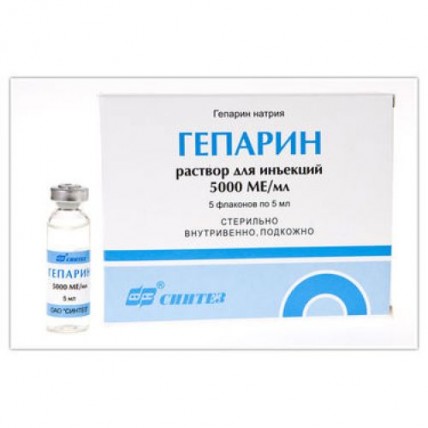
Heparin 5000 IU / ml 5ml 5's injection
- $33.00
Out Of Stock
The instruction
for medical use
of HEPARIN medicine
the Trade name
HEPARIN
the International unlicensed
name Heparin Sodium Dosage Form Solution for injections, 5000 PIECES/ml
Structure
of 1 ml of solution contains
active agent: heparin sodium of 5000 PIECES,
excipients: benzyl alcohol, sodium chloride, water for injections up to 1 ml
the Description
Colourless or light yellow color transparent liquid
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Anticoagulants direct. Heparin and its derivatives
Code of automatic telephone exchange B01AB01
Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Later properties of hypodermic introduction TCmax-of 4-5 h. Communication with proteins of blood plasma – up to 95%, distribution volume very small – 0.06 l/kg (does not leave a vascular bed because of strong linking with proteins of blood plasma). Heparin does not get through a placenta and into breast milk. It is intensively taken endothelial cells and cells of a mononuklearno-macrophagic system (cells of a reticuloendothelial system), concentrates in a liver and a spleen. At an inhalation method of administration (inhalation) it is absorbed by alveolar macrophages, an endothelium of capillaries, big blood and absorbent vessels: these cells are the main place of deposition of heparin from which about it is gradually released, maintaining necessary concentration in blood plasma.
It is metabolized in a liver with participation of N-desulfamidazy and haparinase of thrombocytes joining in metabolism of heparin at later stages. Participation in metabolism of a platelet factor of IV (anti-heparin factor) and also linking of heparin with the system of macrophages explain a fast biological inactivation and short duration of action. Desulfatirovanny molecules under the influence of endoglycosidase of kidneys turn into low-molecular fragments. Elimination half-life of heparin – 1-6 h (on average – 1.5 h), increases in obesity, a liver and/or renal failure, decreases in a pulmonary embolism, infections, malignant tumors. It is allocated with kidneys, mainly in the form of inactive metabolites, and only at introduction of high doses the removal (to 50%) in not changed look is possible. It is not removed by means of a hemodialysis.
The pharmacodynamics
Anticoagulant of direct action, belongs to group of middlemolecular heparins, slows down formation of fibrin. The anticoagulating effect is found in vitro and in vivo, comes directly after intravenous use.
The mechanism of effect of heparin is based first of all on its linking with antithrombin III – inhibitor of the activated blood-coagulation factors: thrombin, IXa, Xa, XIa, XIIa (the ability to inhibit thrombin and the activated factor of X is especially important). Heparin breaks transition of a prothrombin to thrombin, thrombin oppresses and stops formation of fibrin from fibrinogen, and also somewhat reduces aggregation of thrombocytes.
Increases a renal blood stream, increases brain vascular resistance, reduces activity of brain hyaluronidase, activates lipoproteinlipase and possesses hypolipidemic action.
Heparin reduces activity of surfactant in lungs, suppresses excessive synthesis of Aldosteronum in bark of adrenal glands, connects adrenaline, modulates reaction of ovaries to hormonal incentives, enhances activity of parathormone. As a result of interaction with enzymes can increase activity of a tyrosinehydroxylase of a brain, a pepsinogen, DNA polymerase and to reduce miozinovy ATFaza's activity, pyruvatekinases, RNA polymerases, pepsin.
At patients with coronary heart disease (in a combination with acetylsalicylic acid) reduces risk of developing acute thromboses of coronary arteries, a myocardial infarction and sudden death. Reduces the frequency of repeated heart attacks and lethality of the patients who had a myocardial infarction.
