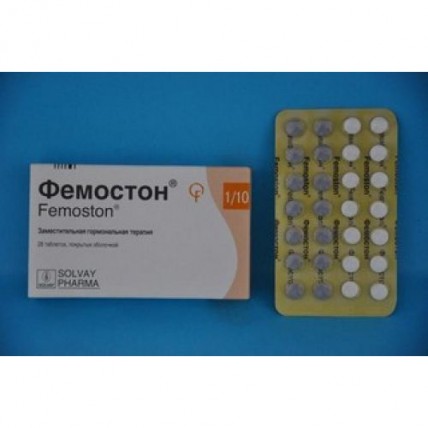
Femoston® (Estradiol/Dydrogesterone) 1/10 mg, 28 film-coated tablets
- $44.80
Sku:
c68047825427
Brand:
Abbott (Netherlands)
Structure
One white film-coated tablet contains the active substance - estradiol hemihydrate 1.03 mg (equivalent to estradiol 1.0 mg),
excipients: lactose monohydrate, hypromellose, corn starch, colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate
shell composition: Opadry® Y-1-7000-white (hypromellose, titanium dioxide (E 171), macrogol 400)
One gray film-coated tablet contains active substances: estradiol hemihydrate 1.03 mg (equivalent to estradiol 1.0 mg), dydrogesterone 10 mg,
excipients: lactose monohydrate, hypromellose (HPMC 2910), corn starch, colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate
shell composition: Opadry® II Gray 85F27664 (polyvinyl alcohol, macrogol 3350, talc, titanium dioxide E171, iron (III) oxide black E172)
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacokinetics
Estradiol
Absorption. The absorption of estradiol depends on the particle size: unlike crystalline estradiol, which is poorly absorbed, micronized estradiol is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Distribution. Estrogens can be considered unleashed or bound. Approximately 98-99% of a dose of estradiol binds to plasma proteins, of which approximately 30-52% to albumin and approximately 46-69% to sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG).
Metabolism. After taking the drug inside, estradiol is rapidly metabolized. The main unconjugated and conjugated metabolites are estrone and estrone sulfate. These metabolites can exhibit estrogenic activity both on their own and after conversion to estradiol. Estrone sulfate undergoes intrahepatic metabolism.
Elimination. Estrone and estradiol are excreted in the urine, mainly in the form of glucuronides. The half-life is 10-16 hours. Estrogens are excreted in the milk of nursing mothers.
Dose and time dependence. With the daily intake of Femoston tablets 1/10 inside, a stable concentration of estradiol is achieved after 5 days of administration, most often by 8-11 days.
Dydrogesterone
Absorption. After oral administration, it is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The time to reach the maximum concentration (Tmax) is from 0.5 to 2.5 hours. The absolute bioavailability of dydrogesterone at a dose of 20 mg orally (compared to 7.8 mg intravenously) is 28%.
Distribution. With a stable concentration of dydrogesterone with intravenous administration, the volume of distribution is about 1400 liters. Dydrogesterone and DHD bind to plasma proteins by more than 90%.
Metabolism. After oral administration, dydrogesterone is rapidly metabolized to DHD. The concentration of the main metabolite 20-α-dihydrodidrogesterone (DHD) peaks approximately 1.5 hours after the dose. The concentration of DHD in blood plasma is significantly higher than that of dydrogesterone. The ratios of AUC (area under the curve) and Cmax (maximum concentration) of DHD and dydrogesterone are approximately 40 and 25, respectively. The half-life of dydrogesterone and DHD averages 5-7 hours and 14-17 hours, respectively. A common feature of all metabolites is that the configuration of the parent compound 4,6-dien-3-one remains unchanged and the absence of 17-alpha-hydroxylation. This explains the lack of estrogenic and androgenic effects of dydrogesterone.
Elimination. After oral administration of labeled dydrogesterone, an average of 63% of the dose is excreted in the urine. Total plasma clearance 6.4 l / min. Complete elimination of dydrogesterone occurs after 72 hours. DHD is excreted in the urine mainly in the form of a glucuronic acid conjugate.
