Instruction
for medical use
of AntiGrippin medicine - P
Trade
name AntiGrippin - P
International unlicensed name
Is not present
the Dosage form
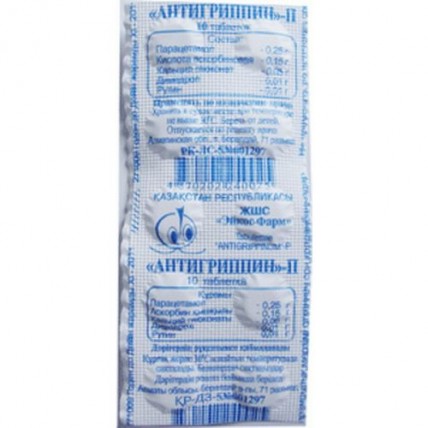
of the Tablet Structure One Tablet contains
active agents: paracetamol – 0.25 g, ascorbic acid – 0.15 g, calcium a gluconate – 0.05 g, Dimedrol – 0.01 g, Rutinum – 0.01 g,
excipients: starch, talc, calcium stearate.
The description
of the Tablet of yellowish color with a flat surface, with a facet and risky.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
For elimination of symptoms of cold and cough. Other combinations of drugs for elimination of symptoms of cold.
The ATX R05X code
Pharmacological properties
the Pharmacological activity of drug is caused by properties of the active ingredients which are its part.
The pharmacokinetics
After intake paracetamol is quickly absorbed from a GIT, widely distributed in fabrics and in fluid mediums of an organism, except for fatty tissue and cerebrospinal fluid. Linking with proteins makes less than 10%. It is metabolized mainly in a liver, removed with urine, mainly in the form of glyukuronidny and sulphatic conjugates. Paracetamol gets through a placental barrier and is emitted with breast milk.
Ascorbic acid is well soaked up after oral administration. About 25% contact plasma proteins, is postponed in plasma and cells, the highest concentration is reached in ferruterous fabrics (generally in bark of adrenal glands and a hypophysis). It is metabolized in a liver, removed with urine in the form of oxalate and in an invariable look.
After intake about 30% of the ionized calcium are soaked up in a GIT. After oral administration the maximum concentration in blood plasma is reached in 1.2-1.3 h. It is brought out of an organism mainly with a stake (80%) and urine (20%).
Dimedrol is quickly absorbed from a GIT. The bioavailability is 50%. Linking with proteins of plasma – 98-99%. Gets through GEB. It is metabolized mainly in a liver, partially – in lungs and kidneys. During the day it is completely removed by kidneys in the form of metabolites. It is removed also with milk and can cause sedation in children of chest age.
The maximum concentration of Rutinum after intake is reached in 1-9 h. It is removed mainly with bile and to a lesser extent – kidneys.
The pharmacodynamics
Paracetamol possesses analgeziruyushchy, febrifugal and weak anti-inflammatory action. The mechanism of action is connected with inhibition of synthesis of prostaglandins, primary influence on the center of thermal control in a hypothalamus.
Ascorbic acid fills shortage of vitamin C in an organism, has the significant antioxidant properties, regulates oxidation-reduction processes, increases body resistance to infections.
Calcium the gluconate has antiallergic, haemo static effect, reduces fragility and permeability of vessels, symptoms of a lack of calcium of an organism, improves reduction of muscles in muscular dystrophy, a myasthenia.
Dimedrol has antiallergic activity, renders mestnoanesteziruyushchy, spasmolytic and moderate ganglioblokiruyushchy action. At intake causes sedative and somnolent effect, has moderate antiemetic effect.
The vasoprotective of routines belongs to group of vitamin P, in combination with ascorbic acid reduces permeability and fragility of capillaries, participates in oxidation-reduction processes, has antioxidant properties.
Indications
Symptomatic treatment of flu and other acute respiratory viral infections which are followed by fever, sore throat, headache, rhinitis.
The route of administration and doses
the Adult appoint inside on 1 tablet 3 times a day, to children 7 years on ½ tablets 3 times a day after a meal within 3-5 days are more senior. The maximum single dose for adults – 2 tablets, daily – 6 tablets, for children is more senior than 7 years – 1 tablet and 3 tablets respectively. More than 5 days without consultation with the doctor are not recommended to use drug. If symptoms remain, follows will see a doctor.
Not to exceed the recommended doses.
