- You cannot add "25 mg hydrochlorothiazide (20 tablets)" to the cart because the product is out of stock.
Description
The instruction for medical use
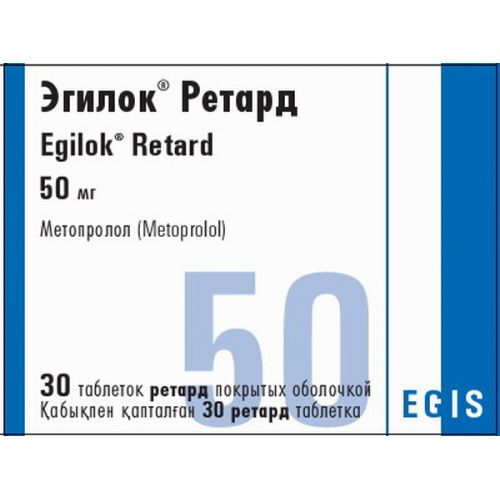
of EGILOK RETARD medicine
the Trade name
Egilok Retard
Mezhdunarodnoye the unlicensed
name Metoprolol Lekarstvennaya
the Tablet form retard, coated, 50 mg, 100 mg
Structure
One tablet contains
active agent – a metoprolol tartrate of 50 mg, 100 mg,
excipients: sugar balls, macrogoal 6000, talc, ethyl cellulose, triethyl citrate, hydroxypropyl cellulose, magnesium stearate, cellulose microcrystalline, silicon dioxide colloidal anhydrous,
structure of a cover: gipromelloza, titan E 171 dioxide, talc, macrogoal 6000.
The description
of the Tablet of oblong shape, with a biconvex surface, coated white or almost white color, with risky on both parties (for a dosage of 50 mg and 100 mg)
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Drugs for treatment of diseases of a cardiovascular system. Selection beta blockers. Metoprolol.
The ATX C07A B02 code
the Pharmacological
Metoprolol Pharmacokinetics properties is quickly and almost completely soaked up from digestive tract (about 95% of the dose accepted inside), however further metoprolol is exposed to considerable presistemny metabolism. The bioavailability is about 35%. Owing to metabolism by polymorphic enzymes, concentration of a metoprolol in blood plasma is subject to considerable individual fluctuations (about 17 times can differ). The curve of dependence of concentration in blood plasma from time has the features characteristic of drugs of the slowed-down release. For 4-6 hours after administration of drug the phase of slow absorption passes into approximately 6-hour plateau (Cmax = 37.4 ng/ml after introduction of a single dose and 54.7 ng/ml in a condition of dynamic equilibrium) then concentration in plasma begins to decrease slowly. The average seeming elimination half-life (t1/2) makes 6-12 hours that is much higher, than own elimination half-life of a metoprolol (about 3 hours). Longer elimination half-life can be explained with the slowed-down absorption (pharmacokinetics like flip-flop). Linking with proteins of blood plasma of 10%. Metoprolol is widely distributed in fabrics and has the high volume of distribution (5.5 l/kg). Metoprolol is metabolized in a liver by enzymes of R-450 cytochrome. Metabolites (O-dezmetilmetoprolol and a-hydroksimetoprolol) have no clinical value and are removed with bile. The bioavailability of a metoprolol can increase in cirrhosis. About 95% of the dose of drug accepted inside are brought by kidneys, out of them about 10% in not changed look. The renal failure does not affect system bioavailability and removal of a metoprolol, however decrease in excretion of metabolites can be observed.
Linearity/nonlinearity of pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics of a metoprolol linear at increase in a dose to 800 mg. At repeated introduction the area under curve (AUC) increases approximately by 20%.
Children and teenagers
the Pharmacokinetic profile of a metoprolol at children and teenagers with arterial hypertension aged from 6 up to 17 years is similar to a profile of adults. The seeming oral clearance (CL/F) linearly increases with body weight.
A pharmacodynamics
Egilok Retard – the cardioselective lipophilic 1 adrenoblocker which does not have internal sympathomimetic or membrane stabilizing activity. Egilok Retard interferes with the stimulating influence of sympathetic nervous system on heart and causes fast decrease in frequency of a warm rhythm and warm emission.