Dose and time dependence. Pharmacokinetics is linear at both single and multiple dosages in the range of 2.5 to 10 mg. Comparison of the kinetics of single and multiple doses shows that the pharmacokinetics of D and DHD do not change as a result of repeated dosing. A stable concentration is achieved after 3 days of treatment.
Pharmacodynamics
Estradiol
The active ingredient in Femoston 1/10, 17-β estradiol, is chemically and biologically identical to endogenous human estradiol. It replaces lost estrogen production in postmenopausal women and relieves symptoms of estrogen deficiency. Estrogens prevent bone loss due to menopause or oophorectomy.
Dydrogesterone
The oral activity of dydrogesterone is comparable to that of parenterally administered progesterone. Since estrogens promote endometrial growth, taking estrogens without the addition of progestogens increases the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. The addition of progestogens significantly reduces the risk of estrogen-related endometrial hyperplasia in women with an unremoved uterus.
The effectiveness of Femoston 1/10 in the treatment of symptoms of estrogen deficiency and dysfunctional uterine bleeding according to the results of clinical studies):
Regular withdrawal bleeding lasting an average of 5 days was observed in 76% of women. Withdrawal bleeding usually began on average on the 28th day of the cycle. Breakthrough bleeding and / or spotting were recorded in 23% of women during the first three months of therapy and in 15% of women during 10–12 months of therapy. During the first year of therapy, amenorrhea (no bleeding or spotting) was observed in 21% of cycles. A decrease in the severity of climacteric symptoms was achieved during the first weeks of treatment.
Prevention of osteoporosis:
Estrogen deficiency in menopause is associated with accelerated bone remodeling and decreased bone mass. The effect of estrogens on bone mineral density is dose dependent. The protection is valid throughout the entire course of therapy. After discontinuation of HRT, bone volume decreases at a rate similar to the rate of bone loss in untreated women. The results of clinical studies indicate that the current use of HRT (alone or in combination with a progestogen prescribed mainly to healthy women) reduces the risk of hip, spinal and other osteoporotic fractures. HRT may also prevent fractures in women with low bone density and / or established osteoporosis, but the evidence is limited.
After two years of taking Femoston 1/10, the bone mineral density (BMD) of the lumbar spine increased by 5.2% ± 3.8% (mean ± standard deviation). During treatment, in 93.0% of women taking Femoston 1/10, the BMD of the lumbar spine remained at the same level or increased. Femoston® 1/10 also affects the BMD of the femur. After two years of taking Femoston, 1/10 BMD increased by 2.7% ± 4.2% in the femoral neck, by 3.5% ± 5.0% in the trochanter of the femur, and by 2.7% ± 6.7% in the Ward's triangle. In 67–78% of women, after Femoston therapy, 1/10 BMD in these 3 femoral regions remained unchanged or increased.
Indications for use
- hormone replacement therapy for symptoms of estrogen deficiency in women during menopause no earlier than 6 months after the last menstruation. Symptoms of estrogen deficiency in women are individual and may include the following disorders: hot flashes, night sweats, sleep disturbances, vaginal dryness, and urinary problems
- prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women with a high risk of fractures in case of intolerance or contraindications to drugs intended for the treatment of osteoporosis
Method of administration and dosage
Estrogen is dosed for continuous use. The progestogen is added during the last 14 days of each 28-day cycle for consistent use. Treatment begins with one white tablet daily for the first 14 days of the cycle and then continues with one gray tablet daily for the next 14 days, as directed on the package for 28 calendar days. Femoston® 1/10 should be taken continuously, without interruptions between packages.
As a rule, sequential combined HRT starts with Femoston 1/10. In the future, the dose of hormones can be changed on an individual basis in accordance with the clinical results of treatment. To switch from another drug for continuous or cyclic therapy, the patient should complete the 28-day cycle and then switch to Femoston® 1/10. When switching from a drug for continuous combination therapy, patients can start taking the drug any day.
