Description
The instruction for medical use
of Nakom® medicine
the Trade name
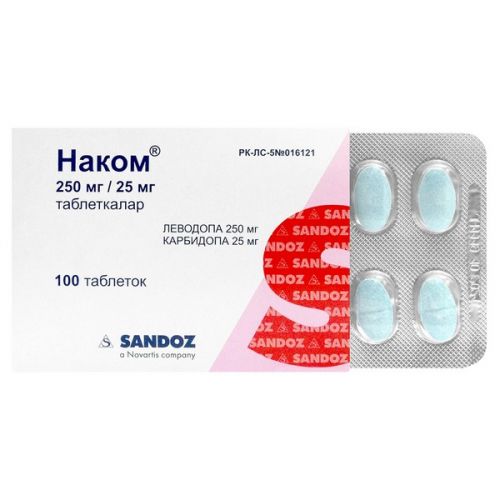
of Nakom®
the International unlicensed name
Is not present
the Dosage form
of the Tablet of 250 mg / 25 mg
Structure
One tablet contains
active agents: a levodopa of 250 mg, karbidopa monohydrate of 27 mg
(25 mg of a karbidopa are equivalent),
excipients: starch prezhelatinirovanny, starch corn, indigo carmine (E 132), cellulose microcrystalline, painted in blue color, magnesium stearate.
The description
of the Tablet of an oval form, with a biconvex surface, blue color, with impregnations, with risky on one party.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antiparkinsonichesky drugs. Dopaminergic drugs. Top and its derivatives. Levodopa + karbidopa.
ATX N04BA02 code
Pharmacological
Pharmacokinetics Levodopa properties. The levodopa is quickly soaked up from digestive tract and actively metabolized. In spite of the fact that, more than 30 various metabolites are formed, generally the levodopa will be transformed to dopamine, adrenaline, noradrenaline, and, after all, to dihydroxyphenyl – acetsilt acid, gomovanilinovy acid and vanil-mandelic acid, also at 3-0 to Methyldopum, present at plasma and cerebrospinal liquid and which value is not known.
After intake on an empty stomach of a single dose of a levodopa by patients with Parkinson’s disease, time of achievement of peak concentration is 0.5-2 hours and keeps at the therapeutic level within 4-6 hours. At peak level, 30% of a levodopa 15% in dopamine and 10% in a top will be transformed to catecholamines. Metabolites are quickly excreted with urine, within two hours about 1/3 doses are removed. From 80 to 90% of metabolites in urine are fenilkarboksilovy acids, mainly gomovanilinovy acid. In 24 hours of 1-2% makes dopamine, and less than 1% – adrenaline, noradrenaline and not changed levodopa.
Elimination half-life (T ½) levodopas in blood plasma makes about 50 minutes. At joint reception of a karbidopa and levodopa, ½ last are extended with T approximately till 1.5 o’clock.
Karbidopa. After intake of a single dose of a karbidopa healthy faces and patients with Parkinson’s disease, time of achievement of peak concentration made 2-4 hours at healthy faces and 1.5-5 hours at patients with Parkinson’s disease. Removal of drug with urine and a stake approximately equally in both groups. Excretion with urine of not changed drug generally comes to the end within 7 hours and is 35%. After this term, metabolites among which there are 14 alpha % methyl-3-metoksi-4-hydroksifenilpropionovaya acid and 10% alpha methyl-3.4-digidroksifenilpropionovaya acid are allocated. In smaller quantities two other metabolites are found. One of them is identified as 3.4-dihydroxyphenyl-acetone, another – is conditional as N-methyl-karbidopa. The maintenance of each of these substances makes less than 5% of total number of metabolites. In urine not changed karbidopa is also found. Conjugates were not found.
Influence of a karbidopa on metabolism of a levodopa. Karbidopa increases concentration of a levodopa in blood plasma. At the previous reception of a karbidopa the concentration of a levodopa in blood plasma increases approximately by 5 times, and time of maintenance of therapeutic concentration in plasma increases from 4 to 8 hours. At a concomitant use of a karbidopa and a levodopa similar results were received.
At reception of a single dose of a levodopa by patients with Parkinson’s disease who accepted previously a karbidopa semi-removal time for a levodopa increased from 3 to 15 hours.
Concentration of a levodopa increases at the expense of a karbidopa at least by 3 times.
Concentration of dopamine and gomovanilinovy acid in blood plasma and in urine decreases at preliminary reception of a karbidopa.
