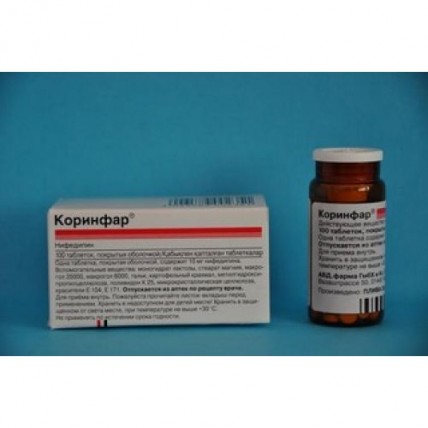
Corinfar 100s 10 mg coated tablets
- $17.00
Sku:
bd9a2a99d7c7
Ingredient:
Nifedipine
The instruction for medical use
of medicine
Corinfarum
the Trade name
of the drug Corinfarum International Unlicensed Name Nifedipine Dosage Form
of the Tablet, coated, 10 mg
Structure
One tablet contains
active agent - nifedipine of 10 mg,
excipients: lactoses monohydrate, potato starch, cellulose microcrystalline, PVP K 25, magnesium stearate, methylhydroxypropyl cellulose, macrogoal 6000, macrogoal 35000, dye quinolinic yellow (E 104), titan dioxide (E 171), talc
Description
Yellow, biconvex, round tablets, coated
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Blockers of slow calcium channels. Blockers of slow calcium channels selection. Dihydropyridinic derivatives. Nifedipine.
The ATX C08CA05 code
the Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Later properties of use inside on an empty stomach active ingredient nifedipine quickly and almost is completely soaked up from digestive tract. Nifedipine is exposed to active metabolism at the first passing through a liver. The bioavailability of Corinfarum is 50 - 70%.
The maximum concentration in plasma or blood serum at use of Corinfarum in the form of solution are reached approximately in 15 minutes, at use in the form of other dosage forms without the prolonged release of active agent - in 15-75 minutes. About 95% of the nifedipine entered into an organism contact proteins of blood plasma (albumine). In a liver nifedipine is almost completely metabolized, first of all due to oxidizing and hydrolytic processes. The metabolites which are formed at the same time have no pharmakodinamichesky activity. In the form of metabolites, nifedipine is removed from an organism mainly through kidneys. At the same time the main metabolite is M-1, 60 - 80% of the accepted nifedipine dose fall to its share. Other amount of medicinal substance is removed in the form of metabolites together with a stake. Only traces of active agent in not changed form meet in urine (less than 0.1%). Elimination half-life makes 2-5 hours. Accumulation of medicinal substance in an organism when performing long-term treatment by therapeutic doses was not described. At the lowered function of a liver the accurate lengthening of elimination half-life of active agent and reduction of the general plasmatic clearance is noted.
The pharmacodynamics
Corinfarum is the representative of antagonists of calcium of group derivative 1.4 dihydropyridines. Antagonists of calcium in a highly specific form react with potentsialzavisimy calcium channels and block receipt of calcium ions through calcium channels like L in a cell. There is lowering of concentration of calcium in cells and by that oppression of intracellular momentum transfer. Corinfarum first of all influences smooth muscle cells of coronary arteries and peripheral vessels. Expansion of coronary and peripheral arterial vessels is a consequence of it. At use in therapeutic doses Corinfarum has practically no direct impact on a myocardium. Corinfarum reduces a muscle tone of coronary vessels therefore there is their expansion and the coronary blood stream increases. Due to the expansion of arterial vessels Corinfarum at the same time reduces peripheric vascular resistance. In an initiation of treatment the heart rate and minute volume of heart reflex can increase. This increase is not rather severe to compensate a vazodilatation. As a result of it blood pressure goes down. At long-term treatment by Corinfarum the increased minute volume returns to initial level again. Especially accurate lowering of blood pressure at treatment by Corinfarum is noted at patients with an arterial hypertension.
Indications
- stable stenocardia (angina of exertion)
- vasospastic stenocardia (Printsmetal's stenocardia, alternative stenocardia)
- essential arterial hypertension
the Route of administration and doses
of the Dose of drug are selected by the doctor individually according to disease severity and sensitivity of the patient to medicine.
1. Stable and vasospastic stenocardia
the Average daily dose – 20-30 mg, frequency rate of appointment on 1 tablet (10 mg) 2-3 times a day.
At insufficient expressiveness of clinical effect perhaps gradual increase in a daily dose of drug to 40 mg, frequency rate of appointment on 2 tablets 2 times a day.
