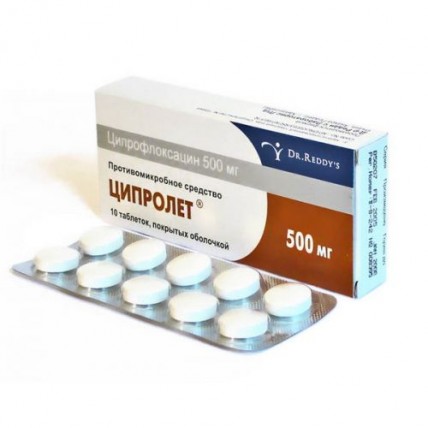
Ciprolet 10s 500 mg coated tablets
- $8.10
The instruction for medical use
of Tsiprolet Torgovoye medicine
Tsiprolet
Mezhdunarodnoye's name the unlicensed
name Ciprofloxacin Dosage Form
of the Tablet, coated, 250 mg, 500 mg
Structure
One tablet contains
active agent ciprofloxacin of 250 mg or 500 mg,
excipients: corn starch, cellulose microcrystalline, sodium of a kroskarmelloz, silicon dioxide kollodny, the talc purified magnesium stearate,
structure of a cover: a gipromelloza, sorbic acid, the titan the dioxide, talc purified, a macrogoal (6000), polysorbate 80, dimetikon.
The description
of the Tablet, coated white color, round, with a biconvex surface and smooth on both sides, height (4.10 & plusmn, 0.20) mm and diameter (11.30 & plusmn, 0.20) mm (for a dosage of 250 mg) or height (5.50 & plusmn, 0.20) mm and diameter (12.60 & plusmn, 0.20) mm (for a dosage of 500 mg).
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antibacterial drugs for system use. Antimicrobial drugs derivative hinolona. Ftorkhinolona. Ciprofloxacin.
The code of automatic telephone exchange J01MA02
The pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Quickly properties is soaked up from digestive tract. The bioavailability after intake is 70%. Meal slightly influences ciprofloxacin absorption. The plasma profile of concentration of ciprofloxacin at oral administration is similar to that, as at intravenous administration therefore oral and intravenous ways of introduction can be considered as interchangeable. Communication with proteins of plasma makes 20 - 40%. Average elimination half-life of ciprofloxacin makes from 6 to 8 hours after a single or multiple dose. Ciprofloxacin well gets into bodies and fabrics: lungs, mucous membrane of bronchial tubes and phlegm, bodies of an urinogenital system, including prostate, bone tissue, cerebrospinal fluid, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, alveolar macrophages. It is allocated mainly with urine and bile.
Tsiprolet's pharmacodynamics - an antibiotic of a broad spectrum of activity from group of ftorkhinolon. Suppresses bacterial DNK-girazu (topoizmeraza II and IV, superspirallings of chromosomal DNA, responsible for process, around nuclear RNA that is necessary for reading of genetic information), breaks DNA synthesis, growth and division of bacteria, causes the significant morphological changes (including a cell wall and membranes) and fast death of a bacterial cell. Affects gram-negative microorganisms during a dormant period bacteriostatically and during division bakteritsidno (t. to influences not only on DNK-girazu, but also causes lysis of a cell wall), on gram-positive microorganisms bakteritsidno only during division. The hypotoxicity for cells of a macroorganism is explained by absence in them DNK-girazy. Tsiprolet it is active concerning the majority of strains of microorganisms of in vitro and in vivo:
- aerobic gram-positive microorganisms: Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Enterococcus faecalis, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus spp., including Staphylococcus aureus, epidermidis, Streptococcus pyogenes, agalactiae, pneumoniae, Streptococcus (groups C, G), Viridans group streptococci,
- aerobic gram-negative microorganisms: Acinetobacter spp., including Acinetobacter anitratus, baumannii, calcoaceticus, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Bordetella pertussis, Citrobacter freundii, diversus, Enterobacter spp., including Enterobacter aerogenes, agglomerans, cloacae, sakazakii, Escherichia coli, Gardnerella vaginalis, Haemophilus ducreyi, influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Helicobacter pylori, Klebsiella spp., including Klebsiella oxytoca, pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Morganella morganii, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitides, including Pasteurella canis, dagmatis, multocida, Proteus mirabilis, vulgaris, Providencia spp., including Pseudomonas aeruginoza, fluorescens, Salmonella spp., Serratia spp., including Serratia marcescens,