If a woman has forgotten to take a pill on time, then it should be taken within 12 hours from the time of proper administration. If more than 12 hours have passed, then the "forgotten" pill must be destroyed and the next pill taken at the usual time. Do not take a double dose to compensate for the missed dose. Skipping the pill may increase the chance of breakthrough bleeding.
Femoston® 1/10 can be taken with or without food.
Elderly. Experience in treating women over 65 years of age is limited.
Children and adolescents. There is no indication for taking Femoston 1/10 in children and adolescents.
Side effects
Side effects most commonly reported in clinical trials are headache, abdominal pain, breast pain / tension, lower back pain.
The following side effects have been observed in clinical trials with the frequency shown below.
Very often (≥ 1/100)
- headache
- abdominal pain
- back pain
- pain / tension in the mammary glands
Often (> 1/100, <1/10)
- vaginal candidiasis
- depression, nervousness
- migraine, dizziness
- nausea, vomiting, flatulence
- skin allergic reactions (including rash, hives, itching)
- menstrual disorders (spotting, uterine bleeding, menorrhagia, amenorrhea, irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea), pelvic pain, cervical secretion
- asthenic conditions (asthenia, fatigue, discomfort), peripheral edema
- increase in body weight
Uncommon (> 1/1000, <1/100)
- an increase in the size of uterine fibroids
- hypersensitivity reactions
- changes in libido
- venous thromboembolism
- dysfunction of the liver, sometimes accompanied by jaundice, asthenia and abdominal pain, dysfunction of the gallbladder
- an increase in the size of the mammary glands, premenstrual syndrome
- weight loss
Rarely (> 1/10000, <1/1000)
- myocardial infarction
angioedema, vascular purpura
Breast Cancer (BC) Risk
In women taking combined estrogen-progestogen-containing drugs for 5 years or more, the risk of breast cancer is up to 2 times higher. Any increase in the risk of breast cancer in users of estrogen-containing drugs is significantly lower than in users of combination drugs. The magnitude of the risk depends on the duration of treatment.
The results of the largest randomized (WHI - Women Helath's Initiative) and pharmaco-epidemiological (MWS - Million Women Study) studies are shown below:
MWS (Million Women Study) - Expected risk of breast cancer after 5 years of treatment.
# is the cumulative risk ratio. This value is not constant, it increases with increasing duration of treatment.
Note: As the incidence of breast cancer varies across Europe, the number of additional breast cancer cases also varies proportionally.
1 - based on the incidence rate in developed countries.
US WHI study - additional risk of breast cancer after 5 years of HRT use
* When the analysis was limited to women who had never taken HRT before enrollment, there was no increase in risk in the first 5 years of treatment: after 5 years, the risk was higher than in those who had never taken HRT.
2 is a group of women in the WHI study with a removed uterus. In whom an increased risk of breast cancer was not found.
Endometrial cancer (ER)
Postmenopausal women with an unremoved uterus
The risk of RE is approximately 5 in every 1000 women with a uterus not using HRT. For women with a uterus, HRT preparations containing only estrogens are not recommended, as this increases the risk of ER. Depending on the duration of estrogen monotherapy and the dose, the increased risk of ER in epidemiological studies ranges from 5 to 55 additional cases diagnosed per 1000 women aged 50-65 years.
Adding progestogens to estrogen monotherapy for at least 12 days of the cycle significantly reduces this increased risk. In the MWS study, the use of combined (cyclic or continuous) HRT regimens did not increase the risk of endometrial cancer (RR - 1 (0.8 - 1.2)).
Ovarian cancer
Long-term use of monoestrogenic and combined HRT is associated with a slight increase in ovarian cancer. According to the results of the MWS study, with HRT over 5 years, there is 1 additional case of ovarian cancer in 2500 users.
Risk of venous thromboembolism
With HRT, the relative risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), that is, deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary artery thrombosis, increases by 1.3-3.0 times. This complication is more likely in the first year of HRT. The results of the WHI study are presented below:
WHI study - additional risk of VTE after 5 years of HRT use
The risk of coronary heart disease is slightly increased in the group of combined HRT users over the age of 60 years.