The maximum daily dose, should not exceed 80 mg, frequency rate of appointment on 4 tablets 2 times a day.
2. Essential hypertensia
the Average daily dose – 20-30 mg, frequency rate of appointment on 1 tablet (10 mg) 2-3 times a day.
At insufficient expressiveness of clinical effect perhaps gradual increase in a daily dose of drug to 40 mg, frequency rate of appointment on 2 tablets 2 times a day.
The maximum daily dose, should not exceed 80 mg, frequency rate of appointment on 4 tablets 2 times a day.
The pill Corinfarum is taken inside after a meal, without chewing and washing down with enough liquid.
At the same time eaten food detains, but does not reduce absorption of active ingredient from digestive tract.
The minimum interval between administrations of drug has to be not less than 4 hours. At double prescribing of drug in day, the recommended interval in reception makes about 12 hours (in the morning and in the evening).
As a rule, treatment by Corinfarum is carried out it is long.
Duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician.
In case of the admission of the next reception of a single dose there is no need to use after that double amount of Corinfarum, and to continue reception on the ordered scheme.
Single dose of smaller amount of Corinfarum (for example, half of a dose) does not lead to any consequences.
At long intake of Corinfarum in very low doses success of treatment is called into question. Sudden interruption of treatment can lead to sharp deterioration in a disease therefore the therapy which is especially carried out by high doses and/or during the long period is stopped a gradual dose decline, after preliminary consultation of the doctor.
Side effects
- a headache, dizziness and fatigue
- rush of blood to the person and a dermahemia (erythema, eritromelalgiya)
- paresthesias are possible at long reception of high doses
- the lowering of arterial pressure is lower than normal
- temporary deterioration in renal function. In the first weeks of treatment
the daily amount of the emitted urine can increase.
Seldom
- tachycardia, strong heartbeat, and owing to a vazodilatation, anklebone hypostasis
- concern, sleep disorders
- erectile dysfunction
- nausea, an abdominal distension and diarrhea, a constipation, dryness in a mouth, an abdominal pain
- the itching, urticaria and rash, an erythema
- pathological hyper sexuality, especially at elderly patients at long-term treatment
- in an initiation of treatment are possible attacks of stenocardia or the frequency, duration and severity of attacks at patients with the available stenocardia
Very seldom
- changes in gums (hypertrophic ulitis)
- myalgias, a tremor, muscular spasms, puffiness of joints
- minor temporary changes in visual perception (can increase at a big dosage)
- anemia, a leukopenia, thrombocytopenia and a Werlhof's disease, an agranulocytosis, a hyperglycemia
In isolated cases
- intra hepatic stagnation of bile, increase in activity of transaminases, jaundice
- esfoliativny dermatitis, a photodermatitis, toxic are epithermal y hypostasis (including throats with a possible zhizneugrozhayushchy outcome)
- a syncope
- reversible anaphylactic tests
- a myocardial infarction
- short wind
-
Contraindication vomiting
- cardiogenic shock
- the profound stenosis of the mouth of an aorta
- unstable stenocardia
- an acute period of a myocardial infarction (within the first 4 weeks)
- at the carried-out treatment by rifampicin
- hypersensitivity to nifedipine
- pregnancy and the period of a lactation
- cirrhosis
- dekompensirovanny liver, renal and heart failure
- arterial hypotension (systolic arterial blood pressure is lower than 90 mm Hg)
- children's and teenage age up to 18 years
- hereditary intolerance of fructose, deficiency of Larr-lactases enzyme, glucose malabsorption - galactoses
Medicinal interactions
the Hypotensive effect of Corinfarum can amplify at simultaneous use of other antihypertensive drugs and also tricyclic antidepressants.
At simultaneous use of Corinfarum and beta-blockers for patients the careful observation since at the same time there can be a sharp falling of arterial blood pressure is established, besides, cases of weakening of warm activity were observed.
Certain medicines from group of blockers of calcium channels can enhance even more the negative inotropic effect (lowering force of warm reduction) of such antiarrhytmic means (the means applied at disturbances of a warm rhythm) as Amiodaronum and quinidine.
At combination therapy with quinidine it is recommended to control the level of concentration of quinidine in blood since in some cases Corinfarum causes lowering it or after cancellation of Corinfarum there is its sharp increase.
Corinfarum can cause increase in level of digoxin (cardiac glycoside) and theophylline (antiasthmatic means) therefore it is necessary to control their content in blood plasma.