- anaerobic microorganisms: Bifidobacterium spp., Clostridium perfringens, Fusobacterium spp., Peptostreptococcus, Propionibacterium spp., Veillonella spp.,
- intracellular microorganisms: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, Chlamydia pneumoniae, psittaci, trachomatis, Legionella spp., including Legionella pneumophila, Mycobacterium spp., including Mycobacterium leprae, tuberculosis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Rickettsia spp.,
To the drug Tsiprolet of a rezistentna Ureaplasma urealyticum, Clostridium difficile, Nocardia asteroids, Bacteroides fragilis, Pseudomonas cepatica, Pseudomonas maltophilia, Treponema pallidum
Indications
the Uncomplicated and oslozhenny infections caused by microorganisms, sensitive to ciprofloxacin:
Adults
- infections of ENT organs (average otitis, antritis, a frontal sinusitis, a mastoiditis, tonsillitis)
- lower respiratory tract infections, the caused Klebsiella spp. caused by gram-negative bacteria, Enterobacter spp., Proteus spp., Esherichia coli, Pseudomonas spp., Haemophilus spp., Branhamella spp., Legionella spp., Staphylococcus spp. (exacerbation of a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchopulmonary infection in a mucoviscidosis or in bronchiectasias, pneumonia)
- the infections of urinary tract (caused gonokokky an urethritis and a cervicitis)
- infections, sexually transmitted which were caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhea, a venereal ulcer, urogenital clamidiosis)
- an epidimit-orchitis, including the cases caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- inflammation of bodies of a small pelvis at women (inflammatory diseases of a small pelvis), including cases Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- infections of an abdominal cavity (bacterial infections of a GIT or biliary tract, peritonitis)
- infections of skin, soft tissues
- a septicaemia, bacteremia, infections or prevention of infections are caused in patients with the weakened immunity (for example, in the patients accepting immunodepressants or with a neuropeniya)
- prevention and treatment of an inhalation anthrax (infection of Bacillus anthracis)
- infections of bones and joints
Children's and teenage age
- at treatment of the complications caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa at children 6 years with a mucoviscidosis
- difficult urinary tract infections are more senior and pyelonephritis
- prevention and treatment of an inhalation anthrax (infection of Bacillus anthracis)
Appoint a route of administration and Tsiprolet's doses in tablets the adult inside, to food or in a break between meals, without chewing, washing down with enough liquid. At reception on an empty stomach active ingredient is soaked up quicker. A pill of ciprofloxacin cannot be taken together with dairy products (for example with milk, yogurt) or fruit juice with addition of minerals.
Doses are defined by character and weight of an infection and also sensitivity of the expected activator, function of kidneys of the patient, and at children and teenagers, the body weight of the patient is considered.
The dose is defined on the basis of the instruction, type and weight of an infection, sensitivity to ciprofloxacin, treatment depends on severity of a disease and also clinical and bacteriological processes.
In treatment of the infections caused by some bacteria (for example, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter or Stafilococ) higher doses of ciprofloxacin are required and can be combined with one or several other suitable antibacterial drugs.
In treatment of some infections (for example, inflammations of bodies of a small pelvis at women, an intra belly infection, an infection at patients with a neutropenia, an infection of bones and joints) combination of one or several compatible antibacterial drugs is possible, depending on pathogenic microorganisms who cause them. It is recommended to appoint drug in the following doses:
Adult
Indications
the Daily dose of mg
Duration of all treatment (including a possibility of initial parenteral treatment with ciprofloxacin)
Infections of lower parts
of airways
From 2 x 500 mg to
2 x 750 mg.