A pharmacodynamics
of Nakom® – the combined protivoparkinsonichesky drug, the containing metabolic predecessor of dopamine – a levodopa and inhibitor of a peripheral dofa-decarboxylase – to a karbidop.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are connected with exhaustion of dopamine in a corpus striatum of a brain. The levodopa, the metabolic predecessor of dopamine, strengthens dofaminergichesky transfer and weakens symptoms due to transformation it in dopamine by decarboxylation in a head brain.
After introduction inside, the levodopa quickly is decarboxylized and turns into dopamine in peripheral fabrics, and only a small amount of not changed levodopa reaches the central nervous system. Thus, high doses of a levodopa with frequent intervals, for adequate medical action are required. The dopamine formed in peripheral fabrics does not participate in implementation of protivoparkinsonichesky effect of a levodopa (does not get into central nervous system) and otvetstven for the majority of its side effects.
Karbidopa who does not get through a blood-brain barrier inhibits extra brain decarboxylation of a levodopa that increases quantity of the levodopa coming to a brain and its transformation into dopamine. As the action of a karbidopa inhibiting a decarboxylase takes place only in peripheral fabrics, use of a karbidopa together with a levodopa makes it more available to receipt in a brain.
After joint reception of a karbidopa and a levodopa, levodopa level in plasma was considerably increased in comparison with that which was observed at introduction of the same doses only of a levodopa while levels of dopamine and gomovanilinovy acid, two main metabolites of a levodopa, were considerably reduced.
At intake of a pyridoxine of a hydrochloride (B6 vitamin), in doses from 10 mg to 25 mg, fast suppression of antiparkinsonichesky effects of a levodopa was noted. Karbidopa prevents this action of a pyridoxine. In a research during which patients accepted from 100 to 500 mg of a pyridoxine a day along with karbidopy and a levodopa, suppression of therapeutic effect was not registered.
The beginning of effect of drug when using usual doses
Therapeutic effect of drug is shown on the same day, sometimes after one dose. The full effective dose of drug is reached for 7 days in comparison with weeks and months of use of a levodopa separately.
Karbidopa who is a part of the drug Nakom® does not reduce the side reactions connected with the central effects of a levodopa. At receipt of bigger quantity of a levodopa in a brain, in particular, in case of lack of such dozolimitiruyushchy factors as nausea and vomiting, are possible certain undesirable influences on central nervous system, for example, dyskinesia (at lower doses quicker during therapy by the drug Nakom® in comparison with a levodopa).
Наком® renders more significant therapeutic effect in comparison with a levodopa, provides long maintenance of therapeutic concentration of a levodopa in plasma at doses which are about 80% lower than those which are required in case of use of one levodopa.
Indications
– Parkinson’s disease
– parkinsonism syndrome
the Route of administration and doses
the Optimum daily dose of the drug Nakom® has to be defined by careful selection for each patient. Tablets contain a karbidopa and a levodopa in the ratio 1:10.
General provisions
in the course of treatment the correction of individually picked up dose and frequency of administration of drug can be required. Researches show that the peripheral dofa-decarboxylase is saturated karbidopy at reception of the last in a dose about 70 – 100 mg a day. The patients receiving smaller quantity of a karbidopa can feel nausea and vomiting.
In case of prescribing of the drug Nakom® the intake of standard drugs for treatment of parkinsonism, except for those which contain one levodopa can be continued, at the same time their doses have to be picked up anew.
The usual initial dose
the Dose is selected the doctor individually according to reaction of the patient to treatment. The initial dose of drug makes ½ tablets, 1 or 2 times a day. However, such dosage can not provide optimum quantity of a karbidopa which is required to the patient. Therefore, ½ tablets or every other day before achievement of optimum effect are in case of need added every day. The effect is observed in the first day, and sometimes – after reception of the first dose. The full effect of drug is reached in terms up to seven days in comparison with weeks and months in case of monotherapy using a levodopa.
The translation of the patients treated by a levodopa
As both therapeutic, and side effects arise quicker at use of the combined drug Nakom® than a levodopa, during selection of a dose for patients the careful observation is necessary. In particular, Nakom® more often than the levodopa, causes involuntary movements. Their emergence can demand reduction of a dose of the drug Nakom®. The nictitating spasm can be precursory symptom of an excess dose at some patients.