Cimetidinum, and to a lesser extent, ranitidine can strengthen effect of Corinfarum.
Special instructions
Under careful observation patients should appoint Corinfarum with an abnormal liver function.
With care to apply the patient with the hypertrophic subaortic stenosis expressed by bradycardia or tachycardia, a sick sinus syndrome, heart failure, slight or moderate arterial hypertension, heavy disturbances of cerebral circulation, impassability of digestive tract.
At patients with high arterial blood pressure or a coronary artery disease after the sudden termination of administration of drug the 'the cancellation phenomenon' which is expressed by sharp increase in arterial blood pressure (hypertensive crisis) or reduction of blood supply of a cardiac muscle (myocardium ischemia) can develop therefore drug should be cancelled gradually.
Features of influence of medicine on ability of control of transport and performance of work, the demanding exact movements.
It is necessary to consider a possibility of delay of the psychomotor reactions connected with a lowering of arterial pressure.
Overdose
Symptoms: a loss of consciousness up to development of a coma, falling of arterial blood pressure, tachycardia or bradycardia, a hyperglycemia, a metabolic acidosis, a hypoxia.
Treatment: drug removal, restoration of a stable condition of a cardiovascular system.
First of all cause vomiting, plentifully wash out a stomach if it is necessary, then in combination with washing of a small intestine. If necessary carrying out a plasma exchange is recommended. At development of bradycardia it is necessary to appoint atropine and/or beta sympathomimetics, in bradycardia, life-threatening – temporarily to implant the patient the pacemaker.
In arterial hypotension in/in enter 1-2 g of a gluconate of calcium, in in by drop infusion – a dopamine (to 25 mkg/kg of body weight/min.), Dobutaminum – up to 15 mkg/kg of body weight/min., adrenaline or noradrenaline – up to 2 ml.
The form of release and packing
On 100 tablets place in a bottle from dark glass with a polyethylene stopper. 1 bottle together with the instruction for use in the state and Russian languages is put in a cardboard pack.
To Store storage conditions in the place protected from light, at a temperature not above 30 °C.
To store out of children's reach!
3 years
not to apply a period of storage after an expiration date.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
PLIVA Producer of Hrvatsk of of the lake
of the island of Prilaz of a barun of Filipovich, 25
10 000 Zagreb, Croatia
the Owner of the registration certificate
of Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, Israel
the Address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products (goods) Representative office Pliva Hrvatsk in the Republic Kazakhstan050040 Respublika Kazakhstang. Almaty, Al-Farabi Avenue 19, Business center of Nurla Tau 1B of office of 603 Phone number, fax (727) 311-09-15, 311-07-34 Teva@teva.kz
to Develop
of medicine
Corinfarum
the Trade name
of the drug Corinfarum International Unlicensed Name Nifedipine Dosage Form
of the Tablet, coated, 10 mg
Structure
One tablet contains
active agent - nifedipine of 10 mg,
excipients: lactoses monohydrate, potato starch, cellulose microcrystalline, PVP K 25, magnesium stearate, methylhydroxypropyl cellulose, macrogoal 6000, macrogoal 35000, dye quinolinic yellow (E 104), titan dioxide (E 171), talc
Description
Yellow, biconvex, round tablets, coated
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Blockers of slow calcium channels. Blockers of slow calcium channels selection. Dihydropyridinic derivatives. Nifedipine.
The ATX C08CA05 code
the Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Later properties of use inside on an empty stomach active ingredient nifedipine quickly and almost is completely soaked up from digestive tract. Nifedipine is exposed to active metabolism at the first passing through a liver. The bioavailability of Corinfarum is 50 - 70%.
The maximum concentration in plasma or blood serum at use of Corinfarum in the form of solution are reached approximately in 15 minutes, at use in the form of other dosage forms without the prolonged release of active agent - in 15-75 minutes. About 95% of the nifedipine entered into an organism contact proteins of blood plasma (albumine). In a liver nifedipine is almost completely metabolized, first of all due to oxidizing and hydrolytic processes. The metabolites which are formed at the same time have no pharmakodinamichesky activity. In the form of metabolites, nifedipine is removed from an organism mainly through kidneys. At the same time the main metabolite is M-1, 60 - 80% of the accepted nifedipine dose fall to its share. Other amount of medicinal substance is removed in the form of metabolites together with a stake. Only traces of active agent in not changed form meet in urine (less than 0.1%). Elimination half-life makes 2-5 hours. Accumulation of medicinal substance in an organism when performing long-term treatment by therapeutic doses was not described. At the lowered function of a liver the accurate lengthening of elimination half-life of active agent and reduction of the general plasmatic clearance is noted.