Risk of ischemic stroke (IS). The use of monoestrogenic and combined HRT drugs is associated with an increase in the relative risk of ischemic stroke by up to 1.5 times. The risk of hemorrhagic stroke is not increased during HRT. The relative risk does not depend on age or duration of HRT, but since the baseline risk strongly depends on age, as a result, the risk of stroke in women on HRT increases with age.
WHI study - additional risk of AI after 5 years of HRT use
Other adverse events known to be associated with the use of combined estrogen-progestogen drugs (including estradiol / dydrogesterone):
- estrogen-dependent benign and malignant neoplasms such as endometrial cancer, ovarian cancer
- an increase in the size of a progestogen-dependent tumor (eg, meningioma)
- hemolytic anemia
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- hypertriglyceridemia
- possible dementia, chorea, exacerbation of epilepsy
- increased keratoconus, contact lens intolerance
- arterial thromboembolism
- pancreatitis (in women with hypertriglyceridemia)
- erythema nodosum multiforme, vascular purpura, chloasma or melasma, which may remain after drug withdrawal
- cramps in the calf muscles
- urinary incontinence
- fibrocystic changes in breast tissue, cervical erosion
- aggravation of porphyria
- increased levels of thyroid hormones
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to active substances or any of the auxiliary components of the drug
- diagnosed in the past or suspected breast cancer
- diagnosed or suspected estrogen-dependent malignant tumors (for example, endometrial cancer or others)
- diagnosed or suspected progestogen-dependent neoplasms (including meningioma)
- bleeding of unknown etiology from the genital tract
- uncontrolled endometrial hyperplasia
- venous thromboembolism in the present or in history (deep vein thrombosis or thromboembolism of the pulmonary vessels)
- diagnosed thrombophilic disorders (deficiency of protein C, protein S or antithrombin)
- active arterial thromboembolism currently or in the recent past (including ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke)
- existing active liver disease (or history) before the normalization of liver tests
- porphyria
- established or suspected pregnancy and breastfeeding period
- for children and adolescence up to 18 years
Drug interactions
No drug interaction studies have been conducted. The doctor should inquire about the medications that the woman is currently taking or took before the appointment of Femoston 1/10.
The effectiveness of estrogens and progestogens may decrease:
Estrogen metabolism can be increased with the simultaneous use of drugs that induce microsomal liver enzymes of the cytochrome P450 system, for example, 2B6, 3A4, 3A5, 3A7. These include anticonvulsants (phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin) and anti-infectious agents (rifampicin, ribavirin, nevirapine, efavirenez).
Ritonavir and nelfinavir, although known as potent inhibitors of CYP450 3A4, A5, A7, on the contrary, induce liver enzymes when used concomitantly with steroid hormones.
Herbal medicines containing the herb St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) increase the metabolism of estrogens and progestogens by suppressing CYP450 3A4.
An increase in the metabolism of estrogens and progestogens can clinically manifest itself in a decrease in efficiency and a change in the nature of the menstrual reaction.
Estrogens can interfere with the metabolism of other drugs:
Estrogens themselves are capable of inhibiting CYP450 enzymes involved in drug metabolism through competitive suppression. This is especially important for drugs with narrow therapeutic indications, such as:
- tacrolimus and cyclosporin A (CYP450 3A4, 3A3)
- fentanyl (CYP450 3A4)
- theophylline (CYP450 1A2).
Clinically, this can be expressed in an increase in the level of these substances in plasma to toxic. Thus, close monitoring of patients over a long period of time and dose reduction of tacrolimus, fentanyl, theophylline and cyclosporine A may be required.
Special instructions
HRT is prescribed when the symptoms of menopause significantly affect a woman's quality of life. All patients need a thorough assessment of the risks and benefits at least once a year. Femoston 1/10 is continued as long as the expected benefits significantly outweigh the possible risks.
Data are limited regarding the risks associated with HRT in the treatment of premature menopause. However, due to the low absolute risk in young women, the balance of benefits and risks may be more favorable for them than for older women.
Medical examination and observation.