Side effects
- the dispeptic phenomena, dryness in a mouth, pain in epigastriums, nausea, vomiting, irritation of a mucous membrane of digestive tract, at prolonged use in high doses paracetamol can have hepatotoxic, nephrotoxic action
- a headache, feeling of fatigue, drowsiness, increase in excitability of central nervous system, a sleep disorder, reduction in the rate of psychomotor reactions, Dimedrol can cause paradoxical development of insomnia, irritability and euphoria in children
- at prolonged use in high doses the oppression of function of the insulyarny device of a pancreas (hyperglycemia, a glucosuria), a hyperoxaluria and formation of urinary stones from calcium oxalate
- decrease in permeability of capillaries and deterioration in a trophicity of fabrics
- a thrombocytosis, thrombocytopenia, a leukopenia, a neutropenia, an agranulocytosis, anemia, hemolytic anemia (especially for patients with deficit glyukozo-6-fosfatdegidrogenazy), a giperprotrombinemiya, an erythropenia, a neutrophylic leukocytosis, a hypopotassemia
- allergic reactions is possible: urticaria, a skin itching, a dermahemia
- the complicated urination (especially at men with the increased prostate)
- the increased viscosity of secretion of respiratory tract
should be reported About all side effects including which are not stated above to the attending physician and to stop administration of drug.
Contraindications
- individual intolerance of any components which are a part of drug
- heavy abnormal liver functions and kidneys
- an alcoholism
- digestive tract erosive cankers (in an aggravation phase)
- gastrointestinal bleedings
- blood diseases with tendency to hemorrhages
- a nephrolithiasis (or presence of this disease in the anamnesis)
- epilepsy
- children's age up to 7 years
- pregnancy and the period of a lactation
- anemia, a leukopenia
- deficit glyukozo-6-fosfatdegidrogenazy
Medicinal interaction
At simultaneous use with the inductors of microsomal enzymes of a liver, means possessing hepatotoxic action (Salicylamidums, barbiturates, antiepileptic means, tricyclic antidepressants, alcohol, rifampicin) arise risk of strengthening of hepatotoxic action of paracetamol (level of toxic metabolites increases).
Simultaneous use with doxorubicine increases risk of an abnormal liver function.
At simultaneous use with oral contraceptives the removal of paracetamol from an organism accelerates and reduction of its analgetic action is possible.
Activated carbon decreases bioavailability of paracetamol.
At simultaneous use with anticoagulants perhaps small or moderate increase in a prothrombin time, the danger of bleedings increases.
At simultaneous use with metaklopromidy and domperidony increase in absorption of paracetamol and increase in its concentration in blood plasma is possible, and holestiramin reduces concentration of paracetamol.
Cases of manifestation of toxic effect of paracetamol at simultaneous use with an isoniazid are described, reduces clearance of paracetamol.
Hepatotoxicity cases at simultaneous use of paracetamol and phenobarbital are described. Hepatotoxic action amplifies in the presence of ethanol.
Carbamazepine, Phenytoinum, phenobarbital, Primidonum reduce efficiency of paracetamol.
Interaction with drugs arises at prolonged use of high doses of ascorbic acid more often.
Ascorbic acid increases concentration in blood of salicylates (increases risk of a crystalluria), ethinylestradiol, benzylpenicillin and tetracyclines.
With estrogen - hormone level in blood serum increases.
With the oral kotratseptiva containing estrogen - the contraceptive effect decreases.
Reduces anti-coagulative effect of derivatives of coumarin and heparin.
Improves absorption in intestines of iron preparations.
Increases the general clearance of alcohol which in turn, reduces concentration of ascorbic acid.
Drugs of a quinolinic row, Calcii chloridum, salicylates, corticosteroids at prolonged use exhaust reserves of ascorbic acid.
Acetylsalicylic acid, oral contraceptives, fresh juice and alkaline drink reduce absorption and digestion of ascorbic acid. At simultaneous use of ascorbic acid with izoprenaliny the chronotropic action of the last decreases. In high doses increases removal of a meksiletin kidneys. Barbiturates and a pyrimidine increase removal of ascorbic acid with urine. Ascorbic acid reduces therapeutic action of antipsychotic HP (neuroleptics) – derivatives of a fenotiazin, a canalicular reabsorption of amphetamine and tricyclic antidepressants.