In high doses it is effective in pulmonary embolism and venous thrombosis, in small – for prevention of venous tromboemboliya, including after surgeries. At intravenous administration the fibrillation slows down almost at once, at intramuscular – in 15-30 min., at hypodermic – in 20-60 min., after inhalation at most of effect – in a day, duration of anti-coagulative effect respectively – 4-5, 6, 8 h and 1-2 weeks, the therapeutic effect – prevention of a thrombogenesis - remains much longer.
The deficiency of antithrombin III in plasma or in the place of thrombosis can reduce antitrombotichesky effect of heparin.
Indications
- a deep vein thrombosis
- a pulmonary embolism
- thrombosis of coronary arteries
- thrombophlebitises
- unstable stenocardia
- an acute myocardial infarction
- an atrial fibrillation
- the IDCS
- prevention and therapy of a microthrombogenesis and disturbance of microcirculation
- thrombosis of renal veins
- a gemolitikouremichesky syndrome
- mitral heart disease
- the bacterial endocarditis
- glomerunefrit
- lupoid nephrite
- prevention of fibrillation during operations with use of extracorporal methods of blood circulation, during the carrying out a hemodialysis, hemosorption, peritoneal dialysis, a cytapheresis, an artificial diuresis, when washing venous catheters
the Route of administration and doses
appoint Heparin in the form of continuous intravenous infusion or in the form of regular intravenous injections and also subcutaneously (to the area of a stomach).
With the preventive purpose – subcutaneously, on 5000 PIECES/days, with intervals of 8-12 h. The ordinary place for subcutaneous injections is the anterolateral wall of a stomach (in exceptional cases enter into the upper area of a shoulder or hip), at the same time use a fine needle which should be entered deeply, perpendicularly, pleated skins, withheld between big and a forefinger before the end of administration of solution. It is necessary to alternate every time injection sites (in order to avoid forming of a hematoma). The first injection needs to be carried out for 1-2 h prior to operation, in the postoperative period to enter within 7-10 days, and in case of need – longer time.
The initial dose of the heparin entered in the medical purposes usually makes 5000 PIECES and is entered intravenously then treatment is continued, using intravenous infusions.
Maintenance doses are defined depending on a route of administration:
- at continuous intravenous infusion appoint 1000-2000 PIECES/h (24000-48000 PIECES/days), dissolving heparin in 0.9% chloride sodium solution,
- at periodic intravenous injections each 4 h appoint 5000-10000 PIECES of heparin.
The adult in thromboses of light and moderate severity drug is appointed intravenously in the dose of 40000-50000 PIECES/days divided into 3-4 times in heavy thrombosis and an embolism – intravenously in the dose of 80000 PIECES/days divided into 4 times with an interval of 6 h. According to vital indications intravenously enter once 25000 PIECES (5 ml), then on 20000 PIECES each 4 h before achievement of a daily dose of 80000-120000 PIECES. At intravenous drop injection it is necessary to add not less than 40000 PIECES of heparin to the daily volume of infusion solution. Heparin doses at intravenous administration select so that the activated partial tromboplastinovy time (APTT) was – 1.5-2.5 times more than control. At hypodermic introduction of small doses (5000 PIECES 2-3 times a day) for prevention of a thrombogenesis of regular control of AChTV it is not required as it increases slightly.
Continuous intravenous infusion is the most effective route of administration of heparin, the best, than regular (periodic) injections as provides more stable hypocoagulation and less often causes bleedings.
When carrying out extracorporal blood circulation enter in a dose 140 - 400 PIECES/kg or on 1500-2000 PIECES on 500 ml of blood. At a hemodialysis enter intravenously 10000 PIECES in the beginning, then in the middle of the procedure – 30000-50000 more PIECES. For elderly people, especially women, doses have to be reduced.
To children the drug is administered intravenously by drop infusion: from 3 to 6 years – 600 ME/kg a day, from 6 to 15 years – 500 ME/kg a day under control of AChTV.