In arterial hypertension metoprolol reduces arterial blood pressure at patients at a physical tension and at rest. The long-term antihypertensive effect of drug is connected with gradual decrease in the general peripheric vascular resistance. Prolonged use of drug in arterial hypertension leads to statistically reliable decrease in mass of a left ventricle and improvement of its diastolic function.
Metoprolol reduces activity of renin of plasma, both at short, and at prolonged use. This effect somewhat can be explained with blocking of renal b1-receptors that leads to decrease in products of renin and corresponding decrease in the vasoconstriction mediated by angiotensin.
Metoprolol reduces the need of a myocardium for oxygen due to reduction of frequency and force of warm reductions, decrease in system arterial blood pressure. Reducing heart rate and respectively extending a diastole, metoprolol improves blood supply and oxygenation of ischemic areas of a myocardium. Thus, drug reduces the frequency, duration and weight of attacks of stenocardia and asymptomatic manifestations of ischemia, and also increases physical effeciency of patients.
Use of drug in the postinfarction period reduces possibility of a recurrence of a myocardial infarction.
In therapeutic doses the peripheral vasopressor and bronkho-konstriktorny effects of a metoprolol are less significant, than such effects non-selective – adrenoblockers.
In comparison with non-selective – adrenoblockers metoprolol influences products of insulin and carbohydrate metabolism less. To a lesser extent influences activity of a cardiovascular system in the conditions of a hypoglycemia and does not increase duration of attacks of a hypoglycemia.
Indications
– arterial hypertension (as monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive drugs), reduces cardiovascular and coronary diseases mortality (including the frequency of sudden death) at patients with hypertensia
– chronic stable stenocardia (as monotherapy or in combination with other anti-anginal means)
– secondary prevention after a myocardial infarction (maintenance therapy)
– chronic heart failure in compensation stage as auxiliary therapy to the main treatment of heart failure
– prevention of disturbance of a warm rhythm (the supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular premature ventricular contraction caused by an inborn syndrome of the extended QT interval)
– the functional cardiac disturbances which are followed by strong heartbeat
– prevention of attacks of migraine
the Route of administration and doses
the Daily dose of drug are recommended to be accepted once a day, in the morning, without chewing, with a small amount of water. A pill Egilok retard can be taken irrespective of meal including at meal time.
In need of a tablet it is possible to halve.
The dose is selected individually in order to avoid excessive bradycardia.
In arterial hypertension the recommended initial dose of 50 mg once a day. At insufficient clinical performance the daily dose can be raised to 100 mg or 200 mg, or to apply Egilok Retard in a combination with other antihypertensive drugs.
In stenocardia the recommended initial dose of 50 mg once a day. At insufficient clinical performance the daily dose can be raised to 100 mg or 200 mg, or to apply Egilok Retard in a combination with other anti-anginal drugs.
Maintenance therapy after a myocardial infarction: the recommended dose – 200 mg once a day.
Chronic heart failure in compensation stage:
To patients with the heart failure stabilized by means of other drugs (i.e. without episodes of exacerbation of heart failure within the last 6 weeks against the background of the main therapy, without its changes within, at least, last 2 weeks), a dose Egilok retard is selected individually.
In heart failure of functional class II on classification of NYHA, the recommended initial dose of drug within the first 2 weeks makes 25 mg once a day. In two weeks the daily dose can be raised to 50 mg once a day, then in two weeks up to 100 mg once a day and two more weeks later to 200 mg once a day.
In heart failure of functional class III-IV on classification of NYHA, the recommended initial dose within the first 2 weeks makes 12.5 mg once a day. In two weeks the daily dose can be raised to 25 mg once a day, then every two weeks a daily dose it is possible to double before achievement of a dose 200 mg once a day. At long-term treatment the maximum dose Egilok retard – 200 mg once a day.
In terms of shipping of doses, the condition of patients after each new dose should be estimated carefully.
At development of hypotonia and/or bradycardia there can be a need of decrease in doses both the drug Egilok retard, and the accompanying therapy.