At simultaneous use, Dimedrol strengthens effect of ethanol and the drugs oppressing central nervous system, barbiturates, somnolent, opiate analgetics. Therefore at combined use of these drugs it is necessary to consult with the doctor for avoidance of the potentiated action.
MAO inhibitors enhance anticholinergic activity of Dimedrol.
Antagonistic interaction is noted at joint appointment with psychostimulants.
Reduces efficiency of Apomorphinum as vomitive at treatment of poisoning.
Enhances anticholinergic effects of drugs with holinoblokiruyushchy activity.
Calcium can reduce absorption of tetracycline antibiotics and drugs of fluorine at their concomitant use. Simultaneous use of vitamin D increases calcium absorption. Because of a possibility of formation of not soaking up complexes calcium can reduce absorption of estramustinum, the etidronat and, perhaps, other bisfosfonat, Phenytoinum, hinolon, oral tetracycline antibiotics and drugs has to make at least 3 h. Absorption of calcium from a GIT can decrease at a concomitant use of some types of food, for example, of spinach, a rhubarb, bran and grain. When assigning high doses of calcium the patient receiving foxglove drugs can increase risk of developing of arrhythmias. Thiazide diuretics reduce excretion of calcium with urine. Therefore it must be kept in mind risk of development of a hypercalcemia at their simultaneous use.
The pharmacological effect of Rutinum amplifies ascorbic acid. Rutinum protects ascorbic acid and adrenaline from oxidation.
Special instructions
not to use others paracetamol the containing drugs at treatment by AntiGrippin - P.S care apply at patients with abnormal liver functions and kidneys. Not to combine with intake of sleeping medicines.
Paracetamol care is appointed in chronic diseases of a liver and kidneys, gout, a peptic ulcer of a stomach and a duodenum (in the anamnesis). It is necessary to consider degree and the nature of functional changes of data of bodies as at these patients the increase in time of semi-removal of paracetamol is possible. Intake of paracetamol can affect results of definition of uric acid in blood by means of phosphatotungstic acid and definition of a glycemia by method glyukozo - oxidases-peroxidases. At administration of drug and during manifestation of its action the consumption of alcoholic beverages is forbidden.
Considering promoting effect of ascorbic acid on synthesis of kortikosterioidny hormones, it is necessary to control function of kidneys and the ABP. Ascorbic acid at patients with quickly proliferating and intensively metastasizing tumors can aggravate during a disease. Ascorbic acid can distort results of various laboratory tests (determination of content of glucose, bilirubin and activity of hepatic transaminases, LDG in blood plasma). Ascorbic acid is appointed with care to patients with a giperoksalaturiya. Calcium patients need to apply a gluconate with care with a renal failure, or in the diseases connected with the increased vitamin D level, sarcoidosis type diseases.
It is necessary to report about all side (unusual) effects including which are not stated above to the attending physician.
In the absence of improvement of health administration of drug it is necessary to stop and see a doctor. If surgical intervention is necessary to the patient, he has to warn the doctor about administration of drug in advance.
Pregnancy and lactation.
Use of drug is not recommended.
Features of influence of drug on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms
With care apply at the patients who are engaged in potentially dangerous types of activity requiring special attention and fast psychomotor reactions.
Overdose
symptoms of overdose of Dimedrol and paracetamol Are observed: nausea, vomiting, dryness in a mouth, expansion of pupils, oppression of central nervous system, a spasm, excitement development (especially at children) or depressions. Signs of a hypercalcemia: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, consciousness disturbance, a nephrocalcinosis, a calciuria and in serious cases arrhythmia and a coma.
Treatment: gastric lavage by water with activated carbon and performing symptomatic therapy, an artificial diuresis, a hemodialysis. Paracetamol antidote Acetylcysteinum.
A form of release and packing
of the Tablet on 10 pieces in planimetric bezjyacheykovy packing from packing paper with a polymeric covering from two parties. Planimetric bezjyacheykovy packings together with the instruction for medical use in the state and Russian languages place in group packing – a cardboard box.
Storage conditions
In the dry, protected from light place at a temperature not above 25 °C.
To store out of children's reach!
A period of storage
2 years
not to use drug after an expiration date.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
Eykos-Pharm LLP Producer, the Republic of Kazakhstan, Almaty region, the settlement Boralday, 71 travel.