Side effects
Sometimes:
- dizziness, headache, nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhea
Seldom:
- thrombocytopenia
- skin necrosis
- the arterial fibrinferments which are followed by development of gangrene, myocardial infarction, stroke
- calcification of soft tissues
- osteoporosis, spontaneous bone fractures
- a hypoaldosteronism
- a passing alopecia
- increase in activity of "hepatic" transaminases
- allergic reactions: sometimes – a dermahemia, medicinal fever, a small tortoiseshell, rhinitis, a skin itching and feeling of heat in soles, it is rare - a bronchospasm, collapse, an acute anaphylaxis
- local reactions: the irritation, pain, hyperaemia, a hematoma and ulcerations in the injection site, bleeding (the risk can be reduced to a minimum at careful assessment of contraindications, regular laboratory control of fibrillation and an exact dosage)
- bleeding from digestive tract and uric ways, in the injection site, in the areas which are exposed to pressure from operational wounds and also hemorrhage in other bodies (adrenal glands, a yellow body, retroperitoneal space)
of the Contraindication
- hypersensitivity to heparin
- hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, a vasculitis
- bleeding
- aneurysm of vessels of a brain, the stratifying aortic aneurysm
- a hemorrhagic stroke
- an anti-phospholipidic syndrome
- an injury (especially craniocereberal)
- uncontrollable arterial hypertension
- digestive tract erosive cankers
- the cirrhosis which is followed by a gullet varicosity
- the menstrual period
- the menacing abortion
- childbirth (including recent)
- recently carried out surgical interventions in the eyes, a brain, a prostate, a liver and bilious ways
- a state after a puncture of a spinal cord
- pregnancy
- the lactation period
- children's age up to 3 years
Medicinal interactions
strengthen Effect of heparin some antibiotics (reduce formation of vitamin K intestinal microflora), the acetylsalicylic acid, Dipiridamolum, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other medicines reducing aggregation of the thrombocytes (remaining the main mechanism of a hemostasis with patients against the background of treatment with heparin), the indirect anticoagulants, medicines blocking canalicular secretion.
Weaken – antihistaminic medicines, fenotiazina, cardiac glycosides, niacin, Acidum etacrynicum, tetracyclines, ergot alkaloids, nicotine, nitroglycerine (intravenous administration), thyroxine, adrenocorticotropic hormone, alkaline amino acids and polypeptides, protamin.
It is impossible to mix in one syringe with other medicines.
Special instructions
With care: to the persons having a polyvalent allergy (including bronchial asthma), arterial hypertension, at dental manipulations, diabetes, endocarditis, pericarditis, in the presence of an intrauterine contraceptive (VMK), active tuberculosis, radiation therapy, a liver failure, chronic kidney disease, advanced age (60 years, especially at the woman are more senior).
Heparin cannot be entered intramusculary as possibly formation of hematomas in the injection site.
Solution of heparin can get a yellow shade that does not change its activity or shipping.
When prescribing heparin in the medical purposes its dose is selected depending on the APTT (the activated partial tromboplastinovy time) value.
During use of heparin it is not necessary to enter intramusculary medicines and to carry out a biopsy of bodies.
For cultivation of heparin use only 0.9% chloride sodium solution.
Though heparin does not get into breast milk, appointment to his nursing mothers in some cases caused fast (during 2-4 weeks) development of osteoporosis and injury of a backbone.
Features of influence of medicine on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms
At use of the drug Heparin can arise: dizziness, a headache, nausea, in this regard for the period of treatment it is necessary to refrain from driving or potentially dangerous mechanisms.
Overdose
Symptoms: symptoms of bleeding
Treatment: in the small bleedings caused by heparin overdose it is enough to stop its use. In extensive bleedings the excess of heparin neutralizes protamin sulfate (1 mg of protamin of sulfate on 100 PIECES of heparin). It must be kept in mind that heparin is quickly removed and if protamin sulfate is appointed in 30 min. after the previous dose of heparin, it is necessary to enter only a half of a necessary dose, the maximum dose of protamin of sulfate makes 50 mg.
The hemodialysis is inefficient.
A form of release and packing
Solution for injections on 5 ml in bottles.
5 bottles in blister strip packaging. 1 blister strip packaging with the instruction for medical use in the state and Russian languages place in a pack from cardboard.
50 bottles with 1-5 iinstruktion on medical use in the state and Russian languages place in a box of cardboard.
To Store storage conditions in the dry, protected from light place at a temperature from 8 °C to 15 °C
to Store out of children's reach!
4 years
not to use a period of storage after an expiration date.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
JSC Sintez Producer.
