended to use these drugs, or it is necessary to use with extreme care.
At a concomitant use with drugs of lithium the frequent control of level of lithium in blood plasma is necessary.
At the patients accepting diuretics in isolated cases perhaps excessive lowering of arterial pressure at the beginning of therapy by lisinopril. Therefore the dose of lisinopril should be reduced at a concomitant use with diuretics.
At joint reception, lisinopril can reduce effect of indometacin.
Special instructions
at patients with heart failure when prescribing lisinopril some lowering of arterial pressure in 6 - 8 hours after administration of drug therefore it is necessary to be careful at the beginning of performing therapy is noted. It is regularly necessary to control a leukocytic formula at patients with collagenoses and diseases of kidneys.
Extremely seldom at treatment by lisinopril the cholestatic jaundice leading to lightning necrosis of a liver can develop. Therefore patients should be careful when prescribing drug with an abnormal liver function.
At patients with a renal failure at treatment by lisinopril the oliguria and/or the progressing azotemia, and in isolated cases - an acute renal failure can develop.
At patients with arterial hypertension and a unilateral or bilateral stenosis of renal arteries it is necessary to control function of kidneys within the first several weeks of treatment by lisinopril. At big surgical interventions or carrying out anesthesia the drugs causing a lowering of arterial pressure, lisinopril can cause hypotension.
Pregnancy and the period of a lactation
Drug is contraindicated to use at pregnancy as APF inhibitors can cause disturbances in a fruit. It is not established whether drug with breast milk is emitted therefore during treatment it is necessary to stop chest feeding.
The feature of influence on ability to run transport and potentially dangerous mechanisms
Should be careful.
The overdose
At overdose is most probable hypotension for which treatment carry usually out intravenous injection of normal saline solution. Lisinopril can be removed by a hemodialysis.
Form of release
Lizorez-2.5: Tablets of 2.5 mg No. 14.
Lizorez-5: Tablets of 5 mg No. 14.
Lizorez-10: Tablets of 10 mg No. 14.
To Store storage conditions in the dry place at the room temperature not over 250C.
To protect from direct sunshine.
To store out of children's reach!
Not to apply an expiration date of 5 years after an expiration date.