The owner of the registration certificate
of Eykos-Pharm LLP, the Republic of Kazakhstan, Almaty region, settlement Boralday, 71 travel
the Address of the organization accepting claims from consumers concerning quality produktsiig. Almaty, Nusupbekov St., 32 ph. 397 64 29, fax: 250 71 78 e-mail:
To Develop pharm@eikos.kz
for medical use
of AntiGrippin medicine - P
Trade
name AntiGrippin - P
International unlicensed name
Is not present
the Dosage form
of the Tablet Structure One Tablet contains
active agents: paracetamol – 0.25 g, ascorbic acid – 0.15 g, calcium a gluconate – 0.05 g, Dimedrol – 0.01 g, Rutinum – 0.01 g,
excipients: starch, talc, calcium stearate.
The description
of the Tablet of yellowish color with a flat surface, with a facet and risky.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
For elimination of symptoms of cold and cough. Other combinations of drugs for elimination of symptoms of cold.
The ATX R05X code
Pharmacological properties
the Pharmacological activity of drug is caused by properties of the active ingredients which are its part.
The pharmacokinetics
After intake paracetamol is quickly absorbed from a GIT, widely distributed in fabrics and in fluid mediums of an organism, except for fatty tissue and cerebrospinal fluid. Linking with proteins makes less than 10%. It is metabolized mainly in a liver, removed with urine, mainly in the form of glyukuronidny and sulphatic conjugates. Paracetamol gets through a placental barrier and is emitted with breast milk.
Ascorbic acid is well soaked up after oral administration. About 25% contact plasma proteins, is postponed in plasma and cells, the highest concentration is reached in ferruterous fabrics (generally in bark of adrenal glands and a hypophysis). It is metabolized in a liver, removed with urine in the form of oxalate and in an invariable look.
After intake about 30% of the ionized calcium are soaked up in a GIT. After oral administration the maximum concentration in blood plasma is reached in 1.2-1.3 h. It is brought out of an organism mainly with a stake (80%) and urine (20%).
Dimedrol is quickly absorbed from a GIT. The bioavailability is 50%. Linking with proteins of plasma – 98-99%. Gets through GEB. It is metabolized mainly in a liver, partially – in lungs and kidneys. During the day it is completely removed by kidneys in the form of metabolites. It is removed also with milk and can cause sedation in children of chest age.
The maximum concentration of Rutinum after intake is reached in 1-9 h. It is removed mainly with bile and to a lesser extent – kidneys.
The pharmacodynamics
Paracetamol possesses analgeziruyushchy, febrifugal and weak anti-inflammatory action. The mechanism of action is connected with inhibition of synthesis of prostaglandins, primary influence on the center of thermal control in a hypothalamus.
Ascorbic acid fills shortage of vitamin C in an organism, has the significant antioxidant properties, regulates oxidation-reduction processes, increases body resistance to infections.
Calcium the gluconate has antiallergic, haemo static effect, reduces fragility and permeability of vessels, symptoms of a lack of calcium of an organism, improves reduction of muscles in muscular dystrophy, a myasthenia.
Dimedrol has antiallergic activity, renders mestnoanesteziruyushchy, spasmolytic and moderate ganglioblokiruyushchy action. At intake causes sedative and somnolent effect, has moderate antiemetic effect.
The vasoprotective of routines belongs to group of vitamin P, in combination with ascorbic acid reduces permeability and fragility of capillaries, participates in oxidation-reduction processes, has antioxidant properties.
Indications
Symptomatic treatment of flu and other acute respiratory viral infections which are followed by fever, sore throat, headache, rhinitis.
The route of administration and doses
the Adult appoint inside on 1 tablet 3 times a day, to children 7 years on ½ tablets 3 times a day after a meal within 3-5 days are more senior. The maximum single dose for adults – 2 tablets, daily – 6 tablets, for children is more senior than 7 years – 1 tablet and 3 tablets respectively. More than 5 days without consultation with the doctor are not recommended to use drug. If symptoms remain, follows will see a doctor.
Not to exceed the recommended doses.