Russian Federation, 640008, Kurgan, Konstitutsii Avenue, 7.
ph./fax (3522) 48-16-89
The owner of the registration certificate
of JSC Sintez, the Russian Federation
To develop the Address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products (goods) of STOFARM LLP, 000100, Republic of Kazakhstan, Kostanay region, Kostanay, Uralskaya St., 14 ph. 714 228 01 79
for medical use
of HEPARIN medicine
the Trade name
HEPARIN
the International unlicensed
name Heparin Sodium Dosage Form Solution for injections, 5000 PIECES/ml
Structure
of 1 ml of solution contains
active agent: heparin sodium of 5000 PIECES,
excipients: benzyl alcohol, sodium chloride, water for injections up to 1 ml
the Description
Colourless or light yellow color transparent liquid
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Anticoagulants direct. Heparin and its derivatives
Code of automatic telephone exchange B01AB01
Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Later properties of hypodermic introduction TCmax-of 4-5 h. Communication with proteins of blood plasma – up to 95%, distribution volume very small – 0.06 l/kg (does not leave a vascular bed because of strong linking with proteins of blood plasma). Heparin does not get through a placenta and into breast milk. It is intensively taken endothelial cells and cells of a mononuklearno-macrophagic system (cells of a reticuloendothelial system), concentrates in a liver and a spleen. At an inhalation method of administration (inhalation) it is absorbed by alveolar macrophages, an endothelium of capillaries, big blood and absorbent vessels: these cells are the main place of deposition of heparin from which about it is gradually released, maintaining necessary concentration in blood plasma.
It is metabolized in a liver with participation of N-desulfamidazy and haparinase of thrombocytes joining in metabolism of heparin at later stages. Participation in metabolism of a platelet factor of IV (anti-heparin factor) and also linking of heparin with the system of macrophages explain a fast biological inactivation and short duration of action. Desulfatirovanny molecules under the influence of endoglycosidase of kidneys turn into low-molecular fragments. Elimination half-life of heparin – 1-6 h (on average – 1.5 h), increases in obesity, a liver and/or renal failure, decreases in a pulmonary embolism, infections, malignant tumors. It is allocated with kidneys, mainly in the form of inactive metabolites, and only at introduction of high doses the removal (to 50%) in not changed look is possible. It is not removed by means of a hemodialysis.
The pharmacodynamics
Anticoagulant of direct action, belongs to group of middlemolecular heparins, slows down formation of fibrin. The anticoagulating effect is found in vitro and in vivo, comes directly after intravenous use.
The mechanism of effect of heparin is based first of all on its linking with antithrombin III – inhibitor of the activated blood-coagulation factors: thrombin, IXa, Xa, XIa, XIIa (the ability to inhibit thrombin and the activated factor of X is especially important). Heparin breaks transition of a prothrombin to thrombin, thrombin oppresses and stops formation of fibrin from fibrinogen, and also somewhat reduces aggregation of thrombocytes.
Increases a renal blood stream, increases brain vascular resistance, reduces activity of brain hyaluronidase, activates lipoproteinlipase and possesses hypolipidemic action.
Heparin reduces activity of surfactant in lungs, suppresses excessive synthesis of Aldosteronum in bark of adrenal glands, connects adrenaline, modulates reaction of ovaries to hormonal incentives, enhances activity of parathormone. As a result of interaction with enzymes can increase activity of a tyrosinehydroxylase of a brain, a pepsinogen, DNA polymerase and to reduce miozinovy ATFaza's activity, pyruvatekinases, RNA polymerases, pepsin.
At patients with coronary heart disease (in a combination with acetylsalicylic acid) reduces risk of developing acute thromboses of coronary arteries, a myocardial infarction and sudden death. Reduces the frequency of repeated heart attacks and lethality of the patients who had a myocardial infarction.
In high doses it is effective in pulmonary embolism and venous thrombosis, in small – for prevention of venous tromboemboliya, including after surgeries. At intravenous administration the fibrillation slows down almost at once, at intramuscular – in 15-30 min., at hypodermic – in 20-60 min., after inhalation at most of effect – in a day, duration of anti-coagulative effect respectively – 4-5, 6, 8 h and 1-2 weeks, the therapeutic effect – prevention of a thrombogenesis - remains much longer.