From 7 to 14 days
Infections of upper parts of airways
Exacerbation of chronic sinusitis
From 2 x 500 mg to
2 x 750 mg
From 7 to 14 days
Chronic purulent average otitis
From 2 x 500 mg to
2 x 750 mg
From 7 to 14 days
Malignant external otitis
2 x 750 mg
From 28 days to 3 months
Infections of urinary tract
Uncomplicated cystitis
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
3 days
to women in the period of a menopause once 500 mg
The complicated cystitis, uncomplicated pyelonephritis
2 x 500 mg
of 7 days
The complicated pyelonephritis
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
Not less than 10 days in certain cases (for example, in abscesses) up to 21 days
Prostatitis
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
2-4 weeks (sharp), 4-6 weeks (chronic)
Infections of genitals
the Fungal urethritis and a cervicitis
of 500 mg
one-time single dose of 500 mg
An orchiepididymitis and inflammatory diseases of bodies of a small pelvis
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
not less than 14 days
Infections of a GIT and intraabdominal infections
the Diarrhea caused by a bacterial infection, including Shigella spp except Shigella dysenteriae of type I and empirical treatment of heavy diarrhea of the traveler
2 x 500 mg
1 day
The diarrhea caused by Shigella dysenteriae of type I
2 x 500 mg
of 5 days
The diarrhea caused by Vibrio cholera
2 x 500 mg
3 days
A typhoid
2 x 500 mg
of 7 days
The intraabdominal infections caused by gram-negative microorganisms
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
From 5 to 14 days
Infections of skin and soft tissues
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
From 7 to 14 days
Infections of joints and bones
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
max. 3 months
Prevention and treatment of infections at patients with a neutropenia: appointment together with other medicines
From 2kh500mg to 2kh750mg is recommended
the erapiya proceeds before the end of the period of a neutropenia
Prevention of the invasive infections caused
by Neisseria meningitides 1kh500mg
Once
Post-contact prevention and treatment of anthrax: treatment should be begun as soon as possible after the assumed or confirmed infection
Of
2kh500mg 60 days from the moment of infection confirmation
The maximum single dose - 750 mg.
The maximum daily dose - 1500 mg
Children's and teenage age
Indications
the Daily dose of mg
Duration of all treatment (including a possibility of initial parenteral treatment with ciprofloxacin)
A mucoviscidosis
of 20 mg/kg of body weight 2 times up to 750 mg a day.
From 10 to 14 days
The complicated cystitis, uncomplicated pyelonephritis
From 10 mg/kg of body weight 2 times to 20mg/kg 2 times and at most 750 mg a day.
From 10 to 14 days
Prevention after contact and radical treatment of an inhalation anthrax at persons who can receive treatment in the oral way if it is clinically necessary. Use of drug should be begun after the suspect or the confirmed contact as soon as possible.
10 mg/kg of body weight 2 times a day up to 15 mg/kg of body weight at the maximum dose of 750 mg a day.
60 days from the date of the confirmed contact with Bacillus anthracis
Other heavy infections
of 20 mg/kg of body weight 2 times a day at the maximum dose of 750 mg a day.
According to type of infections
The maximum daily dose for children over 6 years and teenagers - 750 mg.
Patients of advanced age
Patients of advanced age have to receive the dose chosen according to weight of an infection and clearance of creatinine.
A renal and liver failure
the Recommended initial and maintenance doses for patients with impaired renal function
Clearance of creatinine, ml/min. / 1.73 sq.m
Creatinine of blood plasma, µmol/l
the Oral dose
& gt, 60
& lt, 124
Cm a usual dosage
30-60 124-168 250500 mg each 12 h
& lt, 30
& gt, 169
250500 mg each 24 h
Patients on a hemodialysis
& gt, 169
250500 mg each 24 h (after dialysis)
Patients on peritoneal dialysis
& gt, 169
250500 mg each 24 h
At patients with a liver failure are not present need for ciprofloxacin dosing change.
Researches concerning drug dosing for children with broken by renal and/or hepatic functions were not conducted.
If disease severity of the patient or other reasons (for example if the patient receives an enteroalimentation) do not allow to take a ciprofloxacin pill, coated, it is recommended to pass to therapy in/in a dosage form of ciprofloxacin. Later in/in introductions it is possible to continue treatment by the tableted drug form.