The hypotonia developing in an initiation of treatment or passing deterioration in symptoms of heart failure not necessarily means that the patient does not transfer this dose at chronic treatment. Such patients against the background of careful control of function of kidneys should lower a drug dose to stabilization of a state.
If necessary the dose decline or drug withdrawal is possible.
In an initiation of treatment at use of low doses use of other drugs of a metoprolol of the prolonged action is recommended.
In arrhythmias the recommended dose from 50 mg to 200 mg once a day.
At the functional disturbances of warm activity which are followed by heartbeat: the recommended dose 50-200mg once a day.
For prevention of attacks of migraine 100-200mg once a day.
At elderly patients and patients with renal failures and also in need of carrying out a hemodialysis of change of the mode of dosing it is not required.
At patients with abnormal liver functions the dose of drug should be selected individually depending on a clinical state.
Side effects
Patients usually well transfer treatment metoprololy, the arising side reactions are usually poorly expressed and have passing character.
Very often (& ge, 1/10)
– increased fatigue
Often (from & ge, 1/100 to & lt, 1/10)
– dizziness and a headache
– orthostatic hypotension (it is very rare with a loss of consciousness)
– heartbeat strengthening, bradycardia, a cold snap of extremities
– disturbances of functions of a stomach and intestines (nausea, pain in a stomach, diarrhea, a constipation)
– an asthma at physical activity
Infrequently (from & ge, 1/1000 to & lt, 1/100)
– complaints to paresthesias, muscular spasms
– strengthening of symptoms of heart failure, atrioventricular blockade, pains in a heart/stomach, peripheral hypostases
– an erythema, a small tortoiseshell, psoriazopodobny and dystrophic skin defeats, sweating strengthening
– obstruction of airways
– increase in body weight, disturbance of lipidic exchange. Usually at the normal level of the general cholesterol the decrease in level of LPVP cholesterol and increase in level of triglycerides of blood serum
– a depression, disturbance of concentration of attention, insomnia, drowsiness, dreadful dreams
– vomiting
– a bronchospasm
Seldom (from & ge, 1/10,000 to & lt, 1/1000)
– dryness in a mouth
– disturbances of functions of a liver (increase in levels of transaminases of blood serum)
– nervous irritability, uneasiness
– conjunctivitis, dryness and irritation of eyes (that can cause difficulties in the persons applying contact lenses), illegibility of sight
– disturbance of conductivity, arrhythmia
– impotence, disturbances of potency
– hay fever
Very seldom (& le, 1/10,000)
– thrombocytopenia, a leukopenia
– memory disturbances, amnesia, confusion of consciousness, a hallucination, change of mood
– strengthening of earlier existing disturbance of peripheric circulation (up to a gangrenosis), strengthening of symptoms of the alternating lameness or Raynaud’s disease
– hepatitis
– progressing of psoriasis
– a joint pain (arthralgia)
– a photosensitization with skin rash
– disturbance of taste
– sonitus, decrease in hearing was observed
– Peyroni’s disease (plastic induration of a penis)
At the patients having stenocardia, heart attacks can develop more often or to be more intensive.
Contraindications
– hypersensitivity to a metoprolol or other components of drug
– arterial hypotension
– atrioventricular block of II and III degree
– dekompensirovanny heart failure (with the fluid lungs reduced by a blood-groove or arterial hypotension) and also the periodic or continuous treatment which is followed by increase in sokratitelny ability of a cardiac muscle (agonists – receptors)
– the profound sinus bradycardia (heart rate less than 45 beats per minute)
– a sick sinus syndrome
– cardiogenic shock
– the significant disturbances of peripheric arterial circulation
– an acute myocardial infarction if:
– heart rate less than 45 beats per minute,
– lengthening of an interval of P-Q more 0.24s,
– systolic arterial blood pressure is lower than 100 mm Hg,
– a severe form of heart failure,
– atrioventricular block of II or III degree
– psoriasis
– a concomitant use of inhibitors of a monoaminooxidase (MAO)
– simultaneous intravenous administration of verapamil or other similar
blockers of calcium channels
– not treated pheochromocytoma
– heavy bronchial asthma or a heavy bronchospasm in the anamnesis
– a metabolic acidosis
– the I trimester of pregnancy and the period of a lactation
– children’s and teenage age up to 18 years (due to the lack of enough clinical data)
Medicinal interactions
Antihypertensive effects of the drug Egilok Retard and other antihypertensive drugs are usually summarized therefore in order to avoid development of arterial hypotension the careful observation of a condition of the patients receiving combinations of such means is necessary. However summation of effects of antihypertensive drugs can be used if necessary for achievement of more effective control of arterial blood pressure.