The deficiency of antithrombin III in plasma or in the place of thrombosis can reduce antitrombotichesky effect of heparin.
Indications
- a deep vein thrombosis
- a pulmonary embolism
- thrombosis of coronary arteries
- thrombophlebitises
- unstable stenocardia
- an acute myocardial infarction
- an atrial fibrillation
- the IDCS
- prevention and therapy of a microthrombogenesis and disturbance of microcirculation
- thrombosis of renal veins
- a gemolitikouremichesky syndrome
- mitral heart disease
- the bacterial endocarditis
- glomerunefrit
- lupoid nephrite
- prevention of fibrillation during operations with use of extracorporal methods of blood circulation, during the carrying out a hemodialysis, hemosorption, peritoneal dialysis, a cytapheresis, an artificial diuresis, when washing venous catheters
the Route of administration and doses
appoint Heparin in the form of continuous intravenous infusion or in the form of regular intravenous injections and also subcutaneously (to the area of a stomach).
With the preventive purpose – subcutaneously, on 5000 PIECES/days, with intervals of 8-12 h. The ordinary place for subcutaneous injections is the anterolateral wall of a stomach (in exceptional cases enter into the upper area of a shoulder or hip), at the same time use a fine needle which should be entered deeply, perpendicularly, pleated skins, withheld between big and a forefinger before the end of administration of solution. It is necessary to alternate every time injection sites (in order to avoid forming of a hematoma). The first injection needs to be carried out for 1-2 h prior to operation, in the postoperative period to enter within 7-10 days, and in case of need – longer time.
The initial dose of the heparin entered in the medical purposes usually makes 5000 PIECES and is entered intravenously then treatment is continued, using intravenous infusions.
Maintenance doses are defined depending on a route of administration:
- at continuous intravenous infusion appoint 1000-2000 PIECES/h (24000-48000 PIECES/days), dissolving heparin in 0.9% chloride sodium solution,
- at periodic intravenous injections each 4 h appoint 5000-10000 PIECES of heparin.
The adult in thromboses of light and moderate severity drug is appointed intravenously in the dose of 40000-50000 PIECES/days divided into 3-4 times in heavy thrombosis and an embolism – intravenously in the dose of 80000 PIECES/days divided into 4 times with an interval of 6 h. According to vital indications intravenously enter once 25000 PIECES (5 ml), then on 20000 PIECES each 4 h before achievement of a daily dose of 80000-120000 PIECES. At intravenous drop injection it is necessary to add not less than 40000 PIECES of heparin to the daily volume of infusion solution. Heparin doses at intravenous administration select so that the activated partial tromboplastinovy time (APTT) was – 1.5-2.5 times more than control. At hypodermic introduction of small doses (5000 PIECES 2-3 times a day) for prevention of a thrombogenesis of regular control of AChTV it is not required as it increases slightly.
Continuous intravenous infusion is the most effective route of administration of heparin, the best, than regular (periodic) injections as provides more stable hypocoagulation and less often causes bleedings.
When carrying out extracorporal blood circulation enter in a dose 140 - 400 PIECES/kg or on 1500-2000 PIECES on 500 ml of blood. At a hemodialysis enter intravenously 10000 PIECES in the beginning, then in the middle of the procedure – 30000-50000 more PIECES. For elderly people, especially women, doses have to be reduced.
To children the drug is administered intravenously by drop infusion: from 3 to 6 years – 600 ME/kg a day, from 6 to 15 years – 500 ME/kg a day under control of AChTV.