Side effects
- increased fatigue, perspiration, fever
- a headache, dizziness, migraine, uneasiness, a tremor, drowsiness, dreadful dreams, confusion of consciousness, a depression, hallucinations, psychotic reactions
- a disorder of vision and hearing, sense of smell, tactile sensitivity, disturbance of flavoring feelings, including their loss (restoration happens within several weeks after the treatment termination)
- lengthening of an interval of QT, tachycardia, falling of arterial blood pressure, a syncope
- loss of appetite, nausea, feeling of overflow of a stomach, a mild abdominal pain, a meteorism, diarrhea
- an itching, urticaria, a multimorfny erythema, an allergic pneumonitis, Stephen-Johnson's syndrome, a Lyell's disease or a toxic epidermal necrolysis, a Quincke's edema, a photosensitization
- articulate and muscular pains, muscle weakness, damages of sinews (including a tendovaginitis), damages of muscles (rhabdomyolysis)
- a cholestasia, a liver failure, increase in activity of enzymes of a liver, increase in level of bilirubin, creatinine in blood serum
- a neutropenia, an agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, an eosinophilia, a leukopenia, hemolytic anemia
of the Contraindication
- hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin, other drugs of group of ftorkhinolon or to any of drug excipients
- epilepsy
- damage of sinews after treatment by antibiotics in the anamnesis
- deficit glyukozo-6-fosfatdegidrogenazy
- pseudomembranous colitis
- simultaneous use of ciprofloxacin and a tizanidin
- pregnancy and the period of a lactation
- children's and teenage age up to 6 years
Medicinal interactions
At simultaneous use of ciprofloxacin with didanoziny, absorption of ciprofloxacin decreases owing to formation of complexons of ciprofloxacin with the aluminum and magnesian salts which are contained in the didanozena.
At simultaneous use with warfarin the risk of developing bleeding increases.
The concomitant use of ciprofloxacin and theophylline can lead to increase in concentration of theophylline in blood plasma, at the expense of competitive inhibition in binding sites of a tsitrokhrom of P450 that leads to increase in elimination half-life of theophylline and increase of risk of development of the toxic action connected with theophylline. The concomitant use of antacids and also the drugs containing ions of aluminum, zinc, iron or magnesium can cause decrease in absorption of ciprofloxacin therefore the interval between prescribing of these drugs has to be not less than 4 h.
The special
instructions Treatment can it is appointed only the doctors having experience in treatment of a mucoviscidosis. Ciprofloxacin, can be used for treatment of a heavy infection at children and teenagers if necessary.
At patients of advanced age drug should be used with care.
During treatment it is necessary to avoid excessive solar and artificial ultra-violet radiation in order to avoid a photosensitization. At suspicion of pseudomembranous colitis it is necessary to cancel immediately ciprofloxacin and to begin the corresponding treatment. At use of drug, inflammations of sinews and their gap can be observed. Such reactions were observed mainly at patients of advanced age who at the same time applied corticosteroids. At the first symptoms of pain or inflammation it is necessary to cancel drug immediately. It must be kept in mind that at patients with a brain damage in the anamnesis (a stroke, a severe injury) development of spasms is possible, at insufficiency glyukozo-6-fosfatdegidrogenazy - risk of development of hemolysis. In this regard treatment of such patients with ciprofloxacin should be carried out carefully. It is necessary to be careful when prescribing ciprofloxacin sick diabetes. Use of ciprofloxacin has to be stopped at the first signs of appearance of rash on integuments or any other allergic reaction.
Use for patients from the liver broken by function and kidneys
With care it is necessary to use drug at patients with renal failures as at such patients the elimination half-life of ciprofloxacin increases.
Patients from the liver broken by function do not need dose adjustment. The ciprofloxacin pharmacokinetics at patients with cirrhosis did not change. Change of pharmacokinetics of drug at patients with an acute hepatitis was not studied.
Features of influence of medicine on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms
Ciprofloxacin can cause dizziness and the raised photoharmose, the ability of concentration of attention at control of cars decreases and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Overdose
Symptoms: confusion of consciousness, dizziness, consciousness disturbances, attacks of spasms, gastrointestinal disorders, damages of mucous membranes, lengthening of an interval of QT.
Treatment: symptomatic, specific antidote does not exist. Tsiprolet is not brought by a hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
A form of release and packing
On 10 tablets in blister strip packaging from a film of the polyvinylchloride and printing aluminum foil varnished.
On 1 blister strip packaging together with the instruction for use in the state and Russian languages put in a pack from cardboard bandbox.
Storage conditions
In the dry, protected from light place at a temperature not higher than 25 S. Hranit in the places inaccessible for children!