Reception of a levodopa has to be stopped at least in 12 hours prior to the Nakom® drug treatment (in 24 hours – in case of use of drugs of a levodopa of the prolonged action). The daily dose of the drug Nakom® has to provide about 20% of the previous daily dose of a levodopa.
The recommended initial dose for most of the patients accepting more than 1500 mg of a levodopa makes one tablet of drug Наком® 3 or 4 of time a day.
Maintenance therapy
Treatment has to be individual and is picked up so that to receive desirable result from the carried-out therapy. For the purpose of optimum inhibition of extra brain decarboxylation of a levodopa not less than 70-100 mg of a karbidopa a day have to be applied.
If necessary the dose of the drug Nakom® can be increased by ½ tablets or 1 tablet every day or every other day before achievement of the maximum dose – 8 tablets a day. Experience of use of a daily dose of the karbidopa exceeding 200 mg is limited.
The maximum recommended dose
the Maximum recommended dose makes 8 tablets of the drug Nakom® a day (200 mg of a karbidopa and 2 g of a levodopa). It makes 3 mg/kg of a karbidopa and 30 mg/kg of a levodopa at the body weight of the patient of 70 kg.
Use for children
Safety and efficiency of use of the drug Nakom® for children of younger and middle age is not established, and its use for treatment of children aged up to 18 years is not recommended.
Side effects
the Side effects arising at drug use are connected with the central neuropharmacological effect of dopamine. These reactions can be usually reduced by decrease in a dosage. Among the most widespread undesirable effects the dyskinesia, including horeopodobny, dystonic and other involuntary movements and also nausea is noted. Precursory symptoms on the basis of which the decision on a dose decline can be made are muscular twitchings and a nictitating spasm.
The list of side effects is provided according to manifestation frequency. According to the frequency of the cases described as: very often (≥1/10), it is frequent (≥1/100 to & lt, 1/10), is not frequent (≥1/1000 to & lt, 1/100), is rare (≥1/10000 to & lt, 1/1000), is very rare (& lt, 1/10000) and unknown frequency (which frequency cannot be determined on the basis of the available data).
Very often (& gt, 1/10)
– dyskinesia (including a chorea), dystonia
Often (& gt, 1/100 and & lt, 1/10)
– anorexia
– a sleep disorder, hallucinations, a depression with or without suicide trends, confusion of consciousness
– bradikiniya episodes (“on-off” – a syndrome), dizziness / vertigo, paresthesia, drowsiness, including very rare day somnolention and attacks of sudden backfilling
– heartbeat
– orthostatic effects, including attacks of arterial hypotension
– dispnoe
– diarrhea, vomiting
– a stethalgia
Infrequently (& gt, 1/1000 and & lt, 1/100)
– excitement
– faints
– a small tortoiseshell
– muscular spasms
Seldom (& gt, 1/10000 and & lt, 1/1000)
– an agranulocytosis, a leukopenia, anemia (hemolytic and not hemolytic), thrombocytopenia
– a Quincke’s disease
– episodes of psychotic states (including nonsense and paranoid thinking), increase in a libido
– pathological passion, the raised libido, hyper sexuality, especially at use of drug in high doses (these manifestations disappeared at a dose decline or the termination of therapy by drug)
– dementia, spasms
– dysfunctions of heart
– arterial hypertension, phlebitis
– gastrointestinal bleedings, development of an ulcer of a duodenum, saliva darkening
– a skin itching, Shenleyn-Genokh’s disease, an alopecia, rash, darkening of a secretion of sweat glands
– darkening of urine
of Unknown frequency
– a malignant melanoma
– reduction or increase in body weight, hypostases
– feeling of alarm, a disorientation, euphoria, insomnia, a bruxism
– an ataxy, strengthening of a tremor of hands, extrapyramidal and motive disturbances, a headache, decrease in cogitative activity, activation of the hidden syndrome of Bernard-Horner, numbness, faints, falling, disturbance of gait, okulogirny crises (spasms of external muscles of eyes of an eyeball), the excited state, a lockjaw
– a nictitating spasm, illegibility of sight, expansion of pupils, a diplopia
– ‘inflows’ of blood to face skin, hyperaemia
– hoarseness, breath disturbance
– dryness in a mouth, salivation, a dysphagy, pain and feeling of discomfort in a stomach, a constipation, a meteorism, dyspepsia, burning sensation of language, feeling of bitterness in a mouth, an eructation, nausea
– the increased sweating
– twitching of muscles
– urine incontinence, an urination delay
– a priapism
– an asthenia, hypostasis, fatigue, an indisposition, a malignant antipsychotic syndrome, weakness
– increase in activity of alkaline phosphatase, nuclear heating plant, ALT, lactate dehydrogenase, increase in content of bilirubin, uric acid, urea nitrogen in plasma, increase in content of serumal creatinine, a hyperuricemia, positive test of Koombs, decrease in hemoglobin and a hematocrit, a hyperglycemia, a leukocytosis, a bacteriuria, an erythrocyturia
the Drugs containing a karbidopa and a levodopa can cause false positive reaction to ketone bodies in urine if for definition of a ketonuria test strips are used. This reaction will not change after boiling of tests of urine. False-negative results can be received when using a glyukozooksidazny method of definition of a glucosuria.