Intravenous administration of blockers of calcium channels of type of verapamil is not recommended to the patients accepting – adrenoblockers. Simultaneous use of a metoprolol with blockers of calcium channels of type of verapamil or diltiazem leads to increase in negative inotropic and chronotropic effects.
Simultaneous use of a metoprolol with inhibitors of a monoaminooxidase (iMAO) is not recommended.
It is necessary to be careful at a combination with the following means:
At simultaneous use by oral antiarrhytmic drugs, parasympathomimetics, blockers of calcium channels (like verapamil and diltiazem) risk of developing arterial hypotension, bradycardia, atrioventricular blockade is possible.
It is necessary to be careful at simultaneous use of a metoprolol with antiarrhytmic means as the cardiodepressive effect of a metoprolol and antiarrhytmic means can be summarized. So, for example, propafenon reduces hepatic metabolism of a metoprolol, increasing toxicity of a metoprolol (for example, with development of bradycardia). Amiodaronum at predisposed patients can lower a rhythm of sinus node and weight atrioventricular blockade.
At simultaneous use with cardiac glycosides the risk of developing bradycardia, disturbances of conductivity is possible, metoprolol does not affect positive inotropic effect of drugs of a foxglove.
At simultaneous use with nitrates and other antihypertensive drugs (groups of a guanetidin, reserpine, – Methyldopa, a clonidine and guanfatsin) risk of developing arterial hypotension and/or profound bradycardia is possible.
At combination therapy with a clonidine the reception of the last should be stopped in several days after cancellation of a metoprolol, in order to avoid hypertensive crisis.
At simultaneous use with hypnotic drugs, tranquilizers, three – and tetracyclic antidepressants, neuroleptics and ethanol risk of developing arterial hypotension is possible.
At simultaneous use with a- and b-sympathomimetics the risk of developing the arterial hypertension expressed to bradycardia is possible, the risk of cardiac arrest is possible.
At simultaneous use with ergotamine strengthening of vasoconstrictive effect is possible.
At simultaneous use with b2-sympathomimetics the functional antagonism is possible.
At simultaneous use with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs the reduction of hypotensive action of a metoprolol is possible.
Difengidramin reduces clearance of a metoprolol to a-hydroksimetoprolola by 2.5 times. Strengthening of action of a metoprolol is at the same time observed.
At simultaneous use with estrogen reduction of hypotensive action of a metoprolol.
At a concomitant use with oral anti-diabetic drugs and insulin metoprolol can enhance their hypoglycemic effects and mask hypoglycemia symptoms.
At simultaneous use of the drug Egilok Retard with kurarepodobny muscle relaxants strengthening of neuromuscular blockade.
At simultaneous use of the drug Egilok Retard with inhibitors of microsomal enzymes of a liver (Cimetidinum, gidralazin, inhibitors of the return serotonin reuptake (paroksetin, fluoxetine and sertraline), strengthening of effects of a metoprolol owing to increase in its content in plasma is possible.
At simultaneous use Egilok Retard with inductors of microsomal enzymes of a liver (rifampicin and barbiturates) the acceleration of metabolism of a metoprolol is possible that Egilok Retard leads to decrease in concentration of a metoprolol in blood plasma and to reduction of effect.
Metoprolol is CYP2D6 substrate in this connection, the drugs inhibiting CYP2D6 (quinidine, terbinafin, paroksetin, fluoxetine, sertraline, tselekoksib, propafenon and difengidramin) can increase plasma concentration of a metoprolol.
Quinidine inhibits metabolism of a metoprolol at special group of patients with fast hydroxylation (in Sweden about 90% of the population), causing, mainly, significant increase in plasma concentration of a metoprolol and strengthening of b-blockade. Believe that similar interaction is characteristic also of other b-adrenoblockers in which metabolism P4502D6 cytochrome participates.