A complete medical and family history must be collected before starting or resuming HRT. A medical examination (including examination of the mammary glands and pelvic organs) is carried out in order to identify possible contraindications and conditions requiring precautionary measures. During treatment with Femoston® 1/10, dynamic observation is recommended, the frequency and nature of the studies are determined individually. Patients should be aware that they should immediately report them to the attending physician about all changes in the mammary glands. Special studies, including mammography, are carried out in accordance with accepted screening standards, taking into account clinical indications.
Conditions to be monitored
During treatment with Femoston 1/10, patients should be under close medical supervision if they have or have had in the past the conditions listed below:
- uterine fibroids or endometriosis
- thromboembolism or risk factors for its development
- risk factors for estrogen-dependent tumors, for example, breast cancer in 1st degree relatives
- arterial hypertension
- liver disease (hepatocellular adenoma)
- diabetes mellitus with or without angiopathy
- cholelithiasis
- migraine or (severe) headache
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- history of endometrial hyperplasia
- epilepsy
- bronchial asthma
- otosclerosis.
This applies to those patients in whom the severity of these conditions increased during pregnancy or previous hormonal treatment. It must be borne in mind that when treated with Femoston 1/10, these conditions may recur or become more pronounced.
Reasons for immediate discontinuation of therapy.
Femoston 1/10 should be discontinued if contraindications are identified and in the following situations:
- jaundice or liver dysfunction
- significant increase in blood pressure
- the appearance of a migraine-like headache
- pregnancy
Endometrial hyperplasia and cancer.
The risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer increases with long-term estrogen use. The increased risk of endometrial cancer among users of monoestrogenic HRT drugs is noted from 2 to 12 times compared with non-users, depending on the duration of treatment and the dose of estrogen. After stopping estrogen, the risk remains increased for 10 years.
Adding progestogens for at least 12 days over a 28-day cycle or taking a combination drug significantly reduces this risk in women with an unremoved uterus.
Breakthrough bleeding and spotting bleeding is sometimes seen in the first few months of treatment. In case of breakthrough bleeding or spotting bleeding while taking Femoston 1/10 or after stopping treatment, it is necessary to conduct an examination to identify the cause. This may include an endometrial biopsy to rule out malignancy.
Mammary cancer.
According to current data from clinical and epidemiological studies, women taking combined HRT drugs and, possibly, monoestrogen drugs have an increased risk of breast cancer, and this value depends on the duration of therapy.
Combinations containing estrogen + progestogen
The WHI randomized placebo-controlled study and pharmaco-epidemiological studies have shown an increased risk of breast cancer in women taking combined HRT drugs, which manifests itself 3 years after the start of treatment.
Monotherapy with estrogen-containing drugs
The WHI study found no increased risk of breast cancer in women with a removed uterus who used estrogen-only medications. Observational studies report a modest increase in breast cancer risk, which is much lower than that of women taking combination drugs.
An excess of breast cancer risk is observed in the first few years of treatment, but returns to baseline within several years after discontinuation (maximum 5 years) of treatment. When taking combined HRT drugs, the density of the mammographic image increases, which can have a negative effect on the X-ray diagnosis of breast cancer.
Ovarian cancer
The incidence of ovarian cancer is much less common than breast cancer. Long-term use (at least 5-10 years) of a monoestrogen drug is associated with a slight increase in the risk of ovarian cancer. Several studies, including the WHI, suggest that long-term use of combination HRT may be associated with the same or slightly lower risk.
Venous thromboembolism.
HRT is associated with an increase in the relative risk of developing venous thromboembolism (VTE), that is, deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism, by 1.3-3 times. The likelihood of such a complication is higher in the first year of treatment than in subsequent years.
Patients with a history of VTE or diagnosed thrombophilic conditions have an increased risk of VTE, and HRT may increase this risk. Therefore, HRT is contraindicated in this group of patients.
Risk factors for VTE include: estrogen intake, old age, major surgery, prolonged immobilization, severe obesity (BMI more than 30 kg / m2), pregnancy and the puerperium, systemic lupus erythematosus and cancer. Currently, there is no consensus on the relationship of varicose veins to the risk factors for VTE.