3 years
not to apply a period of storage after the expiry date specified on packing.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
the Dr. of Reddis Laboratoris Limited Producer, India
the Address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products
Representative office the Dr. of Reddis Laboratoris Ltd in the Republic of Kazakhstan: 050057 Almaty, Dzhandosov St., 21
a post office box 7, ph. 8 (727) 3941688, fax: 8 (727) 3941294
To develop
of Tsiprolet Torgovoye medicine
Tsiprolet
Mezhdunarodnoye's name the unlicensed
name Ciprofloxacin Dosage Form
of the Tablet, coated, 250 mg, 500 mg
Structure
One tablet contains
active agent ciprofloxacin of 250 mg or 500 mg,
excipients: corn starch, cellulose microcrystalline, sodium of a kroskarmelloz, silicon dioxide kollodny, the talc purified magnesium stearate,
structure of a cover: a gipromelloza, sorbic acid, the titan the dioxide, talc purified, a macrogoal (6000), polysorbate 80, dimetikon.
The description
of the Tablet, coated white color, round, with a biconvex surface and smooth on both sides, height (4.10 & plusmn, 0.20) mm and diameter (11.30 & plusmn, 0.20) mm (for a dosage of 250 mg) or height (5.50 & plusmn, 0.20) mm and diameter (12.60 & plusmn, 0.20) mm (for a dosage of 500 mg).
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antibacterial drugs for system use. Antimicrobial drugs derivative hinolona. Ftorkhinolona. Ciprofloxacin.
The code of automatic telephone exchange J01MA02
The pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Quickly properties is soaked up from digestive tract. The bioavailability after intake is 70%. Meal slightly influences ciprofloxacin absorption. The plasma profile of concentration of ciprofloxacin at oral administration is similar to that, as at intravenous administration therefore oral and intravenous ways of introduction can be considered as interchangeable. Communication with proteins of plasma makes 20 - 40%. Average elimination half-life of ciprofloxacin makes from 6 to 8 hours after a single or multiple dose. Ciprofloxacin well gets into bodies and fabrics: lungs, mucous membrane of bronchial tubes and phlegm, bodies of an urinogenital system, including prostate, bone tissue, cerebrospinal fluid, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, alveolar macrophages. It is allocated mainly with urine and bile.
Tsiprolet's pharmacodynamics - an antibiotic of a broad spectrum of activity from group of ftorkhinolon. Suppresses bacterial DNK-girazu (topoizmeraza II and IV, superspirallings of chromosomal DNA, responsible for process, around nuclear RNA that is necessary for reading of genetic information), breaks DNA synthesis, growth and division of bacteria, causes the significant morphological changes (including a cell wall and membranes) and fast death of a bacterial cell. Affects gram-negative microorganisms during a dormant period bacteriostatically and during division bakteritsidno (t. to influences not only on DNK-girazu, but also causes lysis of a cell wall), on gram-positive microorganisms bakteritsidno only during division. The hypotoxicity for cells of a macroorganism is explained by absence in them DNK-girazy. Tsiprolet it is active concerning the majority of strains of microorganisms of in vitro and in vivo:
- aerobic gram-positive microorganisms: Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Enterococcus faecalis, Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus spp., including Staphylococcus aureus, epidermidis, Streptococcus pyogenes, agalactiae, pneumoniae, Streptococcus (groups C, G), Viridans group streptococci,
- aerobic gram-negative microorganisms: Acinetobacter spp., including Acinetobacter anitratus, baumannii, calcoaceticus, Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Bordetella pertussis, Citrobacter freundii, diversus, Enterobacter spp., including Enterobacter aerogenes, agglomerans, cloacae, sakazakii, Escherichia coli, Gardnerella vaginalis, Haemophilus ducreyi, influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Helicobacter pylori, Klebsiella spp., including Klebsiella oxytoca, pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Morganella morganii, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitides, including Pasteurella canis, dagmatis, multocida, Proteus mirabilis, vulgaris, Providencia spp., including Pseudomonas aeruginoza, fluorescens, Salmonella spp., Serratia spp., including Serratia marcescens,