Side effects
- the dispeptic phenomena, dryness in a mouth, pain in epigastriums, nausea, vomiting, irritation of a mucous membrane of digestive tract, at prolonged use in high doses paracetamol can have hepatotoxic, nephrotoxic action
- a headache, feeling of fatigue, drowsiness, increase in excitability of central nervous system, a sleep disorder, reduction in the rate of psychomotor reactions, Dimedrol can cause paradoxical development of insomnia, irritability and euphoria in children
- at prolonged use in high doses the oppression of function of the insulyarny device of a pancreas (hyperglycemia, a glucosuria), a hyperoxaluria and formation of urinary stones from calcium oxalate
- decrease in permeability of capillaries and deterioration in a trophicity of fabrics
- a thrombocytosis, thrombocytopenia, a leukopenia, a neutropenia, an agranulocytosis, anemia, hemolytic anemia (especially for patients with deficit glyukozo-6-fosfatdegidrogenazy), a giperprotrombinemiya, an erythropenia, a neutrophylic leukocytosis, a hypopotassemia
- allergic reactions is possible: urticaria, a skin itching, a dermahemia
- the complicated urination (especially at men with the increased prostate)
- the increased viscosity of secretion of respiratory tract
should be reported About all side effects including which are not stated above to the attending physician and to stop administration of drug.
Contraindications
- individual intolerance of any components which are a part of drug
- heavy abnormal liver functions and kidneys
- an alcoholism
- digestive tract erosive cankers (in an aggravation phase)
- gastrointestinal bleedings
- blood diseases with tendency to hemorrhages
- a nephrolithiasis (or presence of this disease in the anamnesis)
- epilepsy
- children's age up to 7 years
- pregnancy and the period of a lactation
- anemia, a leukopenia
- deficit glyukozo-6-fosfatdegidrogenazy
Medicinal interaction
At simultaneous use with the inductors of microsomal enzymes of a liver, means possessing hepatotoxic action (Salicylamidums, barbiturates, antiepileptic means, tricyclic antidepressants, alcohol, rifampicin) arise risk of strengthening of hepatotoxic action of paracetamol (level of toxic metabolites increases).
Simultaneous use with doxorubicine increases risk of an abnormal liver function.
At simultaneous use with oral contraceptives the removal of paracetamol from an organism accelerates and reduction of its analgetic action is possible.
Activated carbon decreases bioavailability of paracetamol.
At simultaneous use with anticoagulants perhaps small or moderate increase in a prothrombin time, the danger of bleedings increases.
At simultaneous use with metaklopromidy and domperidony increase in absorption of paracetamol and increase in its concentration in blood plasma is possible, and holestiramin reduces concentration of paracetamol.
Cases of manifestation of toxic effect of paracetamol at simultaneous use with an isoniazid are described, reduces clearance of paracetamol.
Hepatotoxicity cases at simultaneous use of paracetamol and phenobarbital are described. Hepatotoxic action amplifies in the presence of ethanol.
Carbamazepine, Phenytoinum, phenobarbital, Primidonum reduce efficiency of paracetamol.
Interaction with drugs arises at prolonged use of high doses of ascorbic acid more often.
Ascorbic acid increases concentration in blood of salicylates (increases risk of a crystalluria), ethinylestradiol, benzylpenicillin and tetracyclines.
With estrogen - hormone level in blood serum increases.
With the oral kotratseptiva containing estrogen - the contraceptive effect decreases.
Reduces anti-coagulative effect of derivatives of coumarin and heparin.
Improves absorption in intestines of iron preparations.
Increases the general clearance of alcohol which in turn, reduces concentration of ascorbic acid.
Drugs of a quinolinic row, Calcii chloridum, salicylates, corticosteroids at prolonged use exhaust reserves of ascorbic acid.
Acetylsalicylic acid, oral contraceptives, fresh juice and alkaline drink reduce absorption and digestion of ascorbic acid. At simultaneous use of ascorbic acid with izoprenaliny the chronotropic action of the last decreases. In high doses increases removal of a meksiletin kidneys. Barbiturates and a pyrimidine increase removal of ascorbic acid with urine. Ascorbic acid reduces therapeutic action of antipsychotic HP (neuroleptics) – derivatives of a fenotiazin, a canalicular reabsorption of amphetamine and tricyclic antidepressants.
At simultaneous use, Dimedrol strengthens effect of ethanol and the drugs oppressing central nervous system, barbiturates, somnolent, opiate analgetics. Therefore at combined use of these drugs it is necessary to consult with the doctor for avoidance of the potentiated action.
MAO inhibitors enhance anticholinergic activity of Dimedrol.