It is necessary to take measures to prevent VTE in patients in the postoperative period. In cases where prolonged immobilization after surgery is expected, especially on the abdominal organs or orthopedic operations on the lower extremities, Femoston 1/10 should be discontinued, if possible, for 4-6 weeks. Resumption of treatment is possible only after complete restoration of physical activity.
Women with no history of VTE but a first-degree relative with a history of VTE at a young age should be screened for thrombophilia. In this case, it is necessary to take into account and warn the woman that not all types of blood coagulation pathologies are detected during screening. HRT is contraindicated if family members have a thrombophilic defect (eg, antithrombin, protein S, or protein C deficiency, or a combination of defects). Patients of this risk group, taking anticoagulant therapy, require a careful assessment of the balance of risks and benefits of prescribing HRT.
If VTE develops while taking Femoston 1/10, treatment should be suspended. The patient should know that when the first possible symptoms of VTE appear (painful swelling of the lower extremities, sudden chest pain, shortness of breath), she should immediately consult a doctor.
Coronary artery disease (CHD).
In randomized clinical trials, there is no evidence that HRT (only estrogens or in combination with progestogens) protects against the development of myocardial infarction in women with or without coronary artery disease.
Combinations containing estrogen + progestogen
The relative risk of coronary artery disease during treatment with combined drugs for HRT slightly increases. Since the absolute risk of developing coronary artery disease largely depends on age, the incidence of additional cases of ischemic heart disease in women receiving combined HRT is very low in the group of healthy women at an age close to the onset of menopause, and increases with age.
Monotherapy with estrogen-containing drugs
According to randomized trials, the risk of coronary artery disease in women with a removed uterus, receiving estrogens in monotherapy, does not increase.
Ischemic stroke.
The risk of ischemic stroke in healthy women with HRT with combined HRT drugs increases by 1.5 times. The relative risk does not depend on age or length of time at menopause. However, it is known that the risk of ischemic stroke depends on age, so the risk of stroke in women taking HRT increases with age.
Other conditions
Estrogens contribute to fluid retention, so patients with heart or kidney failure need careful monitoring.
Women with hypertriglyceridemia need careful monitoring during HRT, as there are rare reports of a significant increase in plasma triglycerides, which led to the development of pancreatitis in women with a similar condition who took estrogens.
Estrogens increase the level of thyroid-binding globulin, which leads to an increase in total circulating thyroid hormone, which is measured by the level of protein-bound iodine, T4 and T3. Levels of free T4 or T3 do not change.
Levels of other binding proteins, for example, corticoid binding globulin, sex hormone binding globulin, may increase, resulting in increased levels of circulating corticosteroid and sex hormones, respectively. Concentrations of free or biologically active hormones do not change. Levels of other plasma proteins (substrate angiotensin / renin, α-1-antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin) may also increase.
HRT does not improve cognitive function. There is a risk of possible dementia in women who start HRT over the age of 65.
Patients with rare hereditary galactose intolerance, Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take Femoston 1/10.
Femoston® 1/10 is not a contraceptive.
Pregnancy and lactation
The use of Femoston® 1/10 is not indicated during pregnancy. If pregnancy occurs while taking Femoston® 1/10, treatment should be stopped immediately. Femoston® 1/10 should not be used during breastfeeding.
Features of the influence of the drug on the ability to drive a vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms
Care must be taken when driving vehicles and moving machinery.
Overdose
So far, there have been no reports of symptoms of an overdose of Femoston 1/10. Estradiol and dydrogesterone have low toxicity.
Symptoms: Possible increased side effects of the drug, such as nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness, dizziness, abdominal pain, drowsiness / fatigue, and withdrawal bleeding.
Treatment: symptomatic. There is no specific antidote. It is unlikely that any specific symptomatic treatment will be required. The above data also apply for overdose in children.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30 ° С
Keep out of the reach of children!
Shelf life - 3 years
Do not use after the expiration date.