The concomitant use of food does not render noticeable effect on drug pharmacokinetics.
Special instructions
At the patients accepting Egilok Retard an acute anaphylaxis proceeds more hard.
If against the background of treatment the bradycardia developed, the dose of drug needs to be reduced or it is necessary to cancel drug gradually.
The hypotensive effect of a metoprolol can strengthen symptoms of disturbance of peripheric arterial circulation (for example, symptoms of a Raynaud’s disease or the alternating lameness). – it is necessary to appoint adrenoblockers with extra care at deterioration in symptoms.
It is impossible to stop sharply administration of drug Egilok retard. Drug withdrawal is carried out gradually, reducing a dose approximately within 7-10 days. Sharp cancellation can strengthen symptoms of stenocardia and the myocardial infarction can develop. Patients with coronary artery disease require special attention during drug withdrawal.
Prescribing of the drug Egilok retard to patients with heart failure perhaps only after achievement of a stage of compensation. The stage of compensation has to be supported during the entire period of treatment metoprololy.
In spite of the fact that cardioselective – adrenoblockers to a lesser extent influence respiratory function, in comparison with non-selective – adrenoblockers, it is recommended to avoid whenever possible prescribing of such drugs to patients with chronic obstructive respiratory diseases. In need of purpose of a metoprolol the simultaneous use of b2-adrenomimetik (in tablets and/or in the form of aerosol) or change (increase) of a dose of earlier applied 2 agonists can be required by patients with bronchial asthma.
– adrenoblockers can mask hypoglycemia symptoms, therefore in case of prescribing of such drugs the patients with diabetes to a thicket should control a condition of carbohydrate metabolism and if necessary to carry out dose adjustment of insulin or oral anti-diabetic means.
Metoprolol can mask some clinical manifestations of a thyrotoxicosis (for example, tachycardia). Sharp drug withdrawal at patients with a thyrotoxicosis is contraindicated as it is capable to strengthen symptomatology.
At treatment of patients with a treated pheochromocytoma metoprolol it is necessary to apply in combination with – adrenoblockers.
In a heavy abnormal liver function there can be a need of a dose decline. At patients with cirrhosis the bioavailability of drug can increase.
At the patients accepting – arterial blood pressure can raise adrenoblockers, use of adrenaline and cause (reflex) bradycardia.
Fenilpropanolamin (norefedrin) in a single dose of 50 mg can cause increase in diastolic arterial blood pressure to pathological values in healthy volunteers. Propranolol generally interferes with the increase in the ABP caused fenilpropanolaminy. However, b-adrenoblockers can cause reactions of paradoxical arterial hypertension in the patients receiving high doses of a fenilpropanolamin.
In need of performing surgical intervention and anesthesia it is necessary to warn the anesthesiologist about the carried-out therapy Egilok retard. If the Egilok drug treatment retard needs to be stopped in connection with surgical intervention, then it should be made, at least, in 48 hours prior to operation, except for such cases as a thyrotoxicosis and a pheochromocytoma.
In certain cases use – adrenoblockers before surgical intervention as premedication has the advantages: they can reduce aritmogenny influences during surgical intervention and prevent development of coronary insufficiency in the surgical stress causing prevalence of a sympathetic tone. If for the above-mentioned reasons for the patient it is appointed – adrenoblocker, then it is necessary to use drug for the general anesthesia with the minimum negative inotropic effect to reduce risk of oppression of a myocardium.
Seldom or never already existing, insignificant disturbance of atrioventricular conductivity can become heavier and atrioventricular blockade can develop.
In Printsmetall stenocardia selection – it is necessary to appoint adrenoblockers with extra care.
Patients with rare inherited disorders of tolerance to fructose, glucose galactose absorption disturbances and also with insufficiency of invertase/isomaltase should not take this drug.
Pregnancy and the period of a lactation
– adrenoblockers lower placentary perfusion and, thus, can lead to death of a fruit or to premature births. At the pregnant women accepting for a long time – adrenoblockers concerning weak or moderate and heavy hypertensia the delay of pre-natal fetation was observed.
