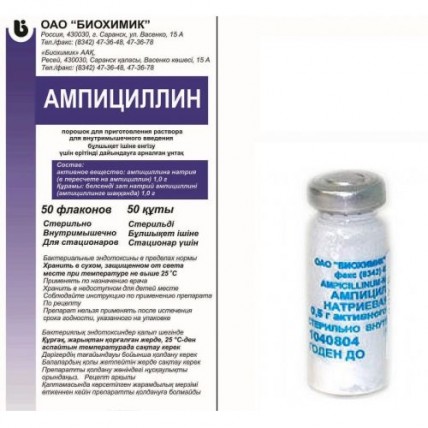
Ampicillin Powder for solution 1g, 1 ampoule
- $2.80
Out Of Stock
The instruction for medical use of AMPICILLIN medicine the Trade name Ampicillin the International unlicensed name Ampicillin Dosage Form Powder for preparation of solution for intramuscular introduction of 1.0 g Structure contains One bottle: active agent - sodium ampicillin (in terms of ampicillin) 1.0 g. Description Powder of white or almost white color. It is hygroscopic Pharmacotherapeutic group Antibacterial drugs for system use. Beta laktamnye antibacterial drugs. Penicillin of a broad spectrum of activity. Ampicillin the ATX J01CA01 Code the Pharmacological Pharmacokinetics Evenly properties is distributed in bodies and body tissues, it is found in therapeutic concentration in pleural, peritoneal, amniotic and synovial liquids, liquor, contents of blisters, urine (high concentrations), a mucous membrane of intestines, bones, a gall bladder, lungs, tissues of female genitals, bile, in a bronchial secret (in a purulent bronchial secret accumulation weak), paranasal sinuses, liquid of a middle ear, saliva, fruit fabrics. Badly gets through a blood-brain barrier (GEB) the permeability increases at inflammation of a meninx. It is removed mainly by kidneys (70-80%), and in urine very high concentrations of not changed antibiotic, partially with bile, at nursing mothers are created - with milk. Does not kumulirut. It is removed at a hemodialysis. A pharmacodynamics the Antibacterial microbicide from group of semi-synthetic penicillin received by acetylation of 6-aminopenicillanic acid by residue of aminophenylacetic acid, kislotoustoychiv. Inhibits a polymerase of a peptidoglikan and transpeptidase, interferes with formation of peptide bonds and breaks late stages of synthesis of a cell wall of the sharing microorganism that leads to decrease in osmotic stability of a bacterial cell and causes its lysis (death). Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus spp., Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium spp., the majority of enterococci, including Enterococcus faecalis) and gram-negative (Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria meningitidis, Proteus mirabilis, Yersinia multocida (Pasteurella), many types of Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Escherichia coli) microorganisms, aerobic asporous bacteria is active concerning gram-positive (Streptococcus (an alpha and beta and hemolytic) (Listeria spp.), Nesseria gonorrhoae. It is inefficient concerning penitsillinazoprodutsiruyushchy strains of Staphylococcus spp., all strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the majority of strains of Klebsiella spp. and Enterobacter spp. Indications the Infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by microorganisms, sensitive to ampicillin, including: – to respiratory infection (bronchitis, pneumonia, lung abscess) – infections of ENT organs (sinusitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, average otitis) – infections of biliary tract (cholecystitis, a cholangitis) – infections of urinary tract (pyelitis, pyelonephritis, an urethritis, cystitis) – digestive tract infections (typhoid and a paratyphoid, dysentery, salmonellosis, a salmonellonositelstvo) – gynecologic infections (cervicitis) – infections of skin and soft tissues (the ugly face, impetigo which are again infected a dermatosis) - musculoskeletal system infections – peritonitis – sepsis - an endocarditis (prevention and treatment) – meningitis – scarlet fever – gonorrhea. The route of administration and doses Before prescribing of ampicillin should be defined sensitivity of an infestant to drug. Ampicillin enter intramusculary (in oil). Solution for intramuscular introduction is prepared by ex tempore, adding to bottle contents (1.0 g) of 4 ml of water for injections. Solutions use right after preparation. The single dose of drug for adults makes 0.5-1.0 g, daily-1-3 g, in heavy infections the daily dose can be increased up to 10 g and more. In infections of a medium-weight course the adult each 6-8 h enter 0.25-0.5 g in oil, at a heavy course of infections - 1-2 g 4 times a day. For treatment of gonorrhea enter 1 g at an interval of 8 or 12 h. In a gonococcal urethritis - 0.5 g in oil 2 times within one day, in a gonococcal uncomplicated urethritis - once 0.5 g. For treatment of bacterial meningitis and sepsis the daily dose of drug makes 150-200 mg/kg which is divided into 6-8 introductions in oil with an interval of 3-4 h. The maximum daily dose in heavy infections – 8-14 g. For prevention of a bacterial endocarditis at the patients from group of high risk who are exposed to dental, endoscopic interventions, small ENT organs surgeries and also operations on bodies of digestive tract or biliary tract – 2 in oil in 30 min. prior to the procedure or operation, if necessary, in 6 h enter repeatedly in a dose 1 g. Listeriosis – on 50 mg/kg each 6 h. Typhus fever – on 25 mg/kg each 6 h. At not heavy course of infections at children it is more preferable to appoint drug in the form of suspension. In heavy and medium-weight infections at children enter: - to children is more senior than 1 month with the body weight of 1.2 - 2 kg each 8 h, with body weight enter on 25-50 mg/kg more than 2 kg – 25-50 mg/kg each 6 h - from 2 months to 1 year - at the rate of 100 mg/kg a day, 1-7 years - 100-150 mg/kg a day, 7-14 years - 100–200 mg/kg a day. The daily dose is divided into 4-6 introductions. In meningitis