Description
The instruction for medical use
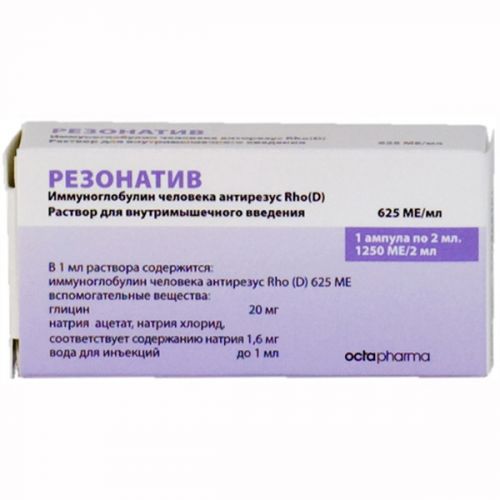
of RezonativTM Lekarstvennaya medicine a form
Solution for intramuscular injections 625ME/ml
Structure
of 1 ml of solution contains
active agent – Anti-D immunoglobulin human 625ME (125 mkg), equivalent to the general protein content of 165 mg (immunoglobulin G not less than 95%),
excipients: glycine of 20 mg, sodium chloride and sodium acetate in terms of sodium of 1.6 mg, mkg polysorbate 80 30, water for injections up to 1 ml.
The description
Transparent or slightly opalescent solution from pale yellow till light brown color. In the course of storage the small turbidity or a small amount of solid particles can appear.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Immunoglobulins specific. Immunoglobulin of anti-D
(Rh)
the ATX J06BB01 Code
the Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Measured properties the level of antibodies is reached approximately in 20 minutes after intramuscular introduction. The maximum serumal concentration of antibodies is reached in 2-3 days. Biological half-life at persons with the normal IgG level makes from 3 to 4 weeks. This elimination half-life can differ at each patient.
IgG and IgG-complexes collapse in cells of a reticuloendothelial system.
The pharmacodynamics
of Anti-D immunoglobulin contains specific antibodies (IgG) against the D (Rh) antigen of erythrocytes of the person.
During pregnancy, especially during childbirth, erythrocytes of Rh-positive blood of a fruit can get to blood circulation of mother and cause isoimmunization in a Rh-negative organism of the woman. Passive immunization of anti-D immunoglobulin prevents Rh (D) – immunization in more than 99% of cases provided that the sufficient dose of anti-D of immunoglobulin soon after penetration of Rh (D) – positive embryonic erythrocytes is entered.
Indications
– preventive Rh(D) immunization of women with negative Rh(D):
– antenatal prevention
– planned antenatal prevention
– antenatal prevention of the subsequent complications of pregnancy,
including abortions/threats of an abortion, an extrauterine pregnancy or a chorioadenoma, intrauterine death of a fruit, transplantsentarny hemorrhages as a result of prenatal hemorrhages, amniocentesis, a chorionic biopsy or obstetric manipulations, for example at external obstetric version, invasive interventions, a kordotsenteza, a stupid injury of a stomach
– post-natal prevention at the birth a Rhesus factor of the positive child.
– treatment of persons with a negative Rhesus factor of Rh (D) after the transfusion of incompatible Rh-positive blood or other blood preparations containing platelet concentrate.
The route of administration and doses
Before use drug should be warmed to body temperature or room temperature. Solution has to be transparent or slightly opalescent, colourless or with pale yellow or light brown coloring.
It is impossible to use muddy solution or solution with not dissolved particles.
Rezonativ it is necessary to enter intramusculary. If high doses are required (for children & gt, 2 ml or & gt, 5 ml for adults), then it is recommended to divide doses and to enter into different places. At hemorrhagic disturbances when contraindicated intramuscular introduction, it is recommended to enter rezonativ subcutaneously. After an injection it is careful to press the place of an injection.
Any unused drug or waste should be utilized according to requirements.
Doses
Anti-D of immunoglobulin define the Dose from calculation that 1 ml of Rh-positive blood is neutralized by about 10 mkg (50ME) Anti-D of immunoglobulin.
Preventive Rh(D) immunization of women with negative Rh(D):
– antenatal prevention: the recommended doses make 50-330 mkg or 250-1650 ME.