- anaerobic microorganisms: Bifidobacterium spp., Clostridium perfringens, Fusobacterium spp., Peptostreptococcus, Propionibacterium spp., Veillonella spp.,
- intracellular microorganisms: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, Chlamydia pneumoniae, psittaci, trachomatis, Legionella spp., including Legionella pneumophila, Mycobacterium spp., including Mycobacterium leprae, tuberculosis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Rickettsia spp.,
To the drug Tsiprolet of a rezistentna Ureaplasma urealyticum, Clostridium difficile, Nocardia asteroids, Bacteroides fragilis, Pseudomonas cepatica, Pseudomonas maltophilia, Treponema pallidum
Indications
the Uncomplicated and oslozhenny infections caused by microorganisms, sensitive to ciprofloxacin:
Adults
- infections of ENT organs (average otitis, antritis, a frontal sinusitis, a mastoiditis, tonsillitis)
- lower respiratory tract infections, the caused Klebsiella spp. caused by gram-negative bacteria, Enterobacter spp., Proteus spp., Esherichia coli, Pseudomonas spp., Haemophilus spp., Branhamella spp., Legionella spp., Staphylococcus spp. (exacerbation of a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchopulmonary infection in a mucoviscidosis or in bronchiectasias, pneumonia)
- the infections of urinary tract (caused gonokokky an urethritis and a cervicitis)
- infections, sexually transmitted which were caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhea, a venereal ulcer, urogenital clamidiosis)
- an epidimit-orchitis, including the cases caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- inflammation of bodies of a small pelvis at women (inflammatory diseases of a small pelvis), including cases Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- infections of an abdominal cavity (bacterial infections of a GIT or biliary tract, peritonitis)
- infections of skin, soft tissues
- a septicaemia, bacteremia, infections or prevention of infections are caused in patients with the weakened immunity (for example, in the patients accepting immunodepressants or with a neuropeniya)
- prevention and treatment of an inhalation anthrax (infection of Bacillus anthracis)
- infections of bones and joints
Children's and teenage age
- at treatment of the complications caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa at children 6 years with a mucoviscidosis
- difficult urinary tract infections are more senior and pyelonephritis
- prevention and treatment of an inhalation anthrax (infection of Bacillus anthracis)
Appoint a route of administration and Tsiprolet's doses in tablets the adult inside, to food or in a break between meals, without chewing, washing down with enough liquid. At reception on an empty stomach active ingredient is soaked up quicker. A pill of ciprofloxacin cannot be taken together with dairy products (for example with milk, yogurt) or fruit juice with addition of minerals.
Doses are defined by character and weight of an infection and also sensitivity of the expected activator, function of kidneys of the patient, and at children and teenagers, the body weight of the patient is considered.
The dose is defined on the basis of the instruction, type and weight of an infection, sensitivity to ciprofloxacin, treatment depends on severity of a disease and also clinical and bacteriological processes.
In treatment of the infections caused by some bacteria (for example, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter or Stafilococ) higher doses of ciprofloxacin are required and can be combined with one or several other suitable antibacterial drugs.
In treatment of some infections (for example, inflammations of bodies of a small pelvis at women, an intra belly infection, an infection at patients with a neutropenia, an infection of bones and joints) combination of one or several compatible antibacterial drugs is possible, depending on pathogenic microorganisms who cause them. It is recommended to appoint drug in the following doses:
Adult
Indications
the Daily dose of mg
Duration of all treatment (including a possibility of initial parenteral treatment with ciprofloxacin)
Infections of lower parts
of airways
From 2 x 500 mg to
2 x 750 mg.