Due to the lack of enough clinical data on use of drug during pregnancy and a lactation, appointment Egilok retard demands careful assessment of a ratio of expected advantage for mother and risk for a fruit and it is possible only in cases when the advantage of drug justifies possible risks. If it is possible, use of a metoprolol should be stopped for 48-72 h to the expected term of childbirth. If administration of drug is inevitable, it is necessary to watch carefully a condition of a fruit and the newborn during the first 48-72 h after the delivery as decrease in an uteroplacental blood-groove can affect a condition of a fruit, and receipt of a metoprolol in a blood stream of a fruit can cause bradycardia, respiratory depression, arterial hypotension. In spite of the fact that metoprolol gets through a placental barrier, proofs of adverse influence on a fruit were not revealed so far. Though at reception of a metoprolol in therapeutic doses drug only in insignificant quantities gets into breast milk and probability of manifestation – the blocking effect at the newborn is minimum, in need of use of drug it is necessary to carry out monitoring of warm activity of the child in connection with possible development of bradycardia.
Features of influence of medicine on ability to run the vehicle or potentially dangerous mechanisms.
At patients whose activity requires special attention and speed psychomotor reaction the selection of a dose should be solved only after assessment of individual reaction of the patient to drug.
Overdose
Symptoms: arterial hypotension, profound sinus bradycardia, atrioventricular blockade, heart failure, cardiogenic shock, asystolia, nausea, vomiting, bronchospasm, cyanosis, hypoglycemia, convulsive attacks, loss of consciousness, coma, in certain cases giperkalemiya. The first symptoms of overdose are shown in 20 minutes – 2 hours after administration of drug and, in a hard case, can proceed within several days, despite decrease in plasma concentration of a metoprolol.
Treatment: gastric lavage (if the overdose happened within 4 hours) if washing is impossible and if the patient in consciousness it is possible to cause vomiting, prescribing of adsorbents, symptomatic therapy. Intensive care and careful control of parameters of blood circulation and breath, function of kidneys, glucose level in blood, blood serum electrolytes is necessary. Atropini sulfas is entered intravenously for control of the profound bradycardia. In heavy arterial hypotension, bradycardia and the menacing heart failure – intravenous administration – adrenostimulyator (prenalterol or izoprenalin). At – blockade these drugs can be used in very high doses. In the absence of positive effect apply a dopamine, Dobutaminum or noradrenaline. The glucagon renders positive inotropic and chronotropic effect on heart which does not depend from – adrenoceptors. Introduction can be also useful to treatment of the resistant hypotension and heart failure connected with overdose – a blocker. Diazepam is drug of the first choice for stopping of convulsive attacks. At a bronchospasm it is possible to use b2-agonist or Aminophyllinum. Control of a condition of patients for the purpose of detection of arrhythmias in time and after administration of bronchodilatory drugs is required. Metoprolol cannot be effectively removed by means of a hemodialysis.
The form of release and packing
On 10 tablets place in blister strip packaging from a film of polypropylene and aluminum foil.
On 3 planimetric packs together with the instruction for medical use in the state and Russian languages put in a cardboard pack.
To Store storage conditions at a temperature not over 30C
to Store out of children’s reach!
Not to use a period of storage of 5 years after an expiration date.
Prescription status
According to the prescription
CJSC Pharmatsevtichesky producer
the EGIS 1106 Budapest plant, Keresturi St., 30-38 HUNGARY
Phone: (36-1) 803-5555 Fax: (36-1)803-5529
Proizvedeno Atsino Pharm AG, Switzerland
the Owner of the registration certificate
of CJSC Pharmatsevtichesky the EGIS plant, Hungary
the Address of the organization accepting in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan claims from consumers on quality of products (goods)
Representation in RK CJSC Pharmatsevtichesky
the EGIS 050060 plant, Almaty, Zharokov St. of 286 G
ph. + 7 (727) 247 63 34, + 7 (727) 247 63 33, fax: + 7 (727) 247 61 41
e-mail:
To Develop egis@egis.kz
Additional information
| Ingredient |
|---|














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.