Antagonistic interaction is noted at joint appointment with psychostimulants.
Reduces efficiency of Apomorphinum as vomitive at treatment of poisoning.
Enhances anticholinergic effects of drugs with holinoblokiruyushchy activity.
Calcium can reduce absorption of tetracycline antibiotics and drugs of fluorine at their concomitant use. Simultaneous use of vitamin D increases calcium absorption. Because of a possibility of formation of not soaking up complexes calcium can reduce absorption of estramustinum, the etidronat and, perhaps, other bisfosfonat, Phenytoinum, hinolon, oral tetracycline antibiotics and drugs has to make at least 3 h. Absorption of calcium from a GIT can decrease at a concomitant use of some types of food, for example, of spinach, a rhubarb, bran and grain. When assigning high doses of calcium the patient receiving foxglove drugs can increase risk of developing of arrhythmias. Thiazide diuretics reduce excretion of calcium with urine. Therefore it must be kept in mind risk of development of a hypercalcemia at their simultaneous use.
The pharmacological effect of Rutinum amplifies ascorbic acid. Rutinum protects ascorbic acid and adrenaline from oxidation.
Special instructions
not to use others paracetamol the containing drugs at treatment by AntiGrippin - P.S care apply at patients with abnormal liver functions and kidneys. Not to combine with intake of sleeping medicines.
Paracetamol care is appointed in chronic diseases of a liver and kidneys, gout, a peptic ulcer of a stomach and a duodenum (in the anamnesis). It is necessary to consider degree and the nature of functional changes of data of bodies as at these patients the increase in time of semi-removal of paracetamol is possible. Intake of paracetamol can affect results of definition of uric acid in blood by means of phosphatotungstic acid and definition of a glycemia by method glyukozo - oxidases-peroxidases. At administration of drug and during manifestation of its action the consumption of alcoholic beverages is forbidden.
Considering promoting effect of ascorbic acid on synthesis of kortikosterioidny hormones, it is necessary to control function of kidneys and the ABP. Ascorbic acid at patients with quickly proliferating and intensively metastasizing tumors can aggravate during a disease. Ascorbic acid can distort results of various laboratory tests (determination of content of glucose, bilirubin and activity of hepatic transaminases, LDG in blood plasma). Ascorbic acid is appointed with care to patients with a giperoksalaturiya. Calcium patients need to apply a gluconate with care with a renal failure, or in the diseases connected with the increased vitamin D level, sarcoidosis type diseases.
It is necessary to report about all side (unusual) effects including which are not stated above to the attending physician.
In the absence of improvement of health administration of drug it is necessary to stop and see a doctor. If surgical intervention is necessary to the patient, he has to warn the doctor about administration of drug in advance.
Pregnancy and lactation.
Use of drug is not recommended.
Features of influence of drug on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms
With care apply at the patients who are engaged in potentially dangerous types of activity requiring special attention and fast psychomotor reactions.
Overdose
symptoms of overdose of Dimedrol and paracetamol Are observed: nausea, vomiting, dryness in a mouth, expansion of pupils, oppression of central nervous system, a spasm, excitement development (especially at children) or depressions. Signs of a hypercalcemia: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, consciousness disturbance, a nephrocalcinosis, a calciuria and in serious cases arrhythmia and a coma.
Treatment: gastric lavage by water with activated carbon and performing symptomatic therapy, an artificial diuresis, a hemodialysis. Paracetamol antidote Acetylcysteinum.
A form of release and packing
of the Tablet on 10 pieces in planimetric bezjyacheykovy packing from packing paper with a polymeric covering from two parties. Planimetric bezjyacheykovy packings together with the instruction for medical use in the state and Russian languages place in group packing – a cardboard box.
Storage conditions
In the dry, protected from light place at a temperature not above 25 °C.
To store out of children's reach!
A period of storage
2 years
not to use drug after an expiration date.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
Eykos-Pharm LLP Producer, the Republic of Kazakhstan, Almaty region, the settlement Boralday, 71 travel.
The owner of the registration certificate
of Eykos-Pharm LLP, the Republic of Kazakhstan, Almaty region, settlement Boralday, 71 travel
the Address of the organization accepting claims from consumers concerning quality produktsiig. Almaty, Nusupbekov St., 32 ph. 397 64 29, fax: 250 71 78 e-mail:
To Develop pharm@eikos.kz