Side effects
Sometimes:
- dizziness, headache, nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhea
Seldom:
- thrombocytopenia
- skin necrosis
- the arterial fibrinferments which are followed by development of gangrene, myocardial infarction, stroke
- calcification of soft tissues
- osteoporosis, spontaneous bone fractures
- a hypoaldosteronism
- a passing alopecia
- increase in activity of "hepatic" transaminases
- allergic reactions: sometimes – a dermahemia, medicinal fever, a small tortoiseshell, rhinitis, a skin itching and feeling of heat in soles, it is rare - a bronchospasm, collapse, an acute anaphylaxis
- local reactions: the irritation, pain, hyperaemia, a hematoma and ulcerations in the injection site, bleeding (the risk can be reduced to a minimum at careful assessment of contraindications, regular laboratory control of fibrillation and an exact dosage)
- bleeding from digestive tract and uric ways, in the injection site, in the areas which are exposed to pressure from operational wounds and also hemorrhage in other bodies (adrenal glands, a yellow body, retroperitoneal space)
of the Contraindication
- hypersensitivity to heparin
- hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, a vasculitis
- bleeding
- aneurysm of vessels of a brain, the stratifying aortic aneurysm
- a hemorrhagic stroke
- an anti-phospholipidic syndrome
- an injury (especially craniocereberal)
- uncontrollable arterial hypertension
- digestive tract erosive cankers
- the cirrhosis which is followed by a gullet varicosity
- the menstrual period
- the menacing abortion
- childbirth (including recent)
- recently carried out surgical interventions in the eyes, a brain, a prostate, a liver and bilious ways
- a state after a puncture of a spinal cord
- pregnancy
- the lactation period
- children's age up to 3 years
Medicinal interactions
strengthen Effect of heparin some antibiotics (reduce formation of vitamin K intestinal microflora), the acetylsalicylic acid, Dipiridamolum, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other medicines reducing aggregation of the thrombocytes (remaining the main mechanism of a hemostasis with patients against the background of treatment with heparin), the indirect anticoagulants, medicines blocking canalicular secretion.
Weaken – antihistaminic medicines, fenotiazina, cardiac glycosides, niacin, Acidum etacrynicum, tetracyclines, ergot alkaloids, nicotine, nitroglycerine (intravenous administration), thyroxine, adrenocorticotropic hormone, alkaline amino acids and polypeptides, protamin.
It is impossible to mix in one syringe with other medicines.
Special instructions
With care: to the persons having a polyvalent allergy (including bronchial asthma), arterial hypertension, at dental manipulations, diabetes, endocarditis, pericarditis, in the presence of an intrauterine contraceptive (VMK), active tuberculosis, radiation therapy, a liver failure, chronic kidney disease, advanced age (60 years, especially at the woman are more senior).
Heparin cannot be entered intramusculary as possibly formation of hematomas in the injection site.
Solution of heparin can get a yellow shade that does not change its activity or shipping.
When prescribing heparin in the medical purposes its dose is selected depending on the APTT (the activated partial tromboplastinovy time) value.
During use of heparin it is not necessary to enter intramusculary medicines and to carry out a biopsy of bodies.
For cultivation of heparin use only 0.9% chloride sodium solution.
Though heparin does not get into breast milk, appointment to his nursing mothers in some cases caused fast (during 2-4 weeks) development of osteoporosis and injury of a backbone.
Features of influence of medicine on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms
At use of the drug Heparin can arise: dizziness, a headache, nausea, in this regard for the period of treatment it is necessary to refrain from driving or potentially dangerous mechanisms.
Overdose
Symptoms: symptoms of bleeding
Treatment: in the small bleedings caused by heparin overdose it is enough to stop its use. In extensive bleedings the excess of heparin neutralizes protamin sulfate (1 mg of protamin of sulfate on 100 PIECES of heparin). It must be kept in mind that heparin is quickly removed and if protamin sulfate is appointed in 30 min. after the previous dose of heparin, it is necessary to enter only a half of a necessary dose, the maximum dose of protamin of sulfate makes 50 mg.
The hemodialysis is inefficient.
A form of release and packing
Solution for injections on 5 ml in bottles.
5 bottles in blister strip packaging. 1 blister strip packaging with the instruction for medical use in the state and Russian languages place in a pack from cardboard.
50 bottles with 1-5 iinstruktion on medical use in the state and Russian languages place in a box of cardboard.
To Store storage conditions in the dry, protected from light place at a temperature from 8 °C to 15 °C
to Store out of children's reach!
4 years
not to use a period of storage after an expiration date.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
JSC Sintez Producer.
Russian Federation, 640008, Kurgan, Konstitutsii Avenue, 7.
ph./fax (3522) 48-16-89
The owner of the registration certificate
of JSC Sintez, the Russian Federation
To develop the Address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products (goods) of STOFARM LLP, 000100, Republic of Kazakhstan, Kostanay region, Kostanay, Uralskaya St., 14 ph. 714 228 01 79