Contraindications
– hypersensitivity to active agent or any of excipients
– a concomitant use of non-selective inhibitors of a monoaminooxidase (MAO)
– closed-angle glaucoma
– a melanoma or presence of a melanoma in the anamnesis
– skin diseases of an unknown etiology
– pregnancy and the period of a lactation
– children’s and teenage age up to 18 years
– a heavy renal and liver failure
Medicinal interactions
It is necessary to be careful at simultaneous use of the drug Nakom® and the following medicines:
Antihypertensive drugs
At the patients receiving some antihypertensives, addition of the drug Nakom® caused symptomatic orthostatic hypotension. Therefore, in an initiation of treatment the drug Nakom® correction of a dose of hypotensive drug can be required.
Antidepressants
Were available the separate messages about side reactions including increase in the ABP and dyskinesia in case of the combined use of tricyclic antidepressants and the drug Nakom®.
Non-selective inhibitors of a monoaminooxidase (MAO)
Intake of these drugs has to be finished, at least, in two weeks prior to the Nakom® drug treatment.
Iron preparations
the Bioavailability of a karbidopa and/or levodopa decreases at simultaneous use of iron of sulfate or iron of a gluconate.
Other medicines
Antagonists of D2 of receptors of dopamine (for example, fenotiazina, phenyl propyl ketones and risperidon) and also an isoniazid can reduce therapeutic effect of a levodopa. There are messages about blocking of positive therapeutic impact of a levodopa in Parkinson’s disease as a result of intake of Phenytoinum and a papaverine. For the patients taking this medicine along with the drug Nakom® the careful observation for early detection of decrease in therapeutic action is required.
At simultaneous use of the drug Nakom® with selegiliny – development of heavy orthostatic hypotension is possible.
At some patients who are on a high-protein diet the absorption of a levodopa as the levodopa competes with some amino acids can be broken.
The special
instructions Nakom® it is not recommended for treatment of the extrapyramidal disorders caused by medicines.
Drug can be appointed to the patients who are already receiving the drugs containing only a levodopa, however reception of a levodopa has to be stopped, at least, in 12 hours prior to the Nakom® drug treatment. The daily dose of the drug Nakom® has to provide about 20% of the previous daily dose of a levodopa.
A melanoma
Epidemiological researches showed that patients with Parkinson’s disease are more subject to risk (about 2 – 6 times more often) of development of a melanoma, in comparison with the general population. It is unknown whether the increased risk is connected with Parkinson’s disease or other factors, such as medicines which are applied to treatment of this disease.
For the reasons stated above, patients and their trustees are regularly recommended to do survey of patients for detection of melanomas (at the Nakom® drug treatment), periodically these inspections of skin have to be performed by qualified specialists (for example, dermatologists).
Disturbances of pulse control
during the Nakom® drug treatment the regular monitoring of patients concerning development of disturbances of pulse control has to be carried out.
During the Nakom® drug treatment the patients have to be controlled regularly regarding development of disorders of control over motives. Patients and their trustees need to be informed on possible symptoms of disturbances of pulse control (for example, a game addiction, hyper sexuality, the raised libido, compulsive expenses or purchases, consumption binge/overeating) which were registered at the patients receiving agonists of dopamine and/or other dofaminergichesky treatment using the drugs containing a levodopa, including Nakom®. At development of such symptoms it is recommended to correct treatment.
At the patients accepting earlier a levodopa the dyskinesia since the karbidopa allows bigger quantity of a levodopa to reach a brain, and thus can be observed, a large amount of dopamine is formed. Appearance of dyskinesia can demand a dose decline.