a daily dose - 100-200 mg/kg in 6-8 introductions. Duration of treatment depends on disease severity, dynamics of a course of the disease and is defined by the attending physician (5-10 days and more). Side effects - peeling of skin, an itching, urticaria - rhinitis - conjunctivitis - a Quincke's edema seldom - fever, an arthralgia - an eosinophilia - erythematic and makulopapulezny rash, exfoliative dermatitis, a multiformny exudative erythema (including Stephens-Johnson's syndrome) - the reactions similar to a serum disease very seldom - an acute anaphylaxis - stomatitis, a glossitis - gastritis, dryness in a mouth, change of taste, an abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, pseudomembranous colitis - an abnormal liver function, moderate increase in activity of hepatic transaminases - a leukopenia, a neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, an agranulocytosis, anemia - excitement or aggression, uneasiness, confusion of consciousness, change of behavior, a depression, spasms (at therapy by high doses), - a headache - pain in the injection site, infiltrates at introduction in oil - interstitial nephrite, a nephropathy - superinfection (especially at patients with chronic diseases or reduced resistance of an organism) - vagina candidiasis. Contraindications - hypersensitivity (including to other penicillin, cephalosporins, karbapenema) - an infectious mononucleosis - a lymphoid leukosis - a liver failure - gastrointestinal diseases in the anamnesis (especially the colitis connected with use of antibiotics) - the lactation period - children's age (up to 1 month). With care: - bronchial asthma - seasonal allergic rhinitis and other allergic diseases - a renal failure - bleedings in the anamnesis - pregnancy. Medicinal interactions Pharmaceutical it is incompatible with aminoglycosides. Bactericidal antibiotics (including aminoglycosides, cephalosporins, Cycloserinum, Vancomycinum, rifampicin) have sinergidny effect, bacteriostatic drugs (macroleads, chloramphenicol, linkozamida, tetracyclines, streptocides) - antagonistic. Increases efficiency of indirect anticoagulants (suppressing intestinal microflora, reduces synthesis of vitamin K and the prothrombin ratio), reduces efficiency of estrogensoderzhashchy oral contraceptives (it is necessary to use additional methods of contraception), the medicines (M) in the course of which metabolism paraaminobenzoic acid (PABK) is formed, ethinylestradiol (in the latter case risk of developing bleedings of 'break' increases). Diuretics, Allopyrinolum, oksifenbutazon, phenylbutazone, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NPVP), and other drugs blocking canalicular secretion increase concentration of ampicillin in plasma (due to decrease in canalicular secretion). Allopyrinolum increases risk of developing skin rash. Reduces clearance and increases toxicity of a methotrexate. Strengthens digoxin absorption. Special instructions At course treatment it is necessary to carry out control of a condition of function of bodies of a hemopoiesis, a liver and kidneys. Development of superinfection due to growth of microflora, insensitive to it, is possible that demands corresponding change of antibacterial therapy. At treatment of patients with bacteremia (sepsis) development of reaction of a bacteriolysis (Yarisha-Gerksgeymer's reaction) is possible. At the patients having hypersensitivity to penicillin cross allergic reactions with a beta laktamnymi antibiotics are possible. At treatment of slight diarrhea against the background of course treatment it is necessary to avoid the antidiarrheal drugs reducing an intestines vermicular movement, it is possible to use a kaolin - or attapulgitsoderzhashchy antidiarrheal means, drug withdrawal is shown. In heavy diarrhea it is necessary the adjusting therapy. Treatment has to continue surely for 48-72 more h after disappearance of clinical signs of a disease. At simultaneous use of estrogensoderzhashchy oral contraceptives it is necessary to use whenever possible other or additional methods of contraception. Pregnancy and a lactation use of ampicillin at pregnancy is possible when the advantage for mother exceeds potential risk for a fruit. Ampicillin is emitted with breast milk in low concentration. In need of use of drug in the period of a lactation it is necessary to resolve an issue of the breastfeeding termination. Features of influence of medicine on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms. It is necessary to be careful when driving or potentially dangerous mechanisms. Overdose Symptoms: manifestations of toxic action on the central nervous system (especially at patients with a renal failure), nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, disturbance of water and electrolytic balance (as a result of vomiting and diarrhea). Treatment: drugs for maintenance of water and electrolytic balance and symptomatic. It is removed by means of a hemodialysis. A form of release and packing On 1.0 g of active agent in the bottles hermetically corked by the rubber bungs which are pressed out by caps aluminum. 50 bottles stack in a box of cardboard with an investment of 3-5 instructions for medical use of drug in the state and Russian languages (for hospitals). Storage conditions In the dry, protected from light place, at a temperature not above 25 °C to Store out of children's reach! A period of storage 2 years not to use after expiry date Prescription status According to the prescription
to Develop
to Develop