From 7 to 14 days
Infections of upper parts of airways
Exacerbation of chronic sinusitis
From 2 x 500 mg to
2 x 750 mg
From 7 to 14 days
Chronic purulent average otitis
From 2 x 500 mg to
2 x 750 mg
From 7 to 14 days
Malignant external otitis
2 x 750 mg
From 28 days to 3 months
Infections of urinary tract
Uncomplicated cystitis
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
3 days
to women in the period of a menopause once 500 mg
The complicated cystitis, uncomplicated pyelonephritis
2 x 500 mg
of 7 days
The complicated pyelonephritis
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
Not less than 10 days in certain cases (for example, in abscesses) up to 21 days
Prostatitis
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
2-4 weeks (sharp), 4-6 weeks (chronic)
Infections of genitals
the Fungal urethritis and a cervicitis
of 500 mg
one-time single dose of 500 mg
An orchiepididymitis and inflammatory diseases of bodies of a small pelvis
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
not less than 14 days
Infections of a GIT and intraabdominal infections
the Diarrhea caused by a bacterial infection, including Shigella spp except Shigella dysenteriae of type I and empirical treatment of heavy diarrhea of the traveler
2 x 500 mg
1 day
The diarrhea caused by Shigella dysenteriae of type I
2 x 500 mg
of 5 days
The diarrhea caused by Vibrio cholera
2 x 500 mg
3 days
A typhoid
2 x 500 mg
of 7 days
The intraabdominal infections caused by gram-negative microorganisms
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
From 5 to 14 days
Infections of skin and soft tissues
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
From 7 to 14 days
Infections of joints and bones
From 2 x 500 mg to 2 x 750 mg
max. 3 months
Prevention and treatment of infections at patients with a neutropenia: appointment together with other medicines
From 2kh500mg to 2kh750mg is recommended
the erapiya proceeds before the end of the period of a neutropenia
Prevention of the invasive infections caused
by Neisseria meningitides 1kh500mg
Once
Post-contact prevention and treatment of anthrax: treatment should be begun as soon as possible after the assumed or confirmed infection
Of
2kh500mg 60 days from the moment of infection confirmation
The maximum single dose - 750 mg.
The maximum daily dose - 1500 mg
Children's and teenage age
Indications
the Daily dose of mg
Duration of all treatment (including a possibility of initial parenteral treatment with ciprofloxacin)
A mucoviscidosis
of 20 mg/kg of body weight 2 times up to 750 mg a day.
From 10 to 14 days
The complicated cystitis, uncomplicated pyelonephritis
From 10 mg/kg of body weight 2 times to 20mg/kg 2 times and at most 750 mg a day.
From 10 to 14 days
Prevention after contact and radical treatment of an inhalation anthrax at persons who can receive treatment in the oral way if it is clinically necessary. Use of drug should be begun after the suspect or the confirmed contact as soon as possible.
10 mg/kg of body weight 2 times a day up to 15 mg/kg of body weight at the maximum dose of 750 mg a day.
60 days from the date of the confirmed contact with Bacillus anthracis
Other heavy infections
of 20 mg/kg of body weight 2 times a day at the maximum dose of 750 mg a day.
According to type of infections
The maximum daily dose for children over 6 years and teenagers - 750 mg.
Patients of advanced age
Patients of advanced age have to receive the dose chosen according to weight of an infection and clearance of creatinine.
A renal and liver failure
the Recommended initial and maintenance doses for patients with impaired renal function
Clearance of creatinine, ml/min. / 1.73 sq.m
Creatinine of blood plasma, µmol/l
the Oral dose
& gt, 60
& lt, 124
Cm a usual dosage
30-60 124-168 250500 mg each 12 h
& lt, 30
& gt, 169
250500 mg each 24 h
Patients on a hemodialysis
& gt, 169
250500 mg each 24 h (after dialysis)
Patients on peritoneal dialysis
& gt, 169
250500 mg each 24 h
At patients with a liver failure are not present need for ciprofloxacin dosing change.
Researches concerning drug dosing for children with broken by renal and/or hepatic functions were not conducted.
If disease severity of the patient or other reasons (for example if the patient receives an enteroalimentation) do not allow to take a ciprofloxacin pill, coated, it is recommended to pass to therapy in/in a dosage form of ciprofloxacin. Later in/in introductions it is possible to continue treatment by the tableted drug form.