The pharmacodynamics
Corinfarum is the representative of antagonists of calcium of group derivative 1.4 dihydropyridines. Antagonists of calcium in a highly specific form react with potentsialzavisimy calcium channels and block receipt of calcium ions through calcium channels like L in a cell. There is lowering of concentration of calcium in cells and by that oppression of intracellular momentum transfer. Corinfarum first of all influences smooth muscle cells of coronary arteries and peripheral vessels. Expansion of coronary and peripheral arterial vessels is a consequence of it. At use in therapeutic doses Corinfarum has practically no direct impact on a myocardium. Corinfarum reduces a muscle tone of coronary vessels therefore there is their expansion and the coronary blood stream increases. Due to the expansion of arterial vessels Corinfarum at the same time reduces peripheric vascular resistance. In an initiation of treatment the heart rate and minute volume of heart reflex can increase. This increase is not rather severe to compensate a vazodilatation. As a result of it blood pressure goes down. At long-term treatment by Corinfarum the increased minute volume returns to initial level again. Especially accurate lowering of blood pressure at treatment by Corinfarum is noted at patients with an arterial hypertension.
Indications
- stable stenocardia (angina of exertion)
- vasospastic stenocardia (Printsmetal's stenocardia, alternative stenocardia)
- essential arterial hypertension
the Route of administration and doses
of the Dose of drug are selected by the doctor individually according to disease severity and sensitivity of the patient to medicine.
1. Stable and vasospastic stenocardia
the Average daily dose – 20-30 mg, frequency rate of appointment on 1 tablet (10 mg) 2-3 times a day.
At insufficient expressiveness of clinical effect perhaps gradual increase in a daily dose of drug to 40 mg, frequency rate of appointment on 2 tablets 2 times a day.
The maximum daily dose, should not exceed 80 mg, frequency rate of appointment on 4 tablets 2 times a day.
2. Essential hypertensia
the Average daily dose – 20-30 mg, frequency rate of appointment on 1 tablet (10 mg) 2-3 times a day.
At insufficient expressiveness of clinical effect perhaps gradual increase in a daily dose of drug to 40 mg, frequency rate of appointment on 2 tablets 2 times a day.
The maximum daily dose, should not exceed 80 mg, frequency rate of appointment on 4 tablets 2 times a day.
The pill Corinfarum is taken inside after a meal, without chewing and washing down with enough liquid.
At the same time eaten food detains, but does not reduce absorption of active ingredient from digestive tract.
The minimum interval between administrations of drug has to be not less than 4 hours. At double prescribing of drug in day, the recommended interval in reception makes about 12 hours (in the morning and in the evening).
As a rule, treatment by Corinfarum is carried out it is long.
Duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician.
In case of the admission of the next reception of a single dose there is no need to use after that double amount of Corinfarum, and to continue reception on the ordered scheme.
Single dose of smaller amount of Corinfarum (for example, half of a dose) does not lead to any consequences.
At long intake of Corinfarum in very low doses success of treatment is called into question. Sudden interruption of treatment can lead to sharp deterioration in a disease therefore the therapy which is especially carried out by high doses and/or during the long period is stopped a gradual dose decline, after preliminary consultation of the doctor.
Side effects
- a headache, dizziness and fatigue
- rush of blood to the person and a dermahemia (erythema, eritromelalgiya)
- paresthesias are possible at long reception of high doses
- the lowering of arterial pressure is lower than normal
- temporary deterioration in renal function. In the first weeks of treatment
the daily amount of the emitted urine can increase.