– planned antenatal prevention: a single dose of 250 mkg or 1250 ME on 28-30 week of pregnancy or two doses on 28 and 34 weeks of pregnancy
Antenatal prevention of the subsequent complications of pregnancy:
– up to 12 weeks of pregnancy a single dose make 125 mkg or 625 ME
– after 12 weeks of pregnancy – 250 mkg or 1250 ME, the drug is recommended to be administered within 72 hours and if there is a need to repeat in 6-12 weeks of pregnancy
– after amniocentesis or a chorionic biopsy it is recommended to enter once 250 mkg or 1250 ME.
Post-natal prevention: according to the general managements now the entered doses vary between 100-300 mkg or 500-1500ME.
In case of introduction of low doses (100 mkg or 500 ME) it is necessary to control bleeding degree at a fruit and mother.
Standard dose: 1250 ME (250 mkg).
During the post-natal period the drug should be administered mothers as soon as possible within 72 hours after the birth of the Rh-positive child. If there passed more than 72 hours, it is not necessary to refuse administration of drug and it is recommended to enter as soon as it becomes possible.
In the post-natal period the recommended doses have to be entered even if in blood serum of mother the residual activity after introduction of antenatal doses of drug is noted.
In case of suspicion of massive bleeding at a fruit and mother (& gt, 4 ml (0.7%-0.8% of women)), for example, in anemia at the fruit/newborn or intrauterine death of a fruit, its degree it is necessary to determine by the corresponding methods, for example, the Kleykhauyera-Betke test eluating by acid for definition of fetal HbF or method of a flowing tsitometriya which specially identifies Rh-positive Rh D of a cell. In this case, additional doses of anti-D immunoglobulin should be entered at the rate of 10 mkg or 50ME on 0.5 ml of erythrocytes of fetal blood.
After incompatible blood transfusion
the Recommended dose makes 20 mkg (100ME) of anti-D immunoglobulin on 2 ml of the blood transfused to Rh-positive Rh D or 1 ml of a packed red cells (RBC). Necessary doses should be defined as a result of consultation with the specialist in a hemotransfusion. Control tests for definition of erythrocytes of Rh-positive blood should be carried out each 48 h and further to enter anti-D immunoglobulin before full neutralization of all Rh-positive erythrocytes. In case of transfusion of large volumes of Rh-positive blood of more than 300 ml the maximum dose of 3000 mkg is sufficient (15000ME).
For fast achievement of adequate plasma levels use of alternative drugs for intravenous administration is recommended. In case of lack of drugs for intravenous administration, it is necessary to enter intramusculary high doses within several days.
Side effects
– in the injection site can be observed local pain and morbidity, it can be prevented, fractional introduction of a high dose
fever, an indisposition, a headache, skin reactions and a fever develop in different sites infrequently –
– it is rare
– nausea, vomiting, hypotension, tachycardia
– the allergic or anaphylactic reactions including dispny and shock
–
the Contraindication arthralgia
– hypersensitivity to active agents or to any of excipients.
Medicinal interactions
Live attenuirovanny virus vaccines
Active immunization by live virus vaccines (for example measles, a mumps or a rubella) has to be postponed for 3 months after the last introduction of anti-D of immunoglobulin as the efficiency of live virus vaccine can decrease. If there is a need of introduction of anti-D of immunoglobulin within 2-4 weeks after an inoculation of live virus vaccine, then it is necessary to consider that it will lead to decrease in efficiency of vaccination.
Influence on results of serological tests
After administration of immunoglobulin in blood of the patient antibodies of various passively transferred antigens which can yield false positive results of serological tests can tranzitorno raise. Antibodies of passively transferred erythrocyte antigens, for example A, B, D can affect results of some serological researches on antibodies to erythrocytes, for example the antiglobulinovy test (Koombs’s reaction), in particular at Rh (D) of Rh-positive newborns which mothers received antenatal prevention.
Special indications
of Rezonativ cannot be entered intravenously (because of risk of development of shock). Administration of drug needs to be carried out intramusculary, before administration of drug the piston of the syringe needs to be pulled slightly on itself to be convinced that a needle not to be in a vessel gleam.
Rezonativ newborns cannot enter. Drug is not intended for use at Rh-positive persons and also for immunization to Rh (D) to antigen.
When using after the delivery Rezonativ enter to mothers.
After administration of drug it is necessary to watch patients within, at least, 20 minutes, and at least one hour at accidental intravenous administration of drug in a vein.