As well as the levodopa, Nakom® can cause involuntary movements and mental disorders. It is supposed that these reactions are caused by increase in content of dopamine in a brain. These phenomena can demand a dose decline. All patients accepting Nakom® have to be under observation in connection with a possibility of development of a depression with suicide trends. Patients at whom psychoses were observed demand careful approach at therapy selection.
It is necessary to observe precautionary measures at co-administration of psychotropic medicines and the drug Nakom® (you watch the section “Medicinal Interactions”).
At treatment of Parkinson’s disease, dopamine agonists, including a combination a levodopa / karbidopa, observed pathological gambling, the increased sexuality and increase in a libido.
Наком® patients should appoint with care with a serious illness of a cardiovascular system and lungs, with bronchial asthma, spasms in the anamnesis, with diseases of kidneys, a liver and an endocrine system or having a peptic ulcer of a stomach and duodenum in the anamnesis (because of a possibility of bleeding in an upper part of digestive tract).
As well as in cases of use of a levodopa, when prescribing the drug Nakom® the patients who had a myocardial infarction and having atrial, nodal or ventricular arrhythmias need careful preliminary survey. At such patients the observation of warm activity, with special care is necessary – when assigning the first dose and during selection of doses.
Patients with an open angle glaucoma should appoint drug with care and provided that intraocular pressure is constantly controlled during treatment.
At sudden cancellation of antiparkinsonichesky drugs the symptom complex reminding the malignant antipsychotic syndrome including muscular rigidity, fervescence, mental disturbances and increase of concentration of a serumal kreatinfosfokinaza was described. Therefore careful inspection of patients in the period of a sharp dose decline of the drug Nakom® or its cancellation, in particular, is necessary if the patient receives neuroleptics.
At reception of a levodopa such undesirable phenomena as drowsiness and cases of backfilling were noted. Messages about sudden immersion in a dream during daily activity, in certain cases without understanding or the warning signs, arrived extremely seldom. Patients need to be informed on it and not to recommend driving or operation of potentially dangerous mechanisms during treatment by a levodopa.
As well as in a case with a levodopa, during long-term treatment the drug Nakom® recommends periodic control of function of a liver, the haematogenic, cardiovascular system and kidneys.
If the general anesthesia is required, then the drug Nakom® can be taken until oral input of the fluid and drugs is authorized to the patient.
If treatment is temporarily interrupted, then administration of drug of Nakom® can be resumed in a usual dosage as soon as the patient is able to take the drug orally.
Pregnancy and the period of a lactation
Drug is not appointed at pregnancy.
It is unknown whether the karbidopa with maternal milk is allocated. There is one message about excretion of a levodopa with breast milk for the nursing mother with Parkinson’s disease.
In need of prescribing of drug the woman in the period of a lactation needs to resolve an issue concerning expediency of the termination of feeding by a breast or drug treatment.
The feature of influence of medicine on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms
is not recommended to be engaged in the activity demanding concentration of attention and management of vehicles and moving mechanisms in connection with possible drowsiness and episodes of unexpected backfilling.
Overdose
Symptoms: strengthening of side effects.
Treatment: symptomatic (as well as at overdose of a levodopa), however the pyridoxine is inefficient for neutralization of effect of drug. Control of the ECG, in case of need — performing antiarrhytmic therapy is necessary.
It is necessary to consider a possibility that the patient applied as well other drugs. There are no data on use of dialysis.
The form of release and packing
On 10 tablets place in blister strip packaging from a film of polyvinylchloride and aluminum foil.
On 10 blister strip packagings together with the instruction for medical use in the state and Russian languages place in a pack from cardboard.
To Store storage conditions at a temperature not above 25 °C in the dry, protected from light place.
To store out of children’s reach!
3 years
not to use a period of storage after the expiry date specified on packing.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
the Producer/packer Lek Pharmasyyutikals of of, Slovenia
Verovskova 57, Ljubljana, Slovenia.
Owner of the registration certificate
Lek Pharmasyyutikals of of, Slovenia
Verovskova 57, Ljubljana, Slovenia.
The address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products (goods) Representative office of JSC Sandoz Pharmasyyutikals d. d. in Republic of Kazakhstan Almaty, Luganskogo St. 96, the Phone number – 258 10 48, fax: +7 727 258 10 47 e-mail-mail
to Develop

















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.