Seldom
- tachycardia, strong heartbeat, and owing to a vazodilatation, anklebone hypostasis
- concern, sleep disorders
- erectile dysfunction
- nausea, an abdominal distension and diarrhea, a constipation, dryness in a mouth, an abdominal pain
- the itching, urticaria and rash, an erythema
- pathological hyper sexuality, especially at elderly patients at long-term treatment
- in an initiation of treatment are possible attacks of stenocardia or the frequency, duration and severity of attacks at patients with the available stenocardia
Very seldom
- changes in gums (hypertrophic ulitis)
- myalgias, a tremor, muscular spasms, puffiness of joints
- minor temporary changes in visual perception (can increase at a big dosage)
- anemia, a leukopenia, thrombocytopenia and a Werlhof's disease, an agranulocytosis, a hyperglycemia
In isolated cases
- intra hepatic stagnation of bile, increase in activity of transaminases, jaundice
- esfoliativny dermatitis, a photodermatitis, toxic are epithermal y hypostasis (including throats with a possible zhizneugrozhayushchy outcome)
- a syncope
- reversible anaphylactic tests
- a myocardial infarction
- short wind
-
Contraindication vomiting
- cardiogenic shock
- the profound stenosis of the mouth of an aorta
- unstable stenocardia
- an acute period of a myocardial infarction (within the first 4 weeks)
- at the carried-out treatment by rifampicin
- hypersensitivity to nifedipine
- pregnancy and the period of a lactation
- cirrhosis
- dekompensirovanny liver, renal and heart failure
- arterial hypotension (systolic arterial blood pressure is lower than 90 mm Hg)
- children's and teenage age up to 18 years
- hereditary intolerance of fructose, deficiency of Larr-lactases enzyme, glucose malabsorption - galactoses
Medicinal interactions
the Hypotensive effect of Corinfarum can amplify at simultaneous use of other antihypertensive drugs and also tricyclic antidepressants.
At simultaneous use of Corinfarum and beta-blockers for patients the careful observation since at the same time there can be a sharp falling of arterial blood pressure is established, besides, cases of weakening of warm activity were observed.
Certain medicines from group of blockers of calcium channels can enhance even more the negative inotropic effect (lowering force of warm reduction) of such antiarrhytmic means (the means applied at disturbances of a warm rhythm) as Amiodaronum and quinidine.
At combination therapy with quinidine it is recommended to control the level of concentration of quinidine in blood since in some cases Corinfarum causes lowering it or after cancellation of Corinfarum there is its sharp increase.
Corinfarum can cause increase in level of digoxin (cardiac glycoside) and theophylline (antiasthmatic means) therefore it is necessary to control their content in blood plasma.
Cimetidinum, and to a lesser extent, ranitidine can strengthen effect of Corinfarum.
Special instructions
Under careful observation patients should appoint Corinfarum with an abnormal liver function.
With care to apply the patient with the hypertrophic subaortic stenosis expressed by bradycardia or tachycardia, a sick sinus syndrome, heart failure, slight or moderate arterial hypertension, heavy disturbances of cerebral circulation, impassability of digestive tract.
At patients with high arterial blood pressure or a coronary artery disease after the sudden termination of administration of drug the 'the cancellation phenomenon' which is expressed by sharp increase in arterial blood pressure (hypertensive crisis) or reduction of blood supply of a cardiac muscle (myocardium ischemia) can develop therefore drug should be cancelled gradually.
Features of influence of medicine on ability of control of transport and performance of work, the demanding exact movements.
It is necessary to consider a possibility of delay of the psychomotor reactions connected with a lowering of arterial pressure.
Overdose
Symptoms: a loss of consciousness up to development of a coma, falling of arterial blood pressure, tachycardia or bradycardia, a hyperglycemia, a metabolic acidosis, a hypoxia.
Treatment: drug removal, restoration of a stable condition of a cardiovascular system.
First of all cause vomiting, plentifully wash out a stomach if it is necessary, then in combination with washing of a small intestine. If necessary carrying out a plasma exchange is recommended. At development of bradycardia it is necessary to appoint atropine and/or beta sympathomimetics, in bradycardia, life-threatening – temporarily to implant the patient the pacemaker.
In arterial hypotension in/in enter 1-2 g of a gluconate of calcium, in in by drop infusion – a dopamine (to 25 mkg/kg of body weight/min.), Dobutaminum – up to 15 mkg/kg of body weight/min., adrenaline or noradrenaline – up to 2 ml.
The form of release and packing
On 100 tablets place in a bottle from dark glass with a polyethylene stopper. 1 bottle together with the instruction for use in the state and Russian languages is put in a cardboard pack.
To Store storage conditions in the place protected from light, at a temperature not above 30 °C.
To store out of children's reach!
3 years
not to apply a period of storage after an expiration date.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
PLIVA Producer of Hrvatsk of of the lake
of the island of Prilaz of a barun of Filipovich, 25
10 000 Zagreb, Croatia
the Owner of the registration certificate
of Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, Israel
the Address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products (goods) Representative office Pliva Hrvatsk in the Republic Kazakhstan050040 Respublika Kazakhstang. Almaty, Al-Farabi Avenue 19, Business center of Nurla Tau 1B of office of 603 Phone number, fax (727) 311-09-15, 311-07-34 Teva@teva.kz
to Develop