In rare instances including at patients with resistance to the carried-out therapy by human immunoglobulin, anaphylactoid reactions in the form of a lowering of arterial pressure can develop to human anti-D to immunoglobulin.
At development of symptoms of an allergy or anaphylactoid type of reactions it is required to stop administration of drug immediately.
True reactions of hypersensitivity are rare, but allergic reactions to anti-D to immunoglobulin can develop. Patsiyentov it is necessary to inform on precursory symptoms of reactions of hypersensitivity, including urticaria, generalized rash, constraint in breasts, goose breathing, hypotension and an anaphylaxis. Treatment depends by nature and weights of side effect. In case of development of shock it is necessary to adhere firmly to the standards of treatment of shock adopted now.
Immunoglobulin A content in Rezonativa is small. Though anti-D immunoglobulin was successfully used for treatment of patients with some types of insufficiency of IGA, the attending physician has to compare advantage of administration of drug and possible risk of development of reactions of hypersensitivity. At persons with insufficiency of IGA antibodies to IgA can be developed and arise anaphylactic reactions after introduction of the components of blood supporting IgA. At the patients receiving high doses of anti-D of immunoglobulin as a result of incompatible blood transfusion have to make clinical and laboratory observation because of risk of hemolytic reactions.
Standard actions for prevention of infectious diseases when using the medicines produced from blood or plasma of the person include selection of donors, screening assay of the individual and integrated doses of the handed-over plasma on specific markers of an infection and implementation of the production phases directed to inactivation/removal of viruses. Despite this, at use of medicines from human blood or plasma, it is impossible to exclude a possibility of transfer of infectious agents completely. It also to treat unknown or again formed viruses and other pathogenic agents. The carried-out measures are effective for viruses with a HIV, HBV and HCV cover, and viruses without HAV cover. The taken measures can have limited action on viruses without cover like parvovirus B19. There is an encouraging clinical experience in the relation of lack of transfer of causative agents of a viral hepatitis And yes B19 parvovirus together with immunoglobulins, it is also considered that the maintenance of antibodies makes an important contribution to ensuring virus safety. It is strongly recommended at each introduction Rezonativa to the patient to register the name and the lot number of drug to keep communication between the patient and a consignment of drug.
Drug contains less than 1 mm of sodium (23 mg) in a single dose (5 ml), that is it is considered without sodium.
Any not used part of drug or waste should be destroyed according to requirements.
Pregnancy and a lactation
of Rezonativ it is intended for use at pregnancy.
The feature of influence of medicine on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms
does not affect ability to run transport and mechanisms
the Overdose
Is not present any available data on overdose. At the patients receiving high doses of anti-D of immunoglobulin as a result of incompatible blood transfusion have to make clinical and laboratory observation because of risk of hemolytic reactions.
At Rh-negative Rh (D) of persons the overdose should not lead to increase in frequency of side reactions or more serious side reactions, in comparison, with introduction of a usual dose.
A form of release and packing
On 625 ME/1.0 ml of drug in ampoules from colourless glass.
Solution for intramuscular injections 625ME/ml of 1 ml in ampoule No. 1.
Solution for intramuscular injections 625ME/ml2ml (1250 ME) in ampoule No. 1.
Solution for intramuscular injections 625ME/ml of 2 ml (1250 ME) in ampoule No. 10.
On one or 10 ampoules place in a box of cardboard together with the instruction for use in the state and Russian languages.
To Store storage conditions in the place protected from light at a temperature from +2 to +8.
Not to freeze!
In the period of an expiration date drug can be stored at a temperature not over 250C up to 1st month, at the same time it is not necessary to store it in the fridge again and if after this period drug was not used it it is necessary to destroy.
To store out of children’s reach!
The period of storage
of 30 months
Solution after opening of an ampoule has to be used immediately.
After expiry date not to use.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
the Producer Octapharma AB SE-112 75 Stockholm, Sweden Address of the Organization, the accepting claim on quality of drug in the territory of Kazakhstan
Predstavitelstvo Oktafarm AG in RK, Almaty, Dostyk Ave. 180, office 42.
Phone number +7 727 3201542, fax +7 727 3201541, e-mail address:
To Develop svetlana.safarova@octapharma.com





















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.