Side effects
- increased fatigue, perspiration, fever
- a headache, dizziness, migraine, uneasiness, a tremor, drowsiness, dreadful dreams, confusion of consciousness, a depression, hallucinations, psychotic reactions
- a disorder of vision and hearing, sense of smell, tactile sensitivity, disturbance of flavoring feelings, including their loss (restoration happens within several weeks after the treatment termination)
- lengthening of an interval of QT, tachycardia, falling of arterial blood pressure, a syncope
- loss of appetite, nausea, feeling of overflow of a stomach, a mild abdominal pain, a meteorism, diarrhea
- an itching, urticaria, a multimorfny erythema, an allergic pneumonitis, Stephen-Johnson's syndrome, a Lyell's disease or a toxic epidermal necrolysis, a Quincke's edema, a photosensitization
- articulate and muscular pains, muscle weakness, damages of sinews (including a tendovaginitis), damages of muscles (rhabdomyolysis)
- a cholestasia, a liver failure, increase in activity of enzymes of a liver, increase in level of bilirubin, creatinine in blood serum
- a neutropenia, an agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, an eosinophilia, a leukopenia, hemolytic anemia
of the Contraindication
- hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin, other drugs of group of ftorkhinolon or to any of drug excipients
- epilepsy
- damage of sinews after treatment by antibiotics in the anamnesis
- deficit glyukozo-6-fosfatdegidrogenazy
- pseudomembranous colitis
- simultaneous use of ciprofloxacin and a tizanidin
- pregnancy and the period of a lactation
- children's and teenage age up to 6 years
Medicinal interactions
At simultaneous use of ciprofloxacin with didanoziny, absorption of ciprofloxacin decreases owing to formation of complexons of ciprofloxacin with the aluminum and magnesian salts which are contained in the didanozena.
At simultaneous use with warfarin the risk of developing bleeding increases.
The concomitant use of ciprofloxacin and theophylline can lead to increase in concentration of theophylline in blood plasma, at the expense of competitive inhibition in binding sites of a tsitrokhrom of P450 that leads to increase in elimination half-life of theophylline and increase of risk of development of the toxic action connected with theophylline. The concomitant use of antacids and also the drugs containing ions of aluminum, zinc, iron or magnesium can cause decrease in absorption of ciprofloxacin therefore the interval between prescribing of these drugs has to be not less than 4 h.
The special
instructions Treatment can it is appointed only the doctors having experience in treatment of a mucoviscidosis. Ciprofloxacin, can be used for treatment of a heavy infection at children and teenagers if necessary.
At patients of advanced age drug should be used with care.
During treatment it is necessary to avoid excessive solar and artificial ultra-violet radiation in order to avoid a photosensitization. At suspicion of pseudomembranous colitis it is necessary to cancel immediately ciprofloxacin and to begin the corresponding treatment. At use of drug, inflammations of sinews and their gap can be observed. Such reactions were observed mainly at patients of advanced age who at the same time applied corticosteroids. At the first symptoms of pain or inflammation it is necessary to cancel drug immediately. It must be kept in mind that at patients with a brain damage in the anamnesis (a stroke, a severe injury) development of spasms is possible, at insufficiency glyukozo-6-fosfatdegidrogenazy - risk of development of hemolysis. In this regard treatment of such patients with ciprofloxacin should be carried out carefully. It is necessary to be careful when prescribing ciprofloxacin sick diabetes. Use of ciprofloxacin has to be stopped at the first signs of appearance of rash on integuments or any other allergic reaction.
Use for patients from the liver broken by function and kidneys
With care it is necessary to use drug at patients with renal failures as at such patients the elimination half-life of ciprofloxacin increases.
Patients from the liver broken by function do not need dose adjustment. The ciprofloxacin pharmacokinetics at patients with cirrhosis did not change. Change of pharmacokinetics of drug at patients with an acute hepatitis was not studied.
Features of influence of medicine on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms
Ciprofloxacin can cause dizziness and the raised photoharmose, the ability of concentration of attention at control of cars decreases and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Overdose
Symptoms: confusion of consciousness, dizziness, consciousness disturbances, attacks of spasms, gastrointestinal disorders, damages of mucous membranes, lengthening of an interval of QT.
Treatment: symptomatic, specific antidote does not exist. Tsiprolet is not brought by a hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
A form of release and packing
On 10 tablets in blister strip packaging from a film of the polyvinylchloride and printing aluminum foil varnished.
On 1 blister strip packaging together with the instruction for use in the state and Russian languages put in a pack from cardboard bandbox.
Storage conditions
In the dry, protected from light place at a temperature not higher than 25 S. Hranit in the places inaccessible for children!
3 years
not to apply a period of storage after the expiry date specified on packing.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
the Dr. of Reddis Laboratoris Limited Producer, India
the Address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products
Representative office the Dr. of Reddis Laboratoris Ltd in the Republic of Kazakhstan: 050057 Almaty, Dzhandosov St., 21
a post office box 7, ph. 8 (727) 3941688, fax: 8 (727) 3941294
To develop