Description
The instruction for medical use
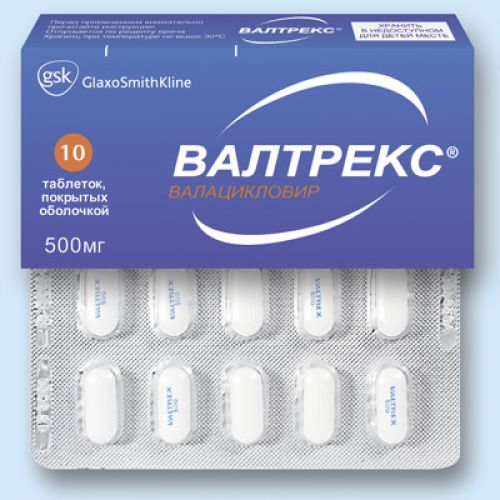
of VALTREKS medicine
A trade name
of VALTREKS
the International unlicensed
name Valatsiklovir Lekarstvennaya
the Tablet form, film coated, 500 mg
Structure
One tablet contains
active agent: valatsiklovir 500 mg (in the form of a valatsiklovir of a hydrochloride of 556 mg),
excipients: microcrystalline cellulose, krospovidon, K90 povidone, magnesium stearate, silicon dioxide colloidal anhydrous,
structure of a cover: dye white concentrate (YS-1-18043): hydroksipropilmetiltsellyuloza, titan dioxide (E171), polyethyleneglycol 400, polysorbate 80, wax of karnaubskiya.
The description
Oblong smooth biconvex tablets, film coated white color with the engraved marking of GX CF1 with white or almost white kernel on a break.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antiviral drugs for system use. Antiviral drugs of direct action. Nucleosides and nucleotides. Valatsiklovir.
The ATX J05AB11 code
the Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Later properties of intake valatsiklovir is well soaked up from digestive tract, quickly and almost completely turning into acyclovir and valine. At reception of a valatsiklovir in a dose from 1000 mg the bioavailability of acyclovir is 54% and does not depend on meal. Bioavailability of acyclovir from a valatsiklovir in 3.3-5.5 times more, than at oral administration of acyclovir (according to historical observations). The pharmacokinetics of a valatsiklovir is not proportional to the entered dose, extent of absorption of a valatsiklovir decreases with increase in a dose of the taken drug. The pharmacokinetics of a valatsiklovir and acyclovir is not broken at the patients infected with viruses of the herpes simplex (HS) and the Varicella zoster (BVZ) virus.
After single dose of a valatsiklovir in a dose of 250-2000 mg the average peak concentration of acyclovir in plasma at healthy volunteers with normal function of kidneys averages 2.2-8.3 mkg/ml, and a median of time of achievement of this concentration 1-2 hours with average AUC 25-131 values of h µmol/l. Peak concentration of a valatsiklovir in plasma makes only 4% of concentration of acyclovir, the median of time of its achievement of 30-100 minutes after reception of a dose, in 3 hours the level of peak concentration remains former or decreases. Valatsiklovir and acyclovir have similar pharmacokinetic parameters after single and repeated intakes. Extent of linking of a valatsiklovir with proteins of plasma is very low (only 15%).
Valatsiklovir is brought from an organism with urine mainly in the form of acyclovir (more than 80% of a dose) and an acyclovir metabolite – a 9-karboksimetoksimetilguanin, in not changed look less than 1% of drug eliminirutsya. valatsiklovir, acyclovir are not metabolized by P450 cytochrome enzymes.
At patients with normal function of kidneys the elimination half-life of acyclovir after reception of a valatsiklovir makes about 3 hours of plasma, and at patients with an end-stage of a renal failure the elimination half-life can be extended till 14 o’clock.
In the presence at the patient of a liver failure the reduction in the rate of transition of a valatsiklovir to acyclovir without influence on the size of final indicators and elimination half-life of acyclovir is observed.
In the late stages of pregnancy the steady daily indicator of AUC (the area under a ratio curve plasma concentration / time) after reception of 1000 mg of a valatsiklovir was approximately twice more, than that at intake of acyclovir in a dose of 1200 mg a day.
Reception of VALTREKSA in a dose of 1000 mg or 2000 mg does not break a disposition and pharmacokinetic indicators of a valatsiklovir at HIV-positive patients in comparison with healthy faces.
At recipients of transplants of the bodies receiving valatsiklovir in a dose of 2000 mg 4 times a day, the peak of concentration of acyclovir is equal or exceeds that at the healthy volunteers receiving the same dose of drug, and daily indicators the area under a curve at them are much higher.
VALTREKS pharmacodynamics antiviral drug, L-valinovy ether of acyclovir which is an analog of a purine (guanine) nucleoside.
In vitro acyclovir has the specific inhibiting activity against the herpes simplex viruses (HSV) of the 1st and 2nd types, the Varicella zoster (VVZ) virus, a cytomegalovirus (CMV), the Epstein-Burra’s virus (EBV) and a virus of herpes of the person of the 6th type. Acyclovir inhibits synthesis of virus DNA right after phosphorylation and transformation into an active form – acyclovir triphosphate.
The first stage of phosphorylation demands activity of virus-specific enzymes. For VPG, VVZ and VEB such enzyme is the virus thymidinekinase which is present only at the cells affected with a virus. The partial selectivity of phosphorylation remains at a cytomegalovirus and is mediated through a product of a gene of UL 97 phosphotransferase. Acyclovir activation by specific virus enzyme considerably explains its selectivity. Process of phosphorylation of acyclovir comes to the end with cellular kinases. Acyclovir triphosphate competitively inhibits a virus DNA polymerase and, being a nucleoside analog, is built in virus DNA that leads to an obligate rupture of a chain, the termination of synthesis of DNA and, therefore, to blocking of replication of a virus.
In extremely exceptional cases at patients with heavy disturbance of immunity, for example, after bone marrow transplantation and other bodies, at the patients receiving chemotherapy in oncological diseases and at HIV-positive patients the decrease in sensitivity to acyclovir can be observed. The resistance is usually caused by deficit of a thymidinekinase that leads to excessive spread of a virus in the owner’s organism. Sometimes decrease in sensitivity to acyclovir is caused by emergence of virus strains with disturbance of structure of a virus thymidinekinase or DNA polymerase. Virulence of these types of a virus reminds that at its wild strain.
It was proved what valatsiklovir reduces risk of transfer of genital herpes at immunocompetent adults at reception of this means as overwhelming therapy, along with safety of sexual contacts.
Prevention of CMV by means of a valatsiklovir at patients to whom transplantation of parenchymatous bodies was executed (a kidney, heart) reduces the probability of acute graft rejection, opportunistic infections and other types of a virus of herpes.
The indications
of the Infection caused by the Varicella zoster (VZV) virus – the surrounding herpes
– the surrounding herpes (shingles) and oftalmogerpes at adult immunocompetent patients
– the surrounding herpes at adult patients with an easy or moderate immunodeficiency
of the Infection, caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV)
of VALTREKS is shown for treatment and suppression of an infection of the skin and mucous membranes caused by VPG including:
– treatment for the first time of the revealed genital herpes immunocompetent adults and teenagers and also adults with reduced immunity
– treatment of recurrent genital herpes at immunocompetent adults and teenagers and also at adults with reduced immunity
have a suppression of a recurrence of genital herpes at immunocompetent adults and teenagers and also adults with reduced immunity
have a treatment and suppression of the eye infections caused by VPG
the Cytomegaloviral (CMV) infection
– prevention of a Cytomegaloviral infection (CMV) arising at organ transplantation.
The route of administration and doses
Treatment of shingles, including oftalmogerpes
At adults of VALTREKS is appointed in a dose of 1000 mg 3 times a day within 7 days.
Treatment of the infections caused by VPG at adults and teenagers from 12 years with the kept immunity
of VALTREKS is appointed in a dose of 500 mg 2 times a day. In case of a recurrence the treatment has to continue 3 or 5 days. In more hard primary cases the treatment should be begun as soon as possible, and its duration has to be increased from 5 to 10 days.
At VPG recurrence the purpose of VALTREKSA in a prodromal stage or at once after emergence of the first symptoms of a disease is considered ideal. As an alternative for treatment of labial herpes (lip fever) the purpose of VALTREKSA in a dose of 2 g twice within one day is effective. The second dose has to be accepted approximately in 12 hours (but not earlier, than in 6 hours) after reception of the first dose.
When using such mode of dosing duration of treatment should not exceed one day as it as it was shown, does not give additional clinical benefits. Therapy has to be begun at emergence of the earliest symptoms of lip fever (i.e. an itching, burning, tingling).
Prevention (suppression) of a recurrence of the infections caused by VPG at adults and teenagers from 12 years with the kept immunity
At patients with the kept immunity of VALTREKS is appointed in a dose of 500 mg once a day. With very frequent recurrence (10 and more in a year) the additional effect can achieve from patients when assigning VALTREKS in the daily dose of 500 mg divided into 2 receptions (on 250 mg 2 times a day).
Prevention (suppression) of a recurrence of the infections caused by VPG at adults with reduced immunity
For patients with an immunodeficiency the recommended dose of VALTREKS makes 500 mg 2 times a day.
Safety and efficiency of use for children is not established.
Prevention of infection with genital herpes
by the Infected heterosexual adult with the kept immunity and with number of aggravations to 9 times a year, VALTREKS should accept 500 mg once a day.
Data on prevention of infection in other populations of patients do not exist.
Prevention of CMV of an infection
of the Dose for adults and teenagers (from 12 years)
Is recommended to appoint VALTREKS in a dose of 2 g 4 times a day, as soon as possible after transplantation. The dose should be reduced depending on clearance of creatinine. Duration of treatment is 90 days, but at patients with high risk, treatment can be longer.
Patients with a renal failure
Treatment of shingles and the infections caused by VPG, prevention (suppression) and decrease in infection of the healthy partner, prevention of CMV
the Mode of purpose of VALTREKSA at patients with a renal failure has to be set according to this table:
Therapeutic indications
Clearance of creatinine,
ml/min.
VALTREKSA Dose
The surrounding herpes (treatment) at adults with the kept immunity and with an immunodeficiency
50 and
more than from 30 to 49 from 10 to 29
less than 10
1 g 3 times in day
of 1 g 2 times in day
of 1 g of 1 times in day
of 500 mg of 1 times a day
A herpes simplex (treatment)
at adults and teenagers with the kept immunity
30 and
more or less 30
500 mg 2 times in day
of 500 mg of 1 times a day
Labial herpes (treatment) at adults and teenagers with the kept immunity
50 and
more than from 30 to 49 from 10 to 29
less than 10
2 g twice within 1
day 1 g twice within 1 day
of 500 mg twice within 1 day
of 500 mg once
A herpes simplex prevention (suppression):
– adults and teenagers with the kept immunity
– patients with reduced immunity
30 both
more or less 30
30 and
more or less 30
In day
of 250 mg of 1 times in day
of 500 mg 2 times in day
of 500 mg of 1 times a day
Prevention of CMV of an infection at adults and teenagers
75 and more
from 50 to & lt, 75
from 25 to & lt, 50
from 10 to & lt, 25
& lt, 10 or dialysis *
2 g 4 times in day
of 1.5 g 4 times in day
of 1.5 g 3 times in day
of 1.5 g 2 times in day
of 1.5 g of 1 times a day
Decrease in infection with genital herpes
less than 15,250 mg of 1 times a day
To the patients who are on a hemodialysis VALTREKS right after the end of a session of a hemodialysis is recommended to apply 500 mg of 1 times.
* It is necessary to define often clearance of creatinine, especially during the periods when function of kidneys quickly changes, for example, right after transplantation or during engraftment of a transplant, at the same time the dose of VALTREKSA is adjusted according to indicators of clearance of creatinine.
Patients with a liver failure
with poorly and moderate cirrhosis (synthetic function of a liver is kept) the correction of a dose of VALTREKS is not required From patients. Pharmacokinetic data at patients with heavy cirrhosis (with disturbance of synthetic function of a liver and existence of shunts between a portal system and the general vascular bed) also do not confirm need to adjust VALTREKSA doses, however, experience of its clinical use in this pathology is limited.
Use for elderly people
of Correction of a dose is not required, except for a considerable renal failure. It is necessary to maintain adequate water and electrolytic balance.
Side effects
by the Most general side reactions observed at least in one case at the patients receiving the Valtrex drug treatment during clinical trials became a headache and nausea.
The side effects observed in clinical trials and in the post-marketing period are given below and listed depending on anatomo-physiological classification and frequency of occurrence.
Frequency of occurrence is defined as follows: very often (& ge, 1/10), it is frequent (& ge, 1/100 and & lt, 1/10), infrequently (& ge, 1/1,000 and & lt, 1/100), is rare (& ge, 1/10,000 and & lt, 1/1,000), is very rare (& lt, 1/10,000, including separate cases), it is unknown (frequency cannot be determined on the basis of the available data).
Disturbances from nervous system
Very often
– a headache
Often
– dizziness
Infrequently
– confusion of consciousness, a hallucination, reduced mental capacities, a tremor, excitement
Is rare
– an ataxy, a dysarthtia, spasms, encephalopathy, coma, psychotic symptoms.
Disturbances from digestive tract
Often
– nausea
– vomiting
– diarrhea
Seldom
– discomfort in
the Disturbance stomach from a hemopoiesis and lymphatic system
Infrequently
– a leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
Emergence of a leukopenia is mainly observed at patients with reduced immunity.
Very seldom
– thrombocytopenic akroangiotromboz (a Werlhof’s trombogemolitichesky disease), a gemolitiko-uraemic syndrome
of Disturbance from the respiratory system, bodies of a thorax and mediastinum
Infrequently
–
the Disturbance asthma from a gepatobliarny system
Infrequently
– reversible increases in function of a liver (for example, bilirubin, liver enzymes) which sometimes regard as manifestations of hepatitis
of Disturbance from skin and hypodermic fabrics
Often
– rash, including reactions of photosensitivity
– naggers
Infrequently
– a small tortoiseshell
Seldom
– a Quincke’s disease (Quincke’s edema)
of Disturbance from kidneys and urinary tract
Infrequently
– pain in kidneys
Seldom
– a renal failure, an acute renal failure (especially at the people of old age and patients with a renal failure receiving the doses exceeding recommended).
Kidney pain can be connected with a renal failure.
Also there are messages about intratubulyarny precipitation of crystals of acyclovir. During treatment it is necessary to provide adequate consumption of liquid.
The listed above symptoms are reversible and are usually observed at patients with disturbance of renal function or against the background of other contributing states.
At the patients with a transplanted organ receiving high doses (8 g a day) VALTREKSA for prevention of CMV of an infection, neurologic reactions develop more often than at reception of lower doses.
At patients with heavy disturbances of immunity, especially at the patients with far come stage of AIDS receiving high doses of a valatsiklovir (8 g daily) during the long span, cases of a renal failure, mikroangiopatichesky hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia were observed (sometimes in a combination). Similar complications were noted at the patients with the same diseases but who are not receiving valatsiklovir.
Contraindications
– hypersensitivity to a valatsiklovir, acyclovir and to any auxiliary ingredient which is a part of drug
– children’s and teenage age up to 18 years (treatment of shingles, including oftalmogerpes, prevention (suppression) of a recurrence of the infections caused by VPG at patients with reduced immunity, prevention of infection with genital herpes)
– children’s age up to 12 years (prevention of CMV of an infection)
Medicinal interactions
Valtrex’s Combination with nephrotoxic medical means has to be carried out with care, especially at persons with disturbance of renal function. It belongs to simultaneous to reception with the aminoglycosides, organoplatinovy components iodated by contrast means, a methotrexate, pentamidine, foskarnety, cyclosporine and takrolimusy.
Acyclovir is removed generally in an invariable view with urine through active channel secretion of kidneys. After purpose of 1 g of VALTREKSA Cimetidinum and probenetsid, blocking canalicular secretion, raise AUC acyclovir and reduce its renal clearance, however it does not demand correction in dosing of VALTREKSA because of the wide therapeutic index of acyclovir. It is necessary to be careful in case of simultaneous use of VALTREKSA in higher doses (4 g a day) and medicines which compete with acyclovir for a way of elimination as there is a potential threat of increase in plasma of level of one or both drugs or their metabolites. Increase in AUC acyclovir and an inactive metabolite of the mikofenolat of a mofetil – the immunosuppressive drug used at transplantation, at simultaneous use of acyclovir and the mikofenolat of a mofetil was noted. It is necessary to be careful also (to watch change of function of kidneys) at VALTREKSA combination in higher doses (4 g a day and more) with drugs which affect functions of kidneys (for example, cyclosporine, takrolimus).
The special
instructions Extent of Hydration of an Organism
At patients with risk of dehydration, especially at patients of advanced age, it is necessary to provide adequate completion of liquid.
Use in a renal failure and at elderly patients
Acyclovir is removed mainly through kidneys therefore the dose of VALTREKSA has to be reduced at patients with a renal failure (see the Route of administration and doses). Patients of advanced age have a probability of depression of function of kidneys in this connection it is necessary to consider expediency of correction of the appointed dose in connection with high risk of development of neurologic reactions regarding which these patients have to be observed throughout all therapy. These reactions, as a rule, are reversible and disappear after the treatment termination (see. Side effects).
Use of higher doses of VALTREKSA in a liver failure and transplantation of a liver
Is not present data on use of VALTREKSA in higher doses (4 g and any more in day) at patients with a liver disease therefore high doses of VALTREKSA to them have to be appointed with care. Special researches on studying action of VALTREKSA at liver transplantation were not conducted. However, it was shown that preventive prescribing of acyclovir in high doses reduces CMV an infection.
Use for treatment of the surrounding herpes
the careful monitoring of clinical reactions, in particular at patients with reduced immunity Has to be carried out. In case reaction to oral administration is regarded as insufficient, then it is necessary to consider a question of use of intravenous anti-virus therapy.
Patients with the complicated surrounding herpes, i.e. persons with involvement of visceral bodies, widespread shingles, motive neuropatiya, encephalitis and cerebrovascular complications, have to undergo treatment with use of intravenous therapy.
Moreover, patients with the weakened immunity with the ophthalmic surrounding herpes or high risk of spread of a disease with involvement in process of internals, have to receive therapy with use of intravenous therapy.
Use in genital herpes
of Supressivnaya the therapy of VALTREKSOM reduces risk of transfer of genital herpes, but does not exclude it completely and does not lead to full treatment. Therapy of VALTREKSOM is recommended in combination with safe sex.
Use for treatment of ophthalmic VPG
U of such patients the careful monitoring of clinical reactions has to be carried out. In case reaction to oral administration is insufficient, then it is necessary to consider a question of use of intravenous antiviral therapy.
Data on efficiency of a valatsiklovir at patients to whom transplantation (~ 200), the diseases subject to high risk connected with CMV (for example, the donor with positive reaction on the CMV/recipient with negative reaction to CMV was carried out or when using induction therapy by antithymocyte globulin) indicate use for treatment of an infection of CMV that VALTREKS for treatment of such patients should be used only in case the potential advantage exceeds potential risk of use of a valgantsiklovir or gantsiklovir.
The high dosage of VALTREKSA necessary for prevention of CMV can cause more frequent side effects, including disturbances from central nervous system, than in case of use of lower doses at other indications. Patients need to undergo careful monitoring of changes of renal function with the corresponding correction of the accepted dose.
Use in pediatrics
Is not present data on use of VALTREKSA for children 12 years for prevention of a recurrence of the infections caused by VPG at patients with the kept immunity and prevention of CMV of an infection are younger. Also there are no data on use of VALTREKSA for children and teenagers 18 years for treatment of shingles, including oftalmogerpes, for prevention of a recurrence of the infections caused by VPG at patients with reduced immunity and prevention of infection with genital herpes are younger.
Pregnancy and the period of a lactation
of Data on use of VALTREKSA at pregnancy are not enough. VALTREKS should be applied at pregnancy only if the potential advantage for mother exceeds potential risk for a fruit.
Data of registration registers on the result of pregnancy at the women accepting VALTREKS did not show increase in number of congenital defects at their children in comparison with the general population. As clinical trials included a small amount of the women accepting VALTREKS during pregnancy, the authentic and certain conclusions about safety of drug at pregnancy cannot be made.
Acyclovir, the main metabolite of a valatsiklovir, is excreted by breast milk. After purpose of VALTREKSA in a dose of 500 mg inside the maximum concentration of acyclovir (Cmax) in breast milk by 0.5-2.3 times (on average by 1.4 times) exceeded the corresponding concentration of acyclovir in mother’s plasma. The relation of AUC of the acyclovir which is in breast milk to AUC acyclovir of plasma of mother fluctuated from 1.4 to 2.6 (average value 2.2). The average value of concentration of acyclovir in breast milk was 2.24 mkg/ml (9.95 mkgm). At reception by mother of a valatsiklovir in a dose of 500 mg 2 times a day the child will undergo the same influence of acyclovir, as at its reception inside in a dose about 0.61 mg/kg/day. Elimination half-life of acyclovir from breast milk same, as from blood plasma. Valatsiklovir in not changed look was not defined in mother’s plasma, breast milk or the child’s urine. VALTREKS should appoint with care to the feeding women.
The feature of influence on ability to run the vehicle and potentially dangerous mechanisms
needs to estimate a clinical condition of the patient and a possibility of development of side effects at drug use in spite of the fact that clinical trials on influence of VALTREKSA on ability to run the vehicle and potentially dangerous mechanisms it was not carried out.
Overdose
Symptoms: data on overdose of VALTREKSA are insufficient. Single dose of a superdose of acyclovir up to 20 g which was partially absorbed from digestive tract was not followed by toxic effect of drug. Intake within several days of ultrahigh doses of acyclovir was associated with gastrointestinal (nausea and vomiting) and neurologic symptoms (headache and confusion of consciousness). Superdoses at intravenous administration of acyclovir are followed by increase in level of serumal creatinine and the subsequent development of a renal failure, at the same time neurologic complications include confusion of consciousness, a hallucination, excitement, spasms and a coma.
Treatment: patients have to be under careful observation for identification of signs of toxic action. The hemodialysis considerably strengthens removal of acyclovir from blood and can reckon as a choice method at treatment of patients with overdose of VALTREKSA.
Form of release and packing
of the Tablet, film coated, 500 mg. On 10 tablets in blister strip packaging from a film of the polyvinylchloride and printing aluminum foil varnished.
On 1 blister strip packaging together with the instruction for use in the state and Russian languages put in a pack from cardboard.
To Store storage conditions at a temperature not over 30 of C.
To store out of children’s reach!
3 years
not to use a period of storage after an expiration date.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
the Producer Glakso Vellk S.A., Spain
(Avenida de Extremadura 3, 09400 Aranda de Duero, Burgos)
the Packer S.A. GlaksoSmitKlyayn Pharmasyyutikalz, Poland
(ul. Grunwaldzka 189, 60-322 Poznan, Poland)
The owner of the registration certificate
S.A. GlaksoSmitKlyayn, Spain
(Severo Ochoa, 2 28760 Tres Cantos (Madrid) Spain)
VALTREKS is the registered trade mark of group of companies GlaksoSmitKlyayn.
In
Kazakhstan 050059, Almaty, Furmanov St., 273
to Develop the address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products (goods) of Predstavitelstvo GlaksoSmitKlyayn Export Ltd
Additional information
| Ingredient